Unveiling the Global Air Pollution Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Utilizing Air Quality Maps
Related Articles: Unveiling the Global Air Pollution Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Utilizing Air Quality Maps
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Global Air Pollution Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Utilizing Air Quality Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Global Air Pollution Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Utilizing Air Quality Maps

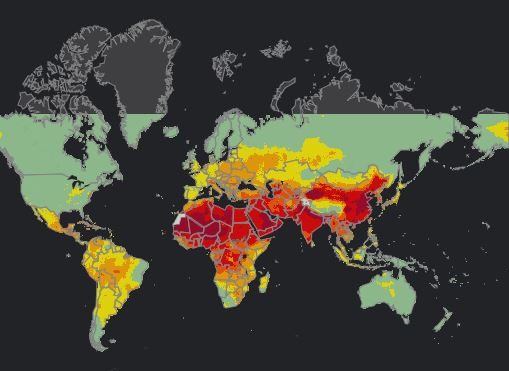
Air pollution, a silent but deadly threat, permeates our planet, impacting both human health and the environment. Understanding the global distribution and severity of air pollution is crucial for informed decision-making and effective mitigation strategies. This comprehensive guide delves into the world of air pollution maps, exploring their significance, functionalities, and applications.
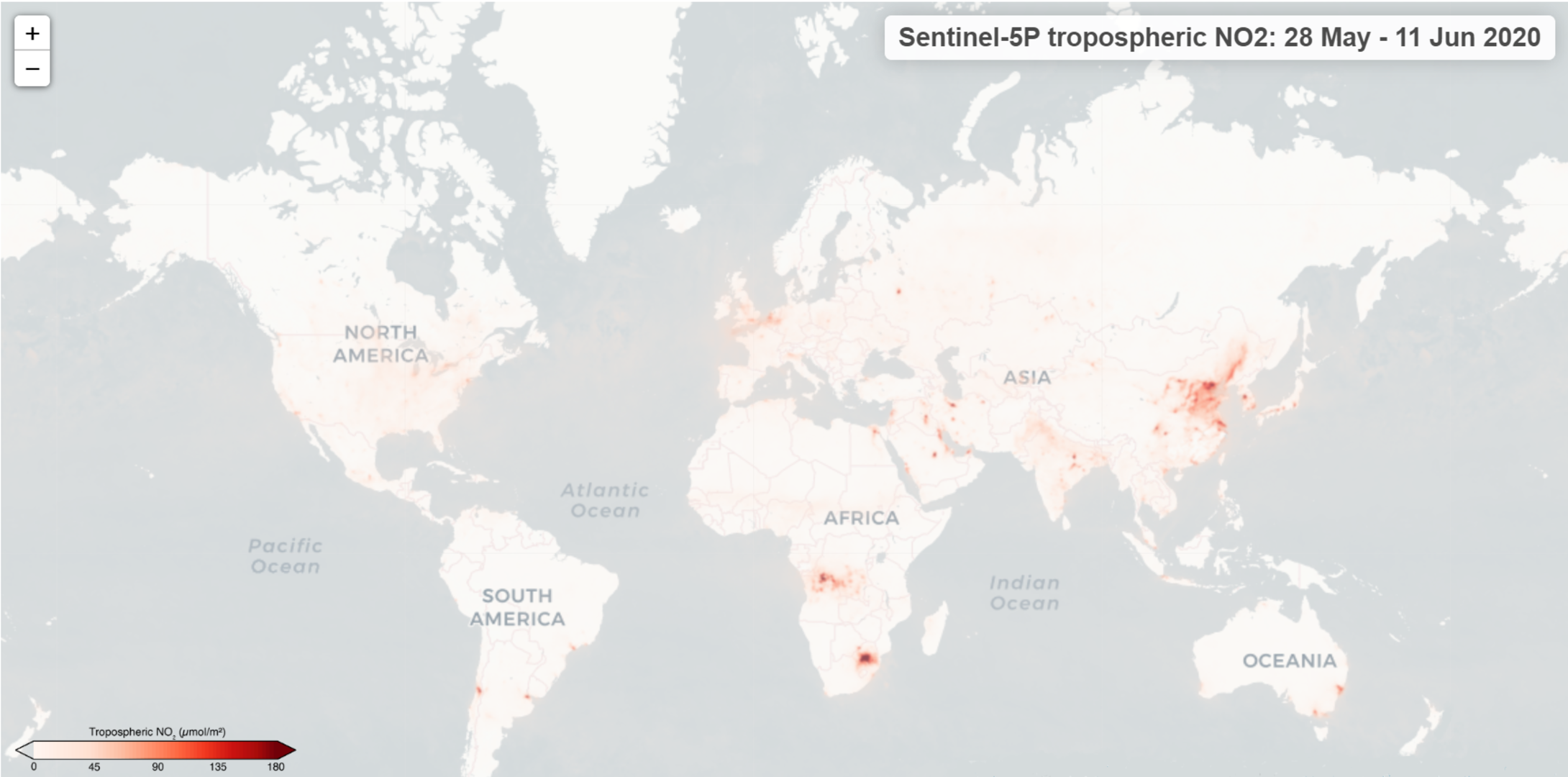
What are Air Pollution Maps?
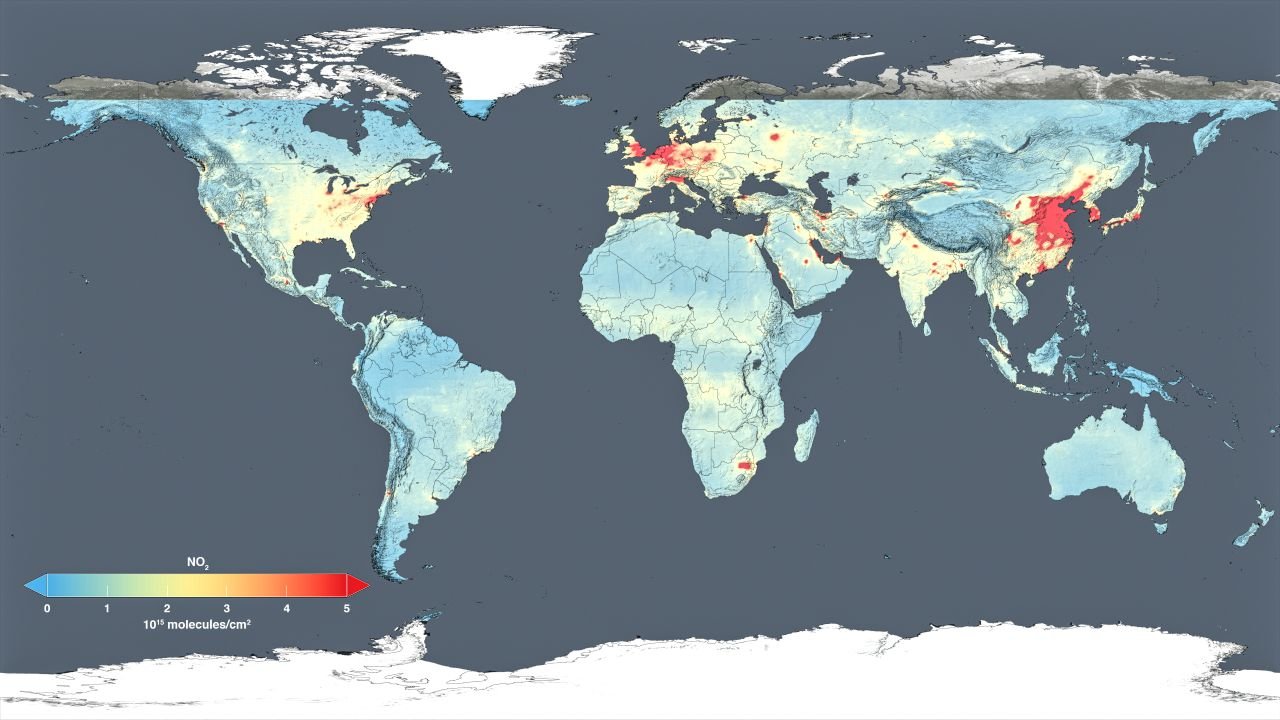
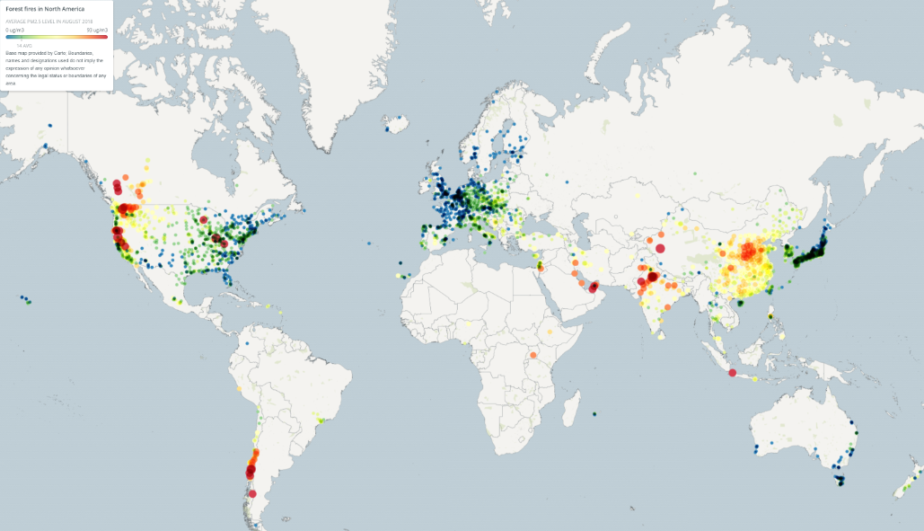
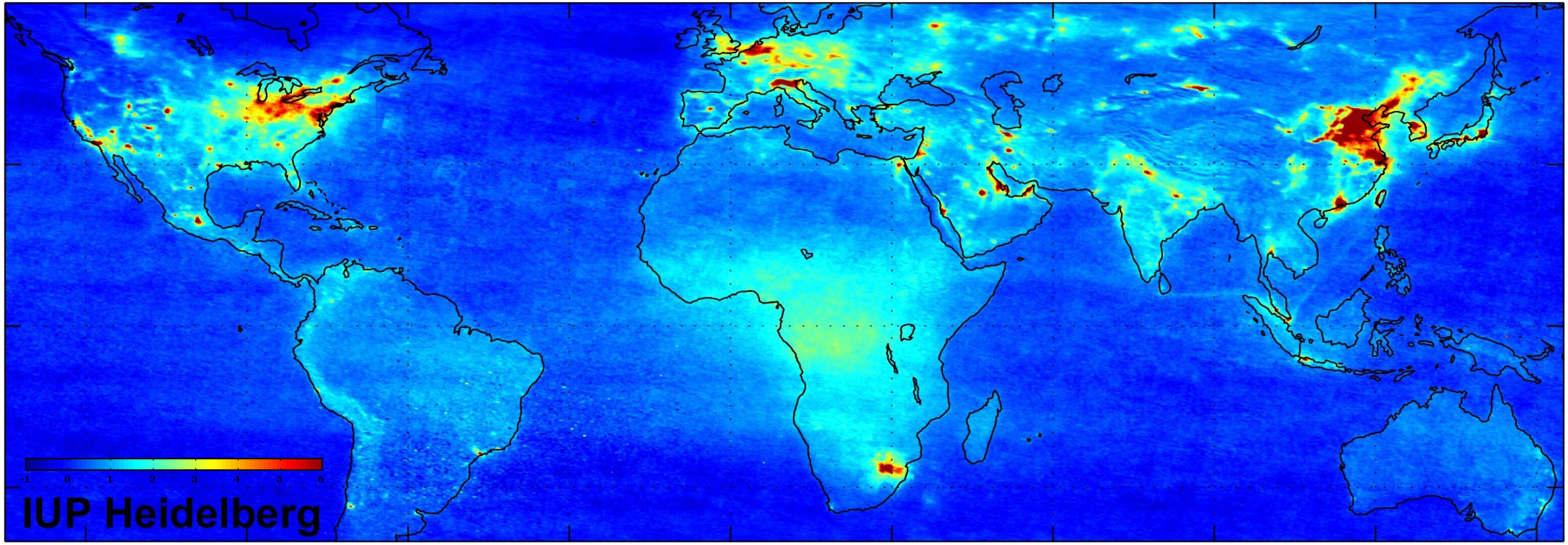
Air pollution maps are visual representations of air quality data collected from various sources, including ground-based monitoring stations, satellite imagery, and modeling systems. These maps display the concentration of different pollutants, such as particulate matter (PM2.5 and PM10), ozone (O3), sulfur dioxide (SO2), nitrogen dioxide (NO2), and carbon monoxide (CO), across geographical areas.
