Unveiling Patterns: A Comprehensive Guide to Geographical Heat Maps
Related Articles: Unveiling Patterns: A Comprehensive Guide to Geographical Heat Maps
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling Patterns: A Comprehensive Guide to Geographical Heat Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling Patterns: A Comprehensive Guide to Geographical Heat Maps
In the realm of data visualization, geographical heat maps emerge as powerful tools for revealing spatial patterns and trends. These maps translate numerical data into a visually compelling representation, using color gradients to highlight areas of high and low concentration. This intuitive approach allows for quick and insightful analysis of various phenomena, from population density and crime rates to product demand and customer engagement.
Understanding the Essence of Geographical Heat Maps
At its core, a geographical heat map employs a color scale to depict the intensity of a specific variable across a geographical area. The color spectrum, typically ranging from cool to warm hues, represents a continuous scale of data values. Areas with higher values are represented by warmer colors, while areas with lower values are depicted in cooler shades. This visual representation allows for immediate identification of hotspots and cold spots, providing a clear picture of spatial variations.
Applications Across Diverse Fields
The versatility of geographical heat maps extends across numerous disciplines, finding practical applications in various sectors:
- Business and Marketing: Analyzing customer demographics, identifying market potential, optimizing store locations, and understanding customer behavior.
- Healthcare: Tracking disease outbreaks, mapping healthcare resource availability, and identifying areas with high risk factors.
- Environmental Studies: Monitoring pollution levels, tracking deforestation patterns, and analyzing climate change impacts.
- Urban Planning: Assessing population density, identifying areas with high crime rates, and optimizing infrastructure development.
- Social Sciences: Studying migration patterns, understanding socioeconomic disparities, and analyzing voting trends.
- Real Estate: Identifying areas with high property values, analyzing market trends, and targeting potential buyers.
Creating Effective Geographical Heat Maps
The effectiveness of a geographical heat map hinges on careful data selection, appropriate visualization techniques, and effective communication. Key considerations include:
- Data Quality: Ensuring data accuracy, completeness, and consistency is crucial for accurate representation.
- Data Aggregation: Determining the appropriate spatial unit for data aggregation (e.g., counties, zip codes, census tracts) is essential for meaningful analysis.
- Color Scheme: Selecting a color scheme that effectively communicates the data range and facilitates clear visual distinction between high and low values is paramount.
- Map Projection: Choosing the appropriate map projection to minimize distortion and ensure accurate representation of geographical features is essential.
- Clarity and Conciseness: Avoiding clutter and ensuring clear labeling of data sources, legend, and map features enhances readability and understanding.
Benefits of Geographical Heat Maps
The use of geographical heat maps offers several advantages:
- Visual Clarity: Provides a clear and intuitive representation of data, facilitating quick understanding of spatial patterns.
- Data Insights: Reveals hidden trends and relationships within data, leading to valuable insights and informed decision-making.
- Data Exploration: Allows for interactive exploration of data, enabling users to zoom in, pan, and filter data based on specific criteria.
- Communication Efficiency: Effectively communicates complex data to a wide audience, regardless of their technical expertise.
- Decision Support: Provides a visual framework for decision-making, enabling informed choices based on data-driven evidence.
FAQs About Geographical Heat Maps
1. What types of data are suitable for geographical heat maps?
Geographical heat maps are best suited for data that can be spatially referenced and aggregated. This includes data like population density, crime rates, sales figures, disease incidence, and environmental pollution levels.
2. How can I create a geographical heat map?
Several software tools and online platforms allow for the creation of geographical heat maps, including:
- GIS software: ArcGIS, QGIS, and MapInfo are powerful GIS tools offering comprehensive mapping and analysis capabilities.
- Data visualization platforms: Tableau, Power BI, and Google Maps offer user-friendly interfaces for creating interactive heat maps.
- Online mapping tools: Mapbox, Leaflet, and Google Maps API provide customizable options for creating custom heat maps.
3. What are the limitations of geographical heat maps?
While powerful, geographical heat maps have limitations:
- Data Aggregation Bias: Aggregated data can mask local variations and potentially lead to misleading interpretations.
