Unveiling the Power of Figure-Ground Perception: A Comprehensive Guide to Visual Organization
Related Articles: Unveiling the Power of Figure-Ground Perception: A Comprehensive Guide to Visual Organization
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Power of Figure-Ground Perception: A Comprehensive Guide to Visual Organization. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Unveiling the Power of Figure-Ground Perception: A Comprehensive Guide to Visual Organization
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unveiling the Power of Figure-Ground Perception: A Comprehensive Guide to Visual Organization
- 3.1 Understanding the Concept of Figure-Ground Perception
- 3.2 The Mechanics of Figure-Ground Perception
- 3.3 The Importance of Figure-Ground Perception in Everyday Life
- 3.4 Figure-Ground Perception and its Applications
- 3.5 Challenges and Limitations of Figure-Ground Perception
- 3.6 FAQs Regarding Figure-Ground Perception
- 3.7 Tips for Utilizing Figure-Ground Perception in Visual Design
- 3.8 Conclusion: The Enduring Significance of Figure-Ground Perception
- 4 Closure
Unveiling the Power of Figure-Ground Perception: A Comprehensive Guide to Visual Organization

In the vast landscape of visual perception, the ability to discern and interpret shapes, forms, and patterns is paramount. This skill, known as figure-ground perception, allows us to effortlessly navigate the world around us, separating objects of interest from their surrounding backgrounds. This seemingly simple ability, however, underlies a complex interplay of cognitive processes, impacting everything from our visual comprehension to our aesthetic preferences.
Understanding the Concept of Figure-Ground Perception
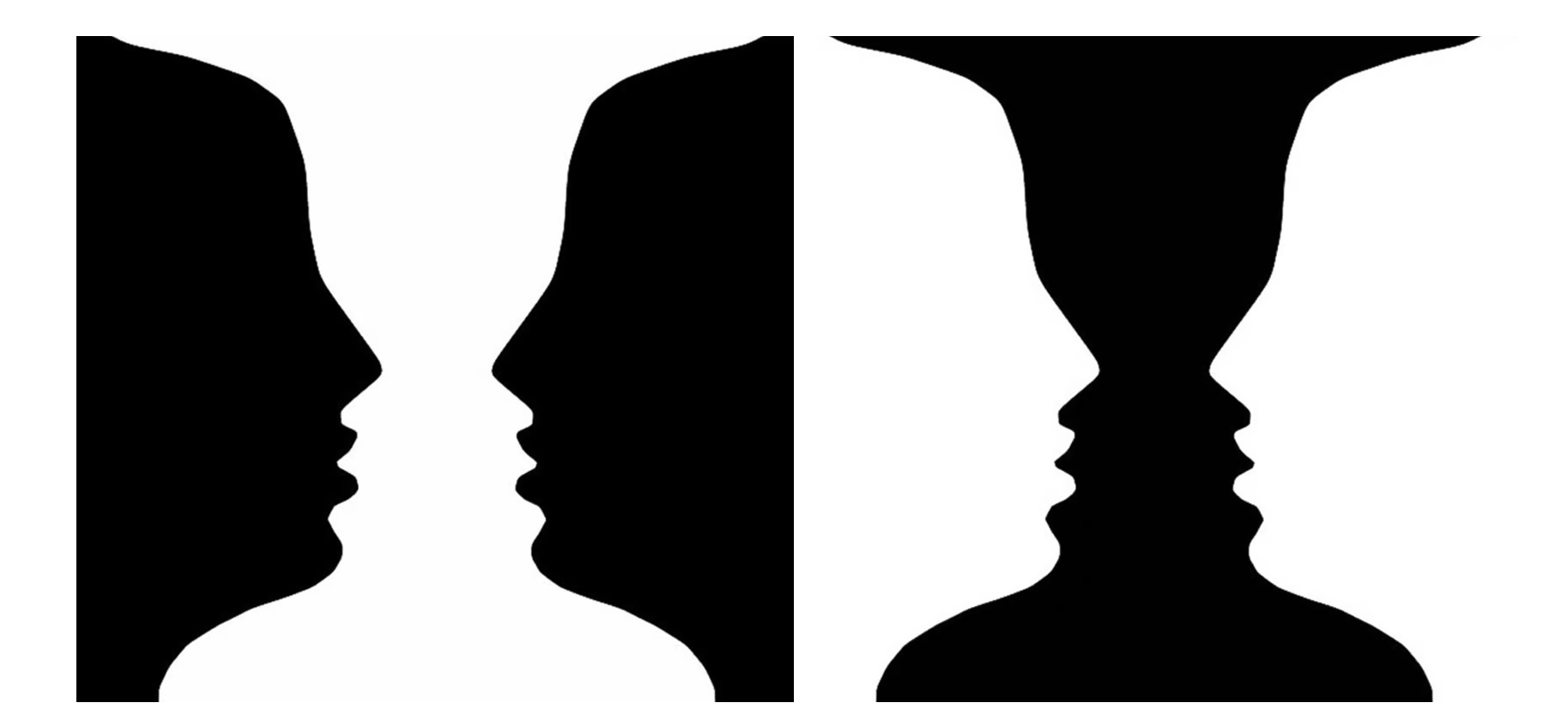
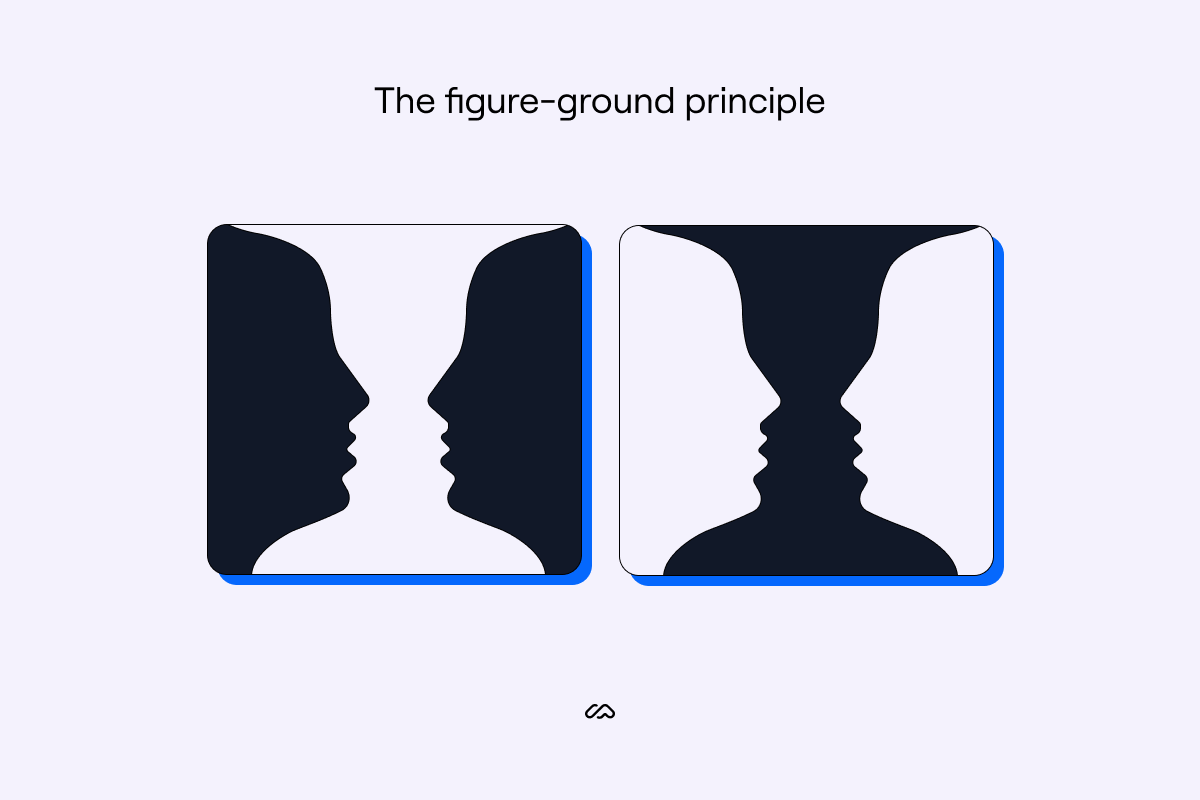
Figure-ground perception, a fundamental principle in Gestalt psychology, describes the visual phenomenon where our brains perceive an image as consisting of two distinct elements: the figure, a prominent object or shape that stands out against the background, and the ground, the less salient background that surrounds the figure. This separation, while seemingly effortless, involves intricate cognitive processes that enable us to isolate and interpret the figure from the surrounding context.
The Mechanics of Figure-Ground Perception
The brain’s ability to distinguish figure from ground relies on several factors:
- Contrast: Differences in color, brightness, texture, or shape between the figure and the ground make it easier to separate them. A dark object against a light background, for example, is readily perceived as the figure.
- Proximity: Objects that are close together are more likely to be perceived as a single unit, forming the figure, while those further apart are perceived as the background.
- Closure: Our brains tend to complete incomplete shapes, filling in gaps to perceive a whole object. This principle, known as closure, contributes to the formation of the figure.
- Symmetry: Symmetrical shapes are often perceived as figures, while asymmetrical shapes are more likely to be perceived as ground.
- Simplicity: Our brains favor the simplest interpretation, preferring to perceive the figure as a simple, cohesive shape rather than a complex, fragmented one.
The Importance of Figure-Ground Perception in Everyday Life
Figure-ground perception is not simply an academic curiosity; it is a vital cognitive function that profoundly impacts our everyday lives. Its influence extends across various domains:
1. Visual Communication and Design:
- Graphic Design: Designers leverage figure-ground relationships to create impactful visuals, ensuring that key elements stand out and communicate effectively. The choice of color, shape, and placement of elements influences how viewers perceive and interpret a design.
- Typography: The arrangement of letters and words within a design heavily relies on figure-ground principles. Distinguishing text from the background is crucial for readability, and designers utilize contrasting colors, fonts, and spacing to enhance legibility.
- Photography: Photographers use figure-ground relationships to create compelling compositions. By isolating a subject against a contrasting background, they emphasize the figure and draw the viewer’s attention to it.
2. Object Recognition and Navigation:
- Identifying Objects: The ability to separate objects from their backgrounds allows us to recognize and identify objects in our environment. This is essential for navigating our surroundings and interacting with the world around us.
- Depth Perception: Figure-ground perception contributes to our understanding of depth and distance. By recognizing the relative sizes and positions of objects against the background, we can gauge their distance from us.
3. Attention and Focus:
- Selective Attention: Figure-ground perception plays a crucial role in selective attention, enabling us to focus on specific objects or information while filtering out distractions. This ability is essential for tasks requiring concentration and sustained focus.
- Task Performance: By separating relevant information from irrelevant noise, figure-ground perception enhances our ability to perform tasks efficiently and effectively.
4. Aesthetics and Art:
- Visual Appeal: Figure-ground relationships contribute to the aesthetic appeal of art and design. The interplay of figure and ground creates a sense of balance, rhythm, and harmony, enhancing the visual impact of the artwork.
- Artistic Expression: Artists utilize figure-ground relationships to create specific effects, such as ambiguity or depth. By manipulating the relationship between figure and ground, they can evoke different emotions and interpretations in the viewer.
Figure-Ground Perception and its Applications
The principles of figure-ground perception extend beyond the realm of visual perception, finding applications in various fields:
1. User Interface Design:
- Website Design: Designers use figure-ground principles to create intuitive and user-friendly interfaces. By ensuring that important elements stand out against the background, they enhance navigation and user experience.
- App Design: Applying figure-ground concepts in app design ensures that key functionalities are easily accessible and understood. Clear visual hierarchy and contrast help users navigate the app smoothly.
2. Marketing and Advertising:
- Visual Branding: Figure-ground principles are employed in creating strong visual branding. By making the brand logo or tagline stand out against the background, marketers ensure its memorability and recognition.
- Product Packaging: Figure-ground relationships contribute to the effectiveness of product packaging. By highlighting the product against a contrasting background, designers attract attention and convey key information.
3. Architecture and Interior Design:
- Space Planning: Architects utilize figure-ground principles to create functional and aesthetically pleasing spaces. By defining different areas within a room through contrasting materials, textures, or colors, they create a sense of order and visual interest.
- Interior Design: Interior designers apply figure-ground concepts to enhance the visual appeal of interior spaces. By selecting furniture and accessories that stand out against the background, they create focal points and add visual interest.
4. Education and Learning:
- Visual Aids: Teachers and educators use figure-ground principles in creating visual aids, such as posters, diagrams, and presentations. By highlighting key information against a contrasting background, they enhance comprehension and retention.
- Learning Materials: Textbooks and other learning materials often utilize figure-ground relationships to present information effectively. By separating key concepts from supporting text, they make the information more accessible and engaging.
Challenges and Limitations of Figure-Ground Perception
While figure-ground perception is a powerful cognitive tool, it is not without its limitations:
- Ambiguity: In some cases, the relationship between figure and ground can be ambiguous, leading to multiple interpretations of the same image. This ambiguity can be exploited in art and design to create intriguing and thought-provoking visuals.
- Context Dependence: Figure-ground perception is influenced by context. The same image can be interpreted differently depending on the surrounding environment and the viewer’s prior knowledge.
- Individual Differences: People vary in their ability to perceive figure and ground, influenced by factors such as age, experience, and cognitive abilities.
FAQs Regarding Figure-Ground Perception
1. What is the difference between figure and ground?
The figure is the prominent object or shape that stands out against the background, while the ground is the less salient background that surrounds the figure.
2. How does figure-ground perception relate to Gestalt psychology?
Figure-ground perception is a fundamental principle in Gestalt psychology, which emphasizes the holistic nature of perception and the brain’s tendency to organize sensory information into meaningful wholes.
3. Can figure-ground perception be manipulated?
Yes, figure-ground perception can be manipulated through various techniques, such as using contrasting colors, shapes, and textures. Designers and artists often exploit these techniques to create specific visual effects.
4. What are some examples of figure-ground perception in everyday life?
Examples include recognizing a person’s face in a crowd, identifying a specific object in a cluttered room, or reading text on a page.
5. How can I improve my figure-ground perception?
Practice visual exercises, such as identifying hidden shapes in images or focusing on specific objects in a cluttered environment.
Tips for Utilizing Figure-Ground Perception in Visual Design
1. Leverage Contrast: Use contrasting colors, shapes, and textures to create a clear distinction between figure and ground, ensuring that the figure stands out and attracts attention.
2. Create Visual Hierarchy: Organize elements in a design based on their importance, using figure-ground principles to guide the viewer’s eye and emphasize key information.
3. Employ Simplicity: Keep designs clean and uncluttered, avoiding unnecessary elements that can distract from the main figure.
4. Consider Context: Design with the intended context in mind, ensuring that the figure-ground relationship is appropriate for the target audience and the intended message.
5. Experiment and Iterate: Don’t be afraid to experiment with different figure-ground relationships and iterate on your designs to find the most effective solutions.
Conclusion: The Enduring Significance of Figure-Ground Perception
Figure-ground perception is an integral aspect of our visual experience, shaping how we perceive and interact with the world around us. Its influence extends across various domains, from visual communication and design to object recognition, attention, and aesthetics. By understanding the principles of figure-ground perception, we can leverage its power to create effective visual designs, enhance communication, and improve our understanding of the visual world.
While the concept may seem simple at first glance, its intricacies and far-reaching applications underscore its importance in shaping our cognitive and sensory experiences. As we continue to explore the complexities of human perception, figure-ground perception remains a vital area of study, offering insights into the fundamental mechanisms that govern our understanding of the visual world.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Power of Figure-Ground Perception: A Comprehensive Guide to Visual Organization. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!