Unveiling the Diverse Landscape of Europe: A Comprehensive Exploration of Relief Maps
Related Articles: Unveiling the Diverse Landscape of Europe: A Comprehensive Exploration of Relief Maps
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Diverse Landscape of Europe: A Comprehensive Exploration of Relief Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Diverse Landscape of Europe: A Comprehensive Exploration of Relief Maps
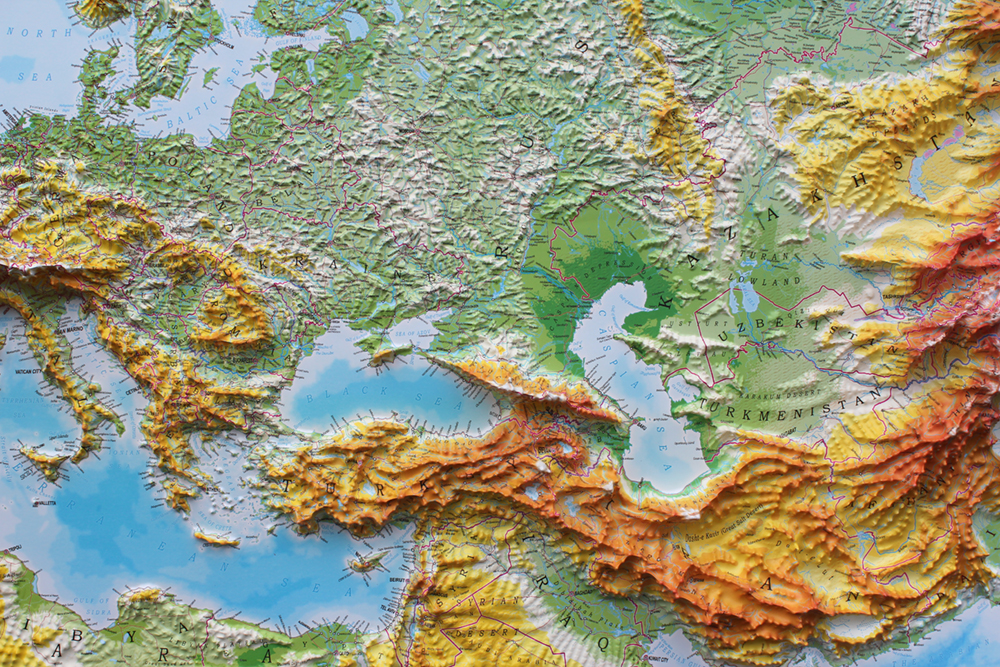
A relief map, a three-dimensional representation of a region’s topography, provides a powerful visual tool for understanding the intricate physical geography of a place. When applied to Europe, this map reveals a continent of dramatic contrasts, from towering mountain ranges to expansive lowlands, sculpted by millennia of geological forces. This exploration delves into the intricacies of European relief maps, highlighting their significance in various fields and providing insights into the continent’s captivating landscape.
Understanding the Relief Map of Europe
The relief map of Europe is a fascinating tapestry woven from diverse geological features, each contributing to the continent’s unique character.
1. The Alpine System: A Spine of Mountains
The majestic Alps, stretching from the Mediterranean Sea to the Balkans, form the most prominent feature on the relief map. This mountain range, a product of tectonic plate collisions, boasts towering peaks like Mont Blanc and the Matterhorn, glaciers that carve deep valleys, and fertile alpine meadows. The Alps not only shape the landscape but also influence the climate, creating distinct microclimates within their valleys.
2. The Pyrenees: A Rugged Frontier
The Pyrenees, separating Spain and France, present another formidable mountain range. Their jagged peaks and deep gorges, sculpted by erosion, offer challenging terrain for mountaineers and breathtaking scenery for nature enthusiasts. The Pyrenees, like the Alps, act as a natural barrier, influencing weather patterns and shaping the cultural identities of the regions they divide.
3. The Carpathians: A Curved Chain of Mountains
The Carpathian Mountains, a crescent-shaped range encircling the Pannonian Basin, offer a different perspective on European topography. Their lower peaks and gentler slopes, compared to the Alps, create a unique landscape characterized by rolling hills, forested valleys, and mineral-rich springs. The Carpathians have historically played a vital role in shaping the cultural and economic landscapes of Eastern Europe.
4. The Scandinavian Mountains: A Land of Fjords and Forests
The Scandinavian Mountains, stretching along the western coast of the Scandinavian Peninsula, showcase a dramatic interplay between mountains and sea. Their rugged peaks, carved by glaciers, plunge into the ocean, creating iconic fjords – deep, narrow inlets with steep cliffs. This mountainous region is also home to vast forests, abundant lakes, and a rich biodiversity.
5. The European Lowlands: A Vast and Fertile Plain
The vast European Lowlands, extending from the North Sea to the Black Sea, stand in stark contrast to the mountainous regions. This expansive plain, shaped by glacial activity and river erosion, offers fertile land for agriculture, fostering dense populations and bustling cities. The lowlands are also characterized by extensive river systems, including the Rhine, Danube, and Volga, which have historically played a crucial role in trade and transportation.
The Importance of Relief Maps in Understanding Europe
Relief maps are invaluable tools for understanding the complex interplay of factors that shape Europe’s physical geography and its impact on human activities.
1. Understanding Climate and Weather Patterns
The relief map reveals how mountains act as barriers, influencing rainfall patterns and creating distinct microclimates. The Alps, for instance, block moisture-laden winds from the Mediterranean, creating a drier climate on their northern slopes. The Scandinavian Mountains, on the other hand, contribute to the abundance of rainfall in Norway’s western coast.
2. Recognizing the Impact on Human Settlements
The relief map illustrates how topography influences human settlements. The fertile lowlands have historically attracted dense populations, while mountainous regions have often been less densely populated, with communities adapting to the challenging terrain. The presence of rivers and valleys has also played a crucial role in shaping urban development and transportation networks.
3. Exploring the Influence on Economic Activities
The relief map highlights the relationship between topography and economic activities. The fertile lowlands are ideal for agriculture, while mountainous regions often offer opportunities for forestry, mining, and tourism. The presence of rivers and coasts has also influenced the development of industries, including fishing, shipping, and hydroelectric power generation.
4. Understanding the Historical Context
The relief map offers insights into historical events and cultural development. Mountain ranges have often served as natural barriers, influencing political boundaries and cultural identities. The Alps, for example, have historically separated northern and southern Europe, contributing to distinct cultural developments on either side.
5. Facilitating Environmental Management and Conservation
The relief map provides a valuable tool for environmental management and conservation. By visualizing the landscape, we can identify areas susceptible to erosion, flooding, or landslides, allowing for targeted interventions. It also helps in understanding the distribution of natural resources, facilitating their sustainable management.
FAQs about Relief Maps of Europe
1. What are the most common types of relief maps used to depict Europe?
The most common types of relief maps used to depict Europe include:
- Contour maps: These maps use lines of equal elevation to represent the terrain, providing a detailed representation of the landscape.
- Shaded relief maps: These maps use shading to create a three-dimensional effect, highlighting the variations in elevation and creating a visually striking representation.
- Physical maps: These maps combine elevation data with other physical features like rivers, lakes, and vegetation, providing a comprehensive overview of the landscape.
2. What are the main geological processes that have shaped the relief of Europe?
The main geological processes that have shaped the relief of Europe include:
- Tectonic plate movement: Collisions between tectonic plates have created mountain ranges like the Alps, Pyrenees, and Carpathians.
- Glacial activity: The Pleistocene ice ages have carved valleys, sculpted mountains, and deposited sediment across the continent.
- Erosion: Wind, water, and gravity have eroded and reshaped the landscape, creating diverse features like canyons, valleys, and coastal cliffs.
3. How do relief maps contribute to our understanding of European history?
Relief maps help us understand how topography has influenced historical events, such as:
- Migration patterns: Mountain ranges and rivers have often acted as natural barriers, influencing migration routes and the spread of cultures.
- Military campaigns: The terrain has played a significant role in military strategies, influencing the outcome of battles and the development of fortifications.
- Trade routes: Rivers and valleys have served as natural corridors for trade, connecting different regions and fostering economic development.
4. What are some of the challenges associated with creating accurate relief maps of Europe?
Creating accurate relief maps of Europe presents several challenges:
- Vastness of the continent: Representing the diverse topography of such a large continent requires careful selection of scale and projection.
- Data accuracy: Obtaining precise elevation data for the entire continent can be challenging, requiring extensive surveys and data analysis.
- Visual representation: Effectively representing the three-dimensional nature of the landscape requires sophisticated techniques to create realistic and informative maps.
Tips for Using Relief Maps of Europe Effectively
1. Choose the right map for your needs: Different types of relief maps are suitable for different purposes. Consider the level of detail, the type of information you need, and the intended audience.
2. Analyze the key features: Pay attention to the major mountain ranges, rivers, and lowlands, understanding their impact on the landscape and human activities.
3. Explore the relationship between relief and other factors: Consider how topography influences climate, settlements, and economic activities.
4. Use the map as a starting point for further research: The relief map can inspire you to delve deeper into specific regions, historical events, or environmental issues.
Conclusion
The relief map of Europe is a powerful tool for understanding the continent’s diverse and captivating landscape. It reveals a tapestry of mountains, plains, and rivers, shaped by geological forces and influencing human activities for millennia. By studying the relief map, we gain insights into the intricate interplay of topography, climate, settlements, and economic development, fostering a deeper appreciation for the unique character of Europe. From the towering peaks of the Alps to the vast expanse of the European Lowlands, the relief map serves as a valuable guide for navigating the continent’s rich history, diverse cultures, and complex environmental challenges.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Diverse Landscape of Europe: A Comprehensive Exploration of Relief Maps. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!