Unveiling the Past: A Journey Through Antiquity Maps
Related Articles: Unveiling the Past: A Journey Through Antiquity Maps
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Past: A Journey Through Antiquity Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Past: A Journey Through Antiquity Maps
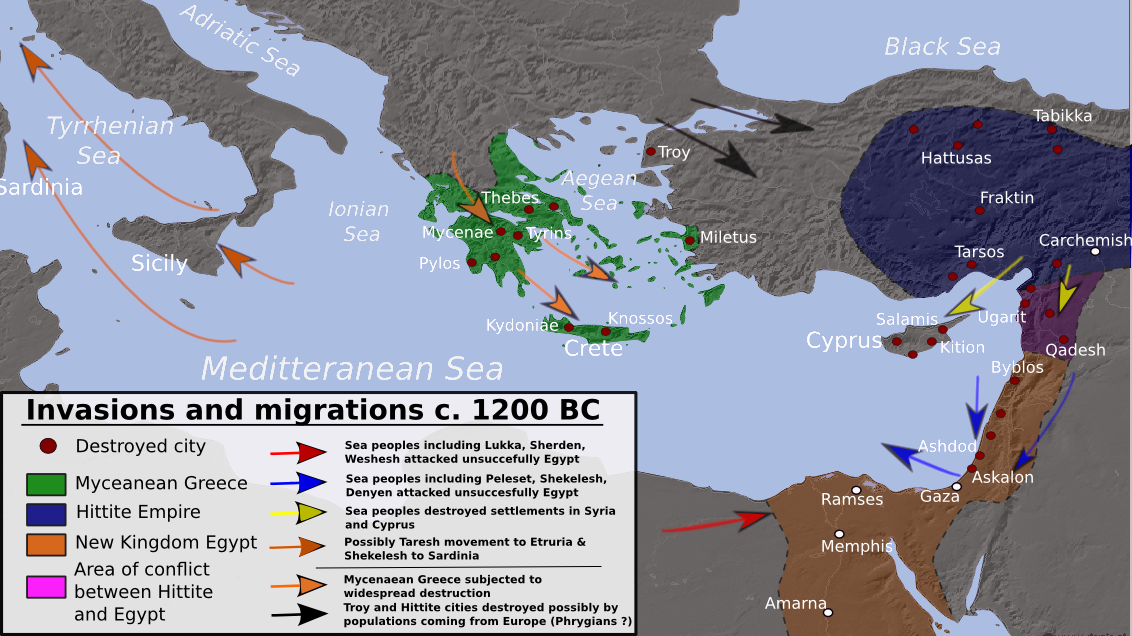
Maps are more than just pieces of paper with lines and markings. They are windows into our past, providing invaluable insights into the world as it was perceived and understood in different eras. Among these, antiquity maps hold a special significance, offering a glimpse into the cartographic knowledge and worldview of ancient civilizations. These maps, often crafted on papyrus, clay tablets, or stone, serve as tangible evidence of the intellectual and cultural achievements of these bygone societies.
The Genesis of Ancient Cartography:
The earliest known maps date back to the Stone Age, with simple representations of landscapes and celestial bodies etched onto cave walls. However, the emergence of organized civilizations in Mesopotamia, Egypt, and the Indus Valley brought about a significant evolution in mapmaking. These ancient societies developed complex systems of navigation, land surveying, and astronomical observation, which formed the foundation for their cartographic endeavors.
Mesopotamian Maps:
Mesopotamian civilization, known for its advanced mathematics and astronomy, produced some of the earliest known maps. Clay tablets from the 7th century BCE depict detailed plans of cities, including roads, canals, and temples. Notably, the Babylonian map of the world, dating back to the 6th century BCE, shows a circular world with Mesopotamia at its center, surrounded by a ring of water. This map exemplifies the geocentric worldview prevalent in ancient Mesopotamia.
