Unlocking the Secrets of the Wet Bulb Temperature Map: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Unlocking the Secrets of the Wet Bulb Temperature Map: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unlocking the Secrets of the Wet Bulb Temperature Map: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unlocking the Secrets of the Wet Bulb Temperature Map: A Comprehensive Guide

The Earth’s climate is a complex system constantly in flux. As human activities continue to alter the delicate balance of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, the planet is experiencing unprecedented warming. This warming trend, coupled with increasing humidity, has led to a growing concern: the rise of extreme heat events. To better understand and prepare for these events, scientists have developed a critical tool: the wet bulb temperature map.
Understanding Wet Bulb Temperature
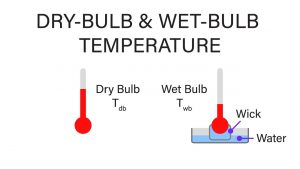
Wet bulb temperature (WBT) is a measure of the human body’s ability to cool itself through sweating. Unlike air temperature, which is simply a measure of the heat in the air, WBT accounts for both air temperature and humidity. When sweat evaporates from the skin, it cools the body. However, in humid conditions, evaporation is hindered, making it more difficult for the body to regulate its temperature.
How the Wet Bulb Temperature Map Works
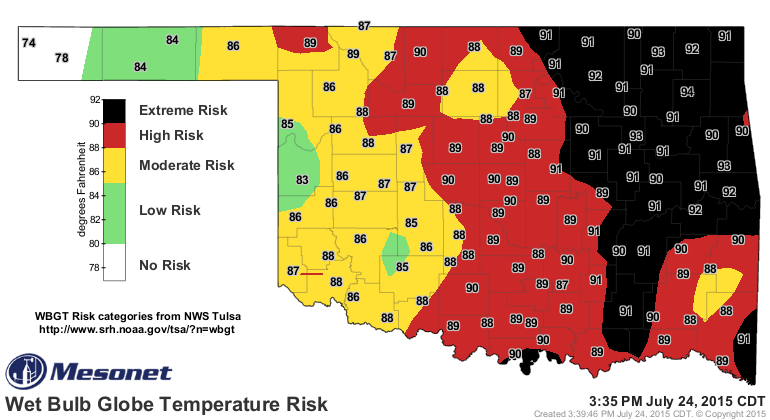
A wet bulb temperature map is a graphical representation of WBT across a geographical region. It typically uses color gradients to depict different WBT values, with warmer colors indicating higher WBTs. These maps are generated using climate models and meteorological data, providing a snapshot of the potential heat stress that different regions may experience.
The Significance of the Wet Bulb Temperature Map
The wet bulb temperature map is an invaluable tool for various reasons:
- Predicting Heat Stress: By showing areas with high WBTs, the map helps identify regions where heat stress is likely to be most severe. This information is crucial for public health officials, emergency responders, and infrastructure planners in developing strategies to mitigate heat-related risks.
- Assessing Heat Vulnerability: The map highlights areas where populations are most vulnerable to extreme heat. This information can be used to target resources and support systems to those communities that need them most.
- Planning for Climate Change: As climate change intensifies, the map provides a vital tool for understanding the future impacts of rising temperatures and humidity. This information can be used to inform climate adaptation strategies, such as urban planning, infrastructure design, and agricultural practices.
- Improving Public Awareness: The map serves as a powerful visual representation of the potential consequences of climate change. By showcasing the severity of heat stress in different regions, it can raise public awareness and encourage individual and collective action to mitigate climate change.
Applications of Wet Bulb Temperature Maps
Wet bulb temperature maps have a wide range of applications across various sectors:
- Public Health: Health officials can use the map to anticipate heat waves and implement early warning systems, educate the public about heat-related health risks, and allocate resources to vulnerable populations.
- Urban Planning: City planners can use the map to design heat-resilient urban environments, such as incorporating green spaces and reflective surfaces, to reduce the urban heat island effect.
- Infrastructure: Engineers and architects can use the map to design buildings, roads, and other infrastructure that can withstand extreme heat conditions.
- Agriculture: Farmers can use the map to identify areas where crops are most vulnerable to heat stress and implement strategies to mitigate the impact of extreme heat on yields.
- Emergency Management: Emergency responders can use the map to anticipate potential heat-related emergencies and prepare for swift and effective responses.
FAQs about Wet Bulb Temperature Maps
Q: What is the difference between air temperature and wet bulb temperature?
A: Air temperature is a measure of the heat in the air, while wet bulb temperature accounts for both air temperature and humidity. WBT reflects the human body’s ability to cool itself through sweating, making it a more accurate indicator of heat stress than air temperature alone.
Q: What is the significance of the 35°C wet bulb temperature threshold?
A: The 35°C wet bulb temperature threshold is considered a critical point beyond which the human body can no longer cool itself through sweating. Prolonged exposure to temperatures above this threshold can lead to heat stroke and even death.
Q: How are wet bulb temperature maps created?
A: Wet bulb temperature maps are generated using climate models and meteorological data. These models incorporate factors such as air temperature, humidity, wind speed, and solar radiation to estimate WBT across different regions.
Q: What are the limitations of wet bulb temperