Unveiling the World: A Comprehensive Exploration of the Earth’s Map
Related Articles: Unveiling the World: A Comprehensive Exploration of the Earth’s Map
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the World: A Comprehensive Exploration of the Earth’s Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Unveiling the World: A Comprehensive Exploration of the Earth’s Map
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unveiling the World: A Comprehensive Exploration of the Earth’s Map
- 3.1 The Evolution of Earth’s Mapping
- 3.2 Understanding the Fundamentals of Earth’s Map
- 3.3 The Importance and Benefits of Earth’s Map
- 3.4 The Evolution of Digital Mapping
- 3.5 FAQs about Earth’s Map
- 3.6 Tips for Using Earth’s Map Effectively
- 3.7 Conclusion: Earth’s Map – A Window to Our World
- 4 Closure
Unveiling the World: A Comprehensive Exploration of the Earth’s Map

The Earth’s map, a visual representation of our planet’s surface, serves as a fundamental tool for understanding our world. Its intricate network of lines, colors, and symbols encapsulates the vastness and diversity of our planet, providing a framework for exploration, navigation, and understanding global interconnectedness.
The Evolution of Earth’s Mapping
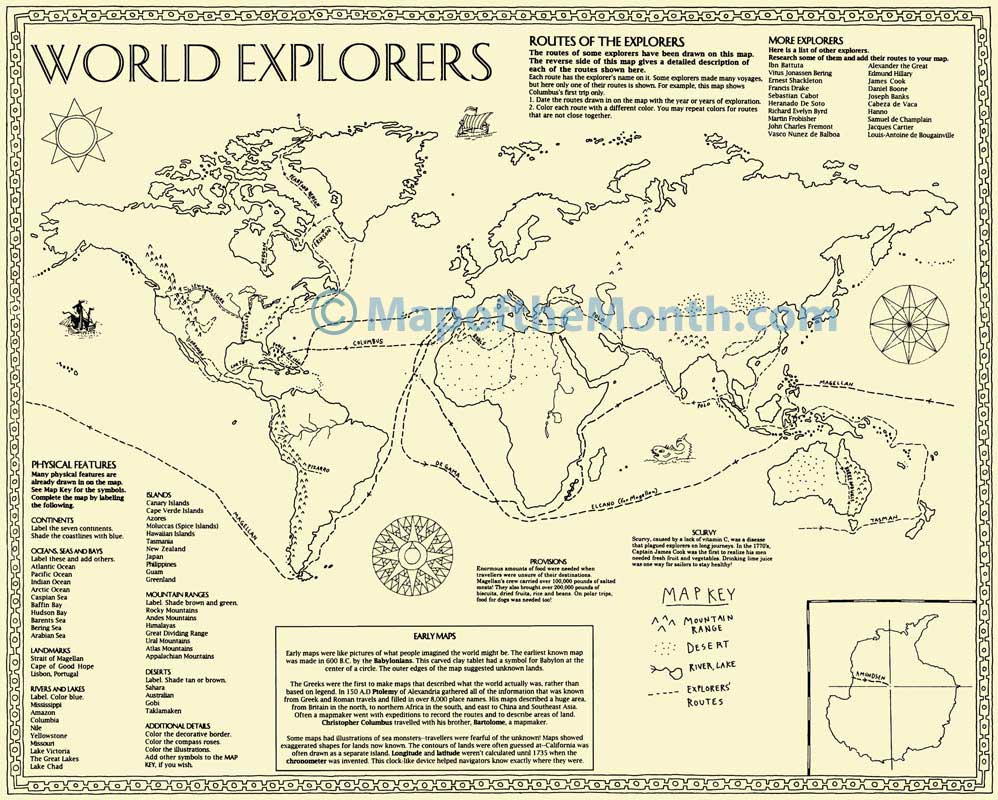
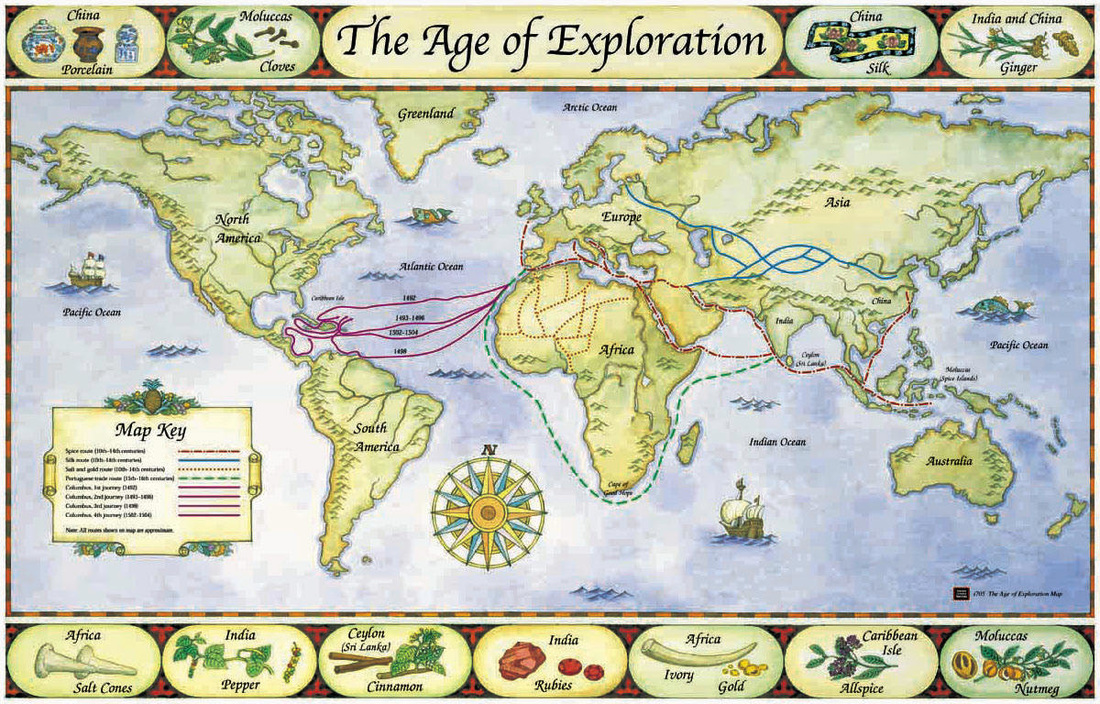
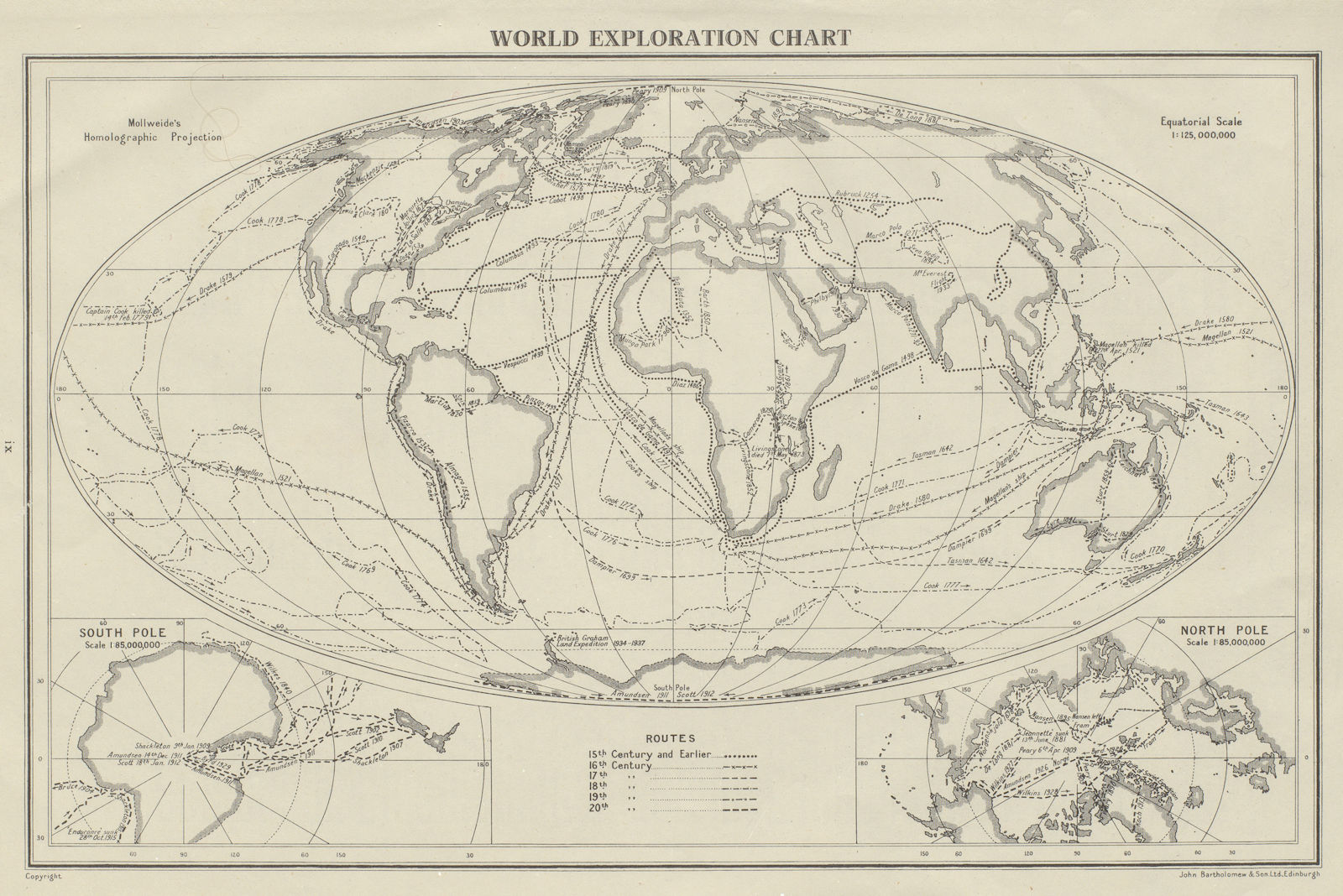
The concept of mapping the Earth has existed for millennia, evolving alongside human civilization. Early civilizations relied on rudimentary maps, often drawn on clay tablets or papyrus, to depict local landscapes and navigate trade routes. The ancient Greeks, renowned for their scientific advancements, developed sophisticated maps incorporating geographical features like mountains, rivers, and coastlines.