- Spatial Resolution: The spatial resolution of the data determines the level of detail that can be visualized, potentially limiting analysis of fine-grained patterns.
- Visual Distortion: Map projections can distort geographical features, potentially affecting the accuracy of visual representations.
- Interpretation Bias: Visual representations can be subjective, leading to potential biases in interpretation.
Tips for Effective Geographical Heat Map Creation
- Start with a clear objective: Define the specific question or problem you aim to address with the heat map.
- Choose appropriate data: Select relevant data that accurately reflects the phenomenon you are studying.
- Optimize data aggregation: Choose the most appropriate spatial unit for data aggregation based on the scale of analysis.
- Select a suitable color scheme: Opt for a color scheme that effectively communicates the data range and facilitates clear visual distinctions.
- Ensure map projection accuracy: Select a map projection that minimizes distortion and ensures accurate representation of geographical features.
- Maintain clarity and conciseness: Avoid clutter, and ensure clear labeling of data sources, legend, and map features.
- Consider interactive elements: Incorporate interactive features like zoom, pan, and filtering to enhance data exploration.
Conclusion: Unlocking Spatial Insights
Geographical heat maps offer a powerful and versatile tool for visualizing and analyzing spatial data. By transforming numerical data into visually compelling representations, these maps provide valuable insights into patterns, trends, and relationships across geographical areas. Their applications extend across diverse fields, enabling informed decision-making in areas like business, healthcare, environmental studies, urban planning, social sciences, and real estate. By embracing the power of geographical heat maps, we unlock the potential for deeper understanding of spatial phenomena and drive informed actions based on data-driven evidence.
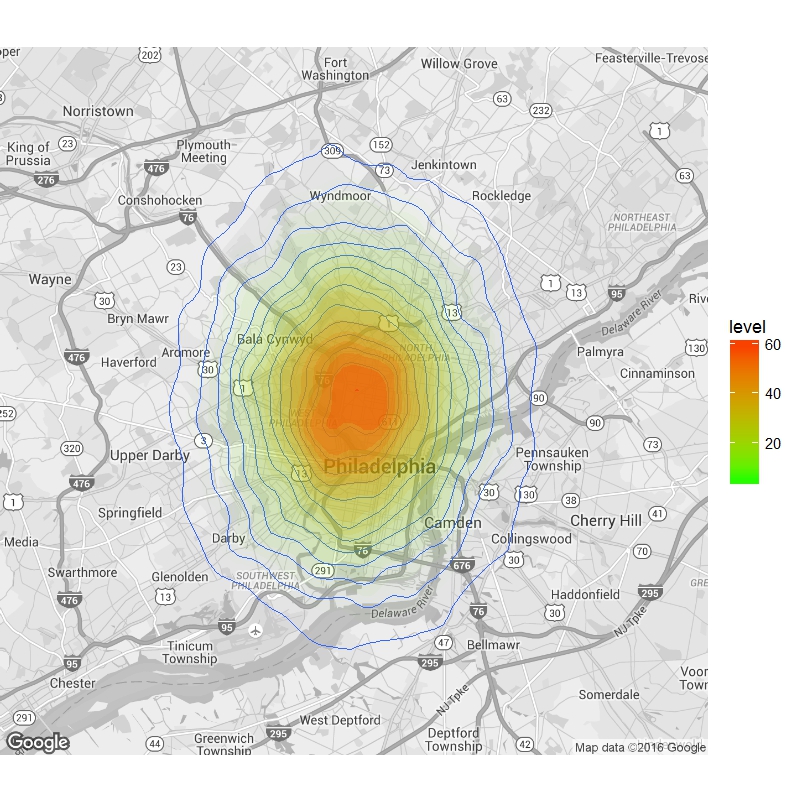

![5 Real Heat Map Examples From Leading Industries [2024] VWO](https://static.wingify.com/gcp/uploads/sites/3/2021/01/Geo-heatmap.jpg)

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling Patterns: A Comprehensive Guide to Geographical Heat Maps. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!