The Importance of Air Pollution Maps
Air pollution maps serve as powerful tools for various stakeholders, including:
- Public Health Officials: Maps provide real-time and historical air quality data, enabling health authorities to monitor pollution levels, identify areas of concern, and issue timely health advisories. This information is crucial for implementing public health measures, such as issuing air quality alerts, recommending respiratory protection, and adjusting outdoor activity schedules.
- Environmental Agencies: Environmental regulators rely on air pollution maps to track pollution trends, identify sources of pollution, and evaluate the effectiveness of pollution control measures. Maps help pinpoint areas where emission reduction strategies need to be strengthened and facilitate the development of targeted interventions.
- Researchers and Scientists: Researchers utilize air pollution maps to study the relationship between air pollution and health outcomes, investigate the impact of pollution on ecosystems, and develop advanced pollution modeling techniques. These maps provide valuable datasets for scientific investigations and contribute to a deeper understanding of air pollution dynamics.
- Individuals and Communities: Air pollution maps empower individuals to make informed decisions about their health and well-being. By accessing real-time air quality data, individuals can choose to avoid areas with high pollution levels, plan outdoor activities during periods of better air quality, and adopt measures to reduce their exposure to pollutants.
- Businesses and Industries: Companies, particularly those operating in pollution-sensitive sectors, can utilize air pollution maps to assess the environmental impact of their operations, comply with regulatory requirements, and implement sustainable practices. Maps help businesses identify areas where emission reduction measures are most effective and facilitate the development of environmentally responsible strategies.
Types of Air Pollution Maps
Air pollution maps can be categorized based on their data sources, spatial resolution, and the pollutants they display. Common types include:
- Ground-Based Monitoring Station Maps: These maps rely on data collected from air quality monitoring stations placed across urban and rural areas. They provide accurate and localized information but are limited by the density and distribution of monitoring stations.
- Satellite-Based Maps: Satellite imagery captures air pollution data across vast geographical areas, offering a comprehensive view of pollution patterns. While satellite data has lower spatial resolution than ground-based measurements, it provides valuable insights into regional and global pollution trends.
- Model-Based Maps: Air quality models combine atmospheric data, emission inventories, and meteorological information to simulate air pollution levels. These maps can provide predictions of future pollution levels and assess the impact of different emission scenarios.
Key Features of Air Pollution Maps
Air pollution maps typically include the following features:
- Interactive Map Interface: Most air pollution maps offer interactive interfaces that allow users to zoom in and out, explore different geographical areas, and access detailed information about specific locations.
- Real-Time Data Display: Maps often present real-time air quality data, providing up-to-the-minute information about pollution levels.
- Historical Data Visualization: Users can access historical air quality data, enabling them to track pollution trends over time.
- Pollution Level Indicators: Maps typically use color-coded scales to represent different pollution levels, making it easy to identify areas with high or low air quality.
- Pollutant Information: Maps display the concentration of various pollutants, allowing users to focus on specific pollutants of interest.
- Data Sources and Methodology: Reliable air pollution maps should provide information about the data sources used, the methodology employed, and the limitations of the data.
Understanding Air Pollution Map Data
Air pollution maps typically display data on various pollutants, each with its own health and environmental implications:
- Particulate Matter (PM2.5 and PM10): Particulate matter refers to tiny particles suspended in the air. PM2.5, with a diameter less than 2.5 micrometers, can penetrate deep into the lungs and bloodstream, posing significant health risks. PM10, with a diameter less than 10 micrometers, can irritate the respiratory system.
- Ozone (O3): Ozone is a gas that forms in the atmosphere through chemical reactions involving nitrogen oxides and volatile organic compounds. Ground-level ozone is a harmful air pollutant that can damage lung tissue and contribute to respiratory problems.
- Sulfur Dioxide (SO2): Sulfur dioxide is a gas released from burning fossil fuels, particularly coal. It can irritate the respiratory system and contribute to acid rain.
- Nitrogen Dioxide (NO2): Nitrogen dioxide is a gas produced from combustion processes, primarily from vehicles and power plants. It can irritate the respiratory system and contribute to smog formation.
- Carbon Monoxide (CO): Carbon monoxide is a colorless and odorless gas produced from incomplete combustion of fossil fuels. It reduces the oxygen-carrying capacity of the blood, leading to health problems, particularly in individuals with cardiovascular conditions.
Navigating Air Pollution Maps Effectively
To maximize the benefits of air pollution maps, it is essential to understand their limitations and use them effectively:
- Data Availability and Accuracy: The accuracy and reliability of air pollution maps depend on the quality and availability of data. Data gaps, inaccuracies, and limitations in monitoring networks can affect the map’s representation of air quality.
- Spatial Resolution: Maps may have different spatial resolutions, meaning the level of detail they provide varies. High-resolution maps provide more localized information, while low-resolution maps offer a broader overview.
- Pollutant-Specific Information: Focus on the pollutants that are most relevant to your location, health concerns, or research interests.
- Data Interpretation: Understand the units used to measure air quality, the color-coded scales, and the meaning of different pollution levels.
- Consult Multiple Sources: Compare data from different air pollution maps to gain a more comprehensive understanding of air quality in a particular area.
- Stay Informed: Regularly check air pollution maps to stay updated on air quality conditions and make informed decisions about your health and activities.
FAQs about Air Pollution Maps
Q: Where can I find reliable air pollution maps?
A: Several websites and apps provide access to air pollution maps. Some notable sources include:
- AirNow (United States): https://www.airnow.gov/
- World Air Quality Index (WAQI): https://waqi.info/
- European Environment Agency (EEA): https://www.eea.europa.eu/
- Global Atmosphere Watch (GAW): https://www.wmo.int/gaw
- NASA Earth Observatory: https://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/
Q: How can I use air pollution maps to protect my health?
A: Air pollution maps can help you:
- Avoid areas with high pollution levels: Plan outdoor activities during periods of better air quality.
- Minimize exposure to pollutants: Reduce time spent outdoors during periods of high pollution.
- Use respiratory protection: Consider wearing masks or respirators when exposed to high pollution levels.
- Stay informed about health advisories: Follow recommendations from health authorities during periods of poor air quality.
Q: What can I do to reduce air pollution?
A: You can contribute to improving air quality by:
- Using public transportation, cycling, or walking: Reduce reliance on private vehicles.
- Conserving energy: Turn off lights and appliances when not in use.
- Supporting renewable energy sources: Advocate for policies that promote clean energy.
- Choosing environmentally friendly products: Consider the environmental impact of your purchases.
- Reducing waste: Recycle and compost to minimize the need for landfill disposal.
Tips for Utilizing Air Pollution Maps
- Customize your map view: Zoom in and out, adjust the display settings, and select specific pollutants to focus on your areas of interest.
- Compare data from different sources: Cross-reference information from multiple air pollution maps to gain a more comprehensive picture of air quality.
- Use historical data to identify trends: Analyze pollution levels over time to understand seasonal variations and long-term trends.
- Share information with others: Raise awareness about air pollution and encourage others to use air pollution maps to protect their health.
- Contact local authorities: Report concerns about air pollution and advocate for policies that improve air quality.
Conclusion
Air pollution maps are invaluable tools for understanding the global air pollution landscape, monitoring pollution levels, and informing decision-making. By leveraging the information provided by these maps, individuals, communities, businesses, and governments can take proactive steps to protect public health, mitigate environmental damage, and build a healthier and more sustainable future.
The fight against air pollution requires a multi-faceted approach, involving technological advancements, policy interventions, and individual actions. Air pollution maps serve as a vital bridge between data and action, empowering us to navigate the complex world of air pollution and work towards a cleaner and healthier planet for all.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Global Air Pollution Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Utilizing Air Quality Maps. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!