The advent of the compass in the 11th century revolutionized navigation, enabling sailors to chart courses with greater accuracy. The subsequent development of cartography during the Age of Exploration led to the creation of more detailed and accurate maps, fueled by the desire to explore new lands and expand trade routes.
Understanding the Fundamentals of Earth’s Map
Earth’s map is a complex representation of our planet’s three-dimensional surface, projected onto a two-dimensional plane. This process inevitably involves distortions, as accurately representing a sphere on a flat surface is inherently challenging. Different map projections address this challenge by emphasizing specific aspects of the Earth, such as preserving area, shape, or direction.
Key Elements of Earth’s Map:
- Latitude and Longitude: A grid system based on imaginary lines that run parallel to the equator (latitude) and converge at the poles (longitude). This system allows for precise location identification.
- Continents and Oceans: The major landmasses and water bodies that define the Earth’s surface.
- Countries and Boundaries: Political divisions that delineate nations and their territories.
- Cities and Towns: Significant population centers, marked with varying levels of detail depending on the map’s scale.
- Physical Features: Mountains, rivers, lakes, deserts, and other geographical elements that shape the Earth’s landscape.
The Importance and Benefits of Earth’s Map
Beyond its aesthetic appeal, Earth’s map plays a crucial role in numerous aspects of human life:
- Navigation and Travel: Maps are essential tools for navigating both land and sea, guiding travelers to their destinations and facilitating trade and exploration.
- Geographic Education: They provide a visual framework for understanding the distribution of landmasses, oceans, and other geographical features, fostering a deeper understanding of the world’s diversity.
- Environmental Awareness: Maps can visualize environmental issues, such as deforestation, pollution, and climate change, raising awareness and facilitating informed decision-making.
- Economic Development: Maps are vital for infrastructure planning, resource management, and identifying potential areas for economic growth.
- Conflict Resolution: Maps can help resolve territorial disputes by providing a clear visual representation of contested boundaries.
The Evolution of Digital Mapping
The advent of digital technology has transformed the way we interact with maps. Online mapping services, such as Google Maps and OpenStreetMap, offer interactive, real-time maps with a wealth of information, including traffic conditions, points of interest, and satellite imagery.
These platforms have democratized access to mapping information, empowering individuals to explore, navigate, and contribute to the ever-evolving digital atlas of our planet.
FAQs about Earth’s Map
1. What are the different types of map projections?
There are numerous map projections, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Some common examples include:
- Mercator Projection: Preserves angles and shapes but distorts areas, particularly at higher latitudes.
- Robinson Projection: Aims to minimize distortion but compromises on shape and area accuracy.
- Mollweide Projection: Preserves area but distorts shapes, particularly near the poles.
2. How is the Earth’s map updated?
Map updates occur continuously, reflecting changes in political boundaries, infrastructure development, and other dynamic aspects of the world. This process involves data collection from various sources, including satellite imagery, aerial photography, and ground surveys.
3. What are some of the challenges of mapping the Earth?
Mapping the Earth presents several challenges, including:
- Distortion: Representing a three-dimensional sphere on a flat surface inevitably introduces distortions.
- Data Accuracy: Maintaining accurate and up-to-date data requires continuous monitoring and updating.
- Political Sensitivity: Mapping political boundaries can be a delicate process, requiring careful consideration of international relations.
Tips for Using Earth’s Map Effectively
- Choose the right map for your needs: Consider the purpose of your map and select a projection that minimizes distortion for the specific area you are studying.
- Understand map scales: Different maps have different scales, indicating the ratio between the map distance and the actual distance on the Earth’s surface.
- Explore interactive online maps: These platforms offer a wealth of information and tools for exploration and analysis.
- Use map legends: Familiarize yourself with the symbols and colors used on the map to interpret the data accurately.
Conclusion: Earth’s Map – A Window to Our World
Earth’s map, a testament to human ingenuity and our desire to understand and explore our planet, continues to evolve and adapt to the changing needs of society. From its humble beginnings as hand-drawn representations of local landscapes to the intricate digital atlases of today, it remains an indispensable tool for navigation, education, and global awareness.
As we continue to explore the Earth’s wonders and confront global challenges, the map will undoubtedly remain a vital guide, revealing the interconnectedness of our planet and inspiring us to preserve its beauty for generations to come.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the World: A Comprehensive Exploration of the Earth’s Map. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!