Unveiling the Global Tapestry of Grasslands: A Vital Ecosystem Under Pressure
Related Articles: Unveiling the Global Tapestry of Grasslands: A Vital Ecosystem Under Pressure
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Global Tapestry of Grasslands: A Vital Ecosystem Under Pressure. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Global Tapestry of Grasslands: A Vital Ecosystem Under Pressure

Grasslands, often referred to as prairies, savannas, or steppes, constitute a vast and diverse biome covering approximately 20% of the Earth’s land surface. These ecosystems are characterized by a dominant presence of grasses, with varying proportions of other herbaceous plants, shrubs, and trees depending on the specific type of grassland. The global distribution of grasslands is influenced by a complex interplay of factors, including climate, soil type, and human activities.
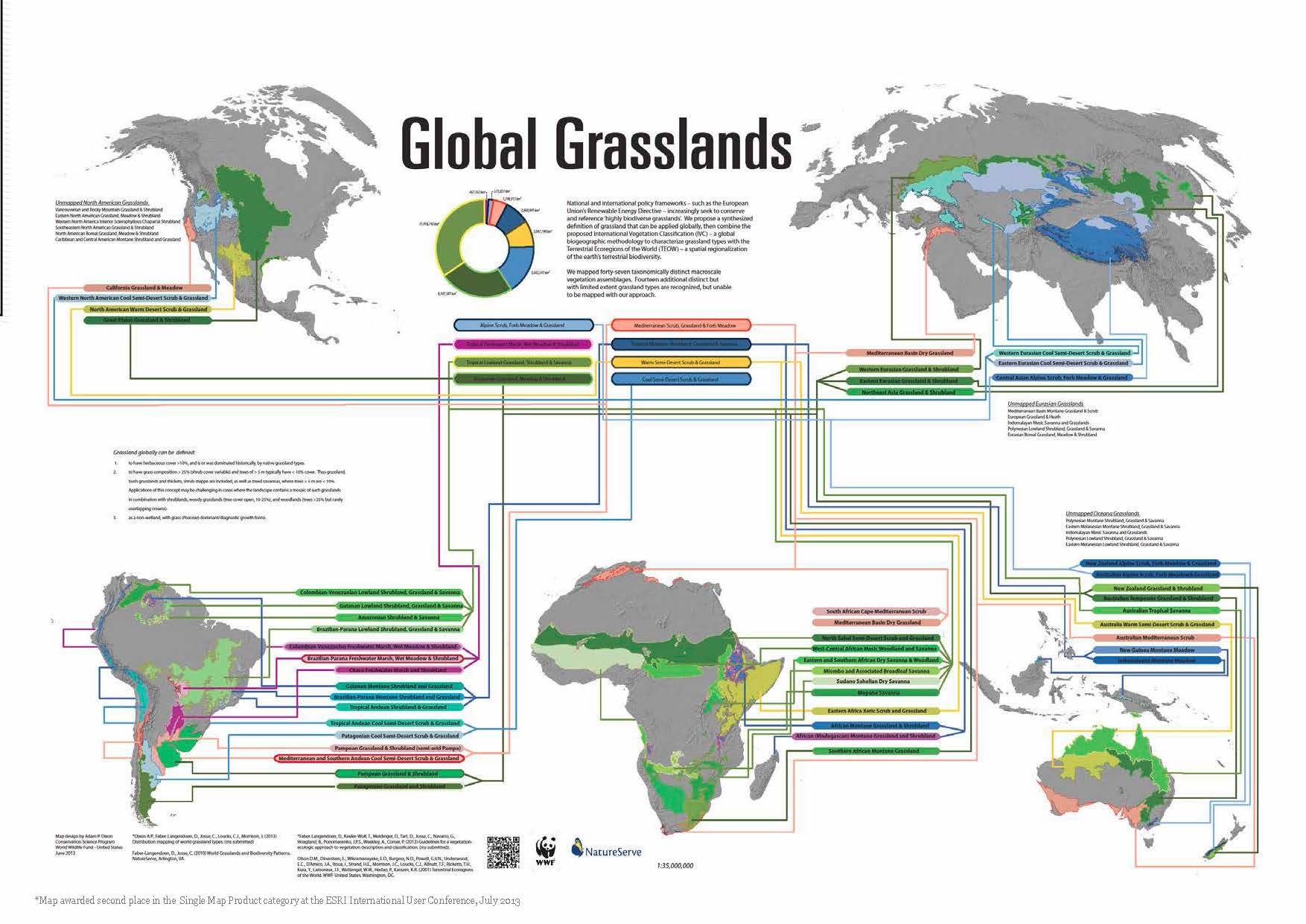
A Map of Global Grasslands: A Visual Journey
To understand the global distribution of grasslands, a map is an invaluable tool. A map of world grasslands provides a visual representation of their location, extent, and diversity. It reveals the vast expanse of these ecosystems, encompassing a wide range of biogeographical regions, from the rolling prairies of North America to the arid savannas of Africa and the temperate steppes of Eurasia.
Understanding the Diversity of Grasslands
The map of world grasslands highlights the remarkable diversity of this biome. Various factors, including climate, precipitation, and soil conditions, contribute to the distinct characteristics of different grassland types. Some key examples include:
-
Temperate Grasslands: Found in mid-latitude regions, these grasslands experience distinct seasons with cold winters and warm summers. Examples include the North American prairies, the Eurasian steppes, and the Pampas of South America.
-
Tropical Savannas: Characterized by a warm climate with distinct wet and dry seasons, these grasslands are found in regions near the equator. The African savannas, with their iconic acacia trees, are a prime example.
-
Mediterranean Grasslands: Located in regions with hot, dry summers and mild, wet winters, these grasslands are found in coastal areas around the Mediterranean Sea, California, and parts of Australia.
The Importance of Grasslands: A Vital Ecosystem
Grasslands play a crucial role in maintaining global ecological balance and supporting human livelihoods. Their importance can be summarized as follows:
-
Biodiversity Hotspot: Grasslands harbor a rich diversity of plant and animal life, including numerous endemic species found nowhere else. They provide vital habitats for a wide range of wildlife, from grazing mammals like bison and zebras to birds, reptiles, and insects.
-
Carbon Sequestration: Grasslands play a significant role in mitigating climate change by absorbing and storing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. Their extensive root systems contribute to soil carbon sequestration, helping to reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
-
Water Regulation: Grassland ecosystems are vital for regulating water cycles. Their vegetation cover helps to prevent soil erosion, maintain water quality, and recharge groundwater aquifers.
-
Food Security: Grasslands provide essential grazing land for livestock, supporting the production of meat, milk, and other dairy products. They also contribute to the cultivation of crops like wheat and barley, ensuring food security for millions of people worldwide.
-
Cultural Heritage: Grasslands have a rich cultural heritage, inspiring art, literature, and music. They have been home to indigenous communities for millennia, who have developed unique traditions and practices adapted to these environments.
Challenges Facing Grasslands: A Looming Threat
Despite their vital importance, grasslands are facing increasing threats from human activities, leading to habitat loss, degradation, and biodiversity decline. Some key challenges include:
-
Land Conversion: Grasslands are being converted to agricultural land, urban areas, and infrastructure development, reducing their extent and fragmenting habitats.
-
Overgrazing: Excessive grazing by livestock can lead to soil erosion, vegetation loss, and desertification, impacting the ecological integrity of grasslands.
-
Climate Change: Changing precipitation patterns, increased drought frequency, and extreme weather events pose significant threats to grassland ecosystems.
-
Invasive Species: Introduced species can outcompete native plants and animals, disrupting ecological balance and reducing biodiversity.
Conservation Efforts: Protecting Our Grasslands
Recognizing the importance of grasslands, conservation efforts are underway to protect and restore these vital ecosystems. Some key strategies include:
-
Protected Areas: Establishing national parks, wildlife sanctuaries, and other protected areas helps to safeguard grassland habitats and their biodiversity.
-
Sustainable Land Management: Implementing practices like rotational grazing, controlled burning, and habitat restoration can help to maintain grassland health and productivity.
-
Policy and Legislation: Strong policies and legislation are needed to regulate land use, protect biodiversity, and address the threats posed by climate change.
-
Community Engagement: Engaging local communities in conservation efforts is crucial, ensuring that their knowledge and perspectives are incorporated into management plans.
FAQs about Grasslands
Q: What is the largest grassland in the world?
A: The largest grassland in the world is the Eurasian Steppe, spanning a vast expanse across eastern Europe and central Asia.
Q: What are some of the key threats to grasslands?
A: Some of the main threats to grasslands include land conversion, overgrazing, climate change, and invasive species.
Q: What are some examples of grassland animals?
A: Grasslands are home to a wide variety of animals, including bison, zebras, lions, elephants, gazelles, kangaroos, and many species of birds.
Q: How can I help conserve grasslands?
A: You can support grassland conservation by supporting organizations that work to protect these ecosystems, advocating for policies that promote sustainable land management, and making conscious choices about your consumption habits.
Tips for Learning More about Grasslands
-
Visit a local grassland: Take a hike or visit a national park to experience the beauty and diversity of grasslands firsthand.
-
Read books and articles: Explore books and articles about grasslands to learn more about their ecology, biodiversity, and conservation challenges.
-
Support conservation organizations: Donate to organizations working to protect grasslands around the world.
-
Educate others: Share your knowledge about grasslands with friends, family, and colleagues to raise awareness about their importance.
Conclusion: A Vital Ecosystem in Need of Our Attention
Grasslands are vital ecosystems that provide essential services to humanity and the planet. Their biodiversity, carbon sequestration capacity, and role in water regulation are critical for maintaining a healthy and sustainable future. However, grasslands are facing significant threats from human activities, requiring urgent action to protect and restore these valuable ecosystems. By understanding the importance of grasslands, supporting conservation efforts, and promoting sustainable land management practices, we can ensure that these vital landscapes continue to thrive for generations to come.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Global Tapestry of Grasslands: A Vital Ecosystem Under Pressure. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!