Egyptian Maps:
Egyptian civilization, with its sophisticated surveying techniques, created maps for various purposes, including land management, construction, and navigation. The famous Turin Papyrus, dating back to the 12th century BCE, showcases a detailed map of gold mines in the Sinai Peninsula, highlighting the importance of cartography in resource management. Egyptian maps also depicted constellations and celestial bodies, reflecting their advanced knowledge of astronomy.
Greek Maps:
Ancient Greek civilization, renowned for its intellectual and philosophical pursuits, made significant contributions to cartography. Greek scholars like Anaximander and Hecataeus developed the concept of a spherical Earth and devised more accurate maps based on astronomical observations and geographical exploration. The famous map of the world by Ptolemy, compiled in the 2nd century CE, became a standard reference for centuries, influencing cartography for generations to come.
Roman Maps:
The Roman Empire, known for its vast territorial expanse, relied heavily on maps for military campaigns, trade, and administration. Roman maps, often crafted on parchment or stone, depicted roads, cities, and geographical features with remarkable accuracy. The Tabula Peutingeriana, a 13th-century CE copy of a Roman road map, provides valuable insights into the Roman road network, spanning from Britain to India.
The Importance of Antiquity Maps:
Antiquity maps offer a unique lens through which to understand the worldviews, knowledge systems, and cultural practices of ancient civilizations. They reveal the following:
- Geospatial Understanding: Antiquity maps provide insights into how ancient civilizations perceived the world, including their understanding of geography, topography, and celestial bodies.
- Technological Advancements: The intricate details and accuracy of some maps demonstrate the advanced surveying, navigation, and astronomical knowledge possessed by ancient societies.
- Cultural and Social Practices: Maps can reveal information about trade routes, settlements, religious sites, and other aspects of daily life in ancient civilizations.
- Historical Evidence: Antiquity maps serve as invaluable historical documents, providing insights into past events, conflicts, and cultural exchanges.
- Artistic Expression: Some antiquity maps, particularly those created by the Greeks and Romans, are not only informative but also aesthetically pleasing, showcasing the artistic talents of their creators.
Beyond the Maps: The Legacy of Ancient Cartography:
The legacy of ancient cartography extends far beyond the maps themselves. The concepts and techniques developed by these civilizations, such as the use of coordinates, projections, and surveying methods, laid the foundation for modern cartography. The pursuit of geographical knowledge, fueled by the curiosity and ingenuity of ancient scholars, continues to inspire cartographers and explorers today.
FAQs about Antiquity Maps:
Q1: What were the primary purposes of antiquity maps?
A1: Antiquity maps served diverse purposes, including navigation, land management, military campaigns, trade, resource management, and religious practices.
Q2: What materials were used to create antiquity maps?
A2: Antiquity maps were crafted on various materials, including papyrus, clay tablets, stone, parchment, and wood.
Q3: How accurate were antiquity maps?
A3: The accuracy of antiquity maps varied depending on the civilization, the map’s purpose, and the available technology. While some maps were remarkably accurate, others were more symbolic or based on limited geographical knowledge.
Q4: What are some notable examples of antiquity maps?
A4: Notable examples include the Babylonian map of the world, the Turin Papyrus, the map of the world by Ptolemy, and the Tabula Peutingeriana.
Q5: How can we learn more about antiquity maps?
A5: Museums, libraries, and online databases offer valuable resources for studying antiquity maps. Archaeological excavations and historical research also contribute to our understanding of ancient cartography.
Tips for Exploring Antiquity Maps:
- Explore Museums and Libraries: Visit museums and libraries with collections of antiquity maps to see them firsthand.
- Consult Online Databases: Explore online databases and digital collections of antiquity maps for a comprehensive overview.
- Read Historical Texts: Study historical texts, including travel accounts and geographical treatises, to gain context for antiquity maps.
- Analyze Map Features: Pay attention to the map’s scale, projection, symbols, and other features to understand its purpose and limitations.
- Consider Cultural Context: Interpret antiquity maps within the context of the civilization that created them, taking into account their beliefs, values, and knowledge systems.
Conclusion:
Antiquity maps serve as invaluable windows into the past, revealing the geographic knowledge, technological advancements, and cultural practices of ancient civilizations. By studying these maps, we gain a deeper understanding of the world as it was perceived and understood in bygone eras, appreciating the ingenuity and intellectual achievements of those who came before us. The legacy of ancient cartography continues to influence our understanding of the world and inspires us to explore and discover new horizons.
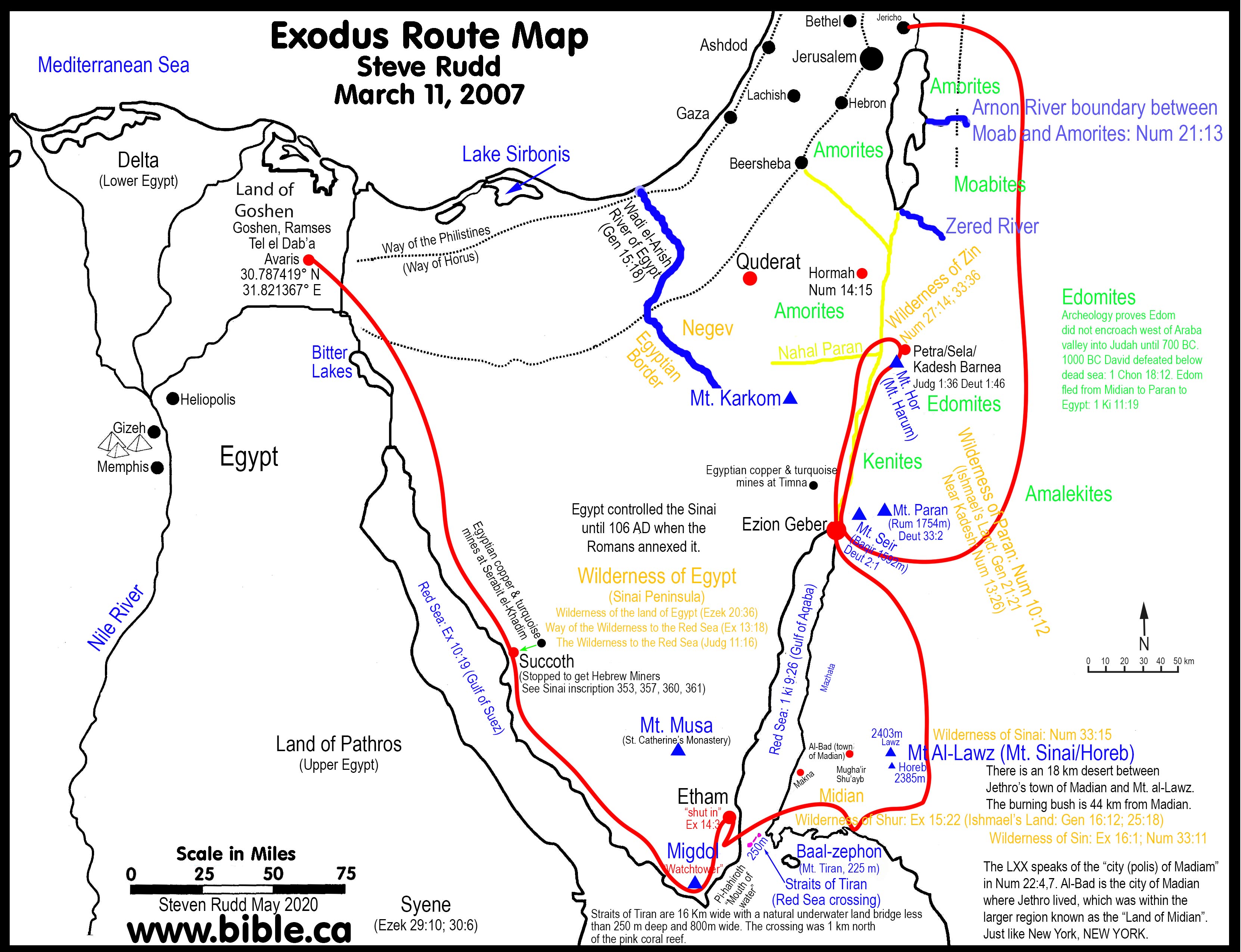
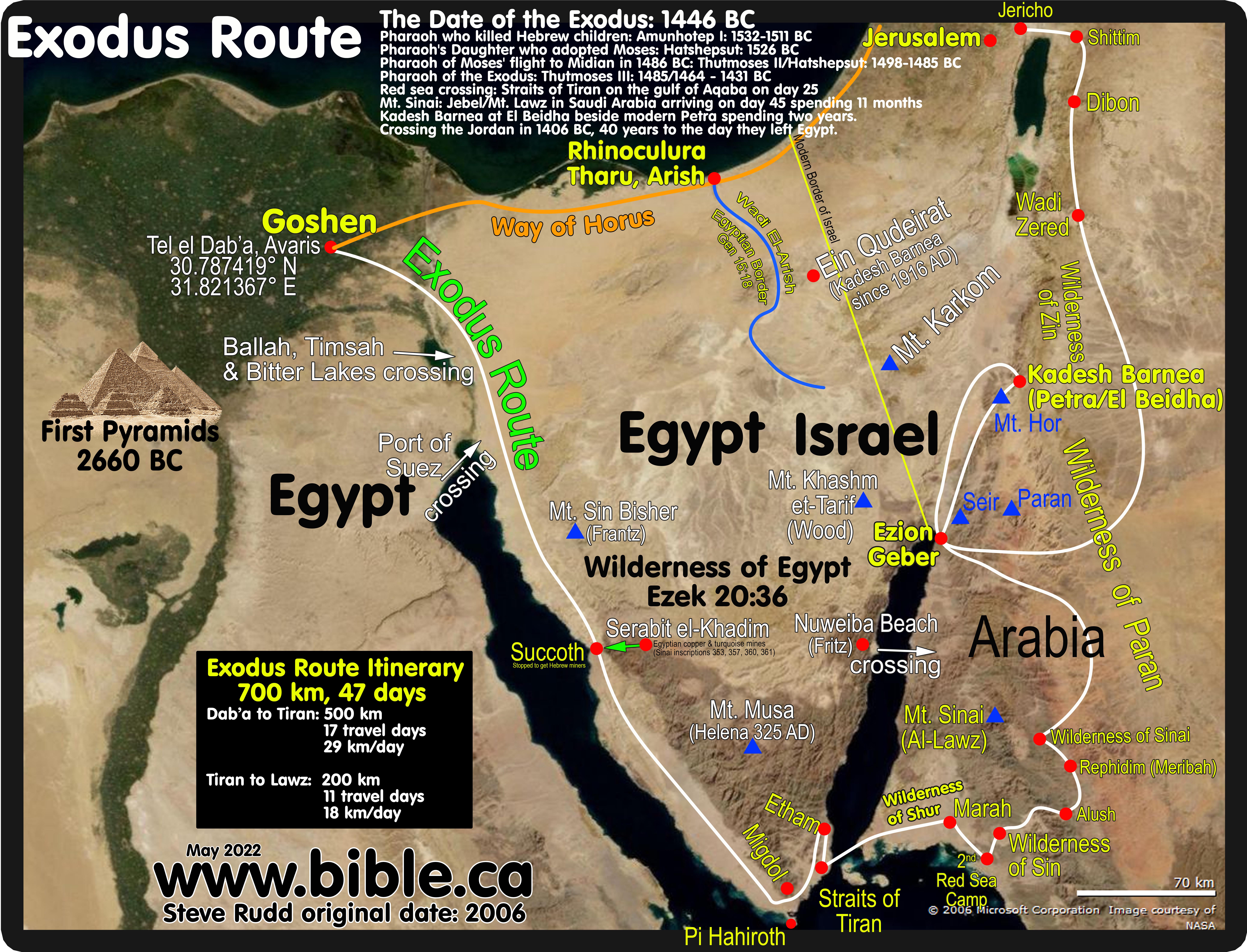



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Past: A Journey Through Antiquity Maps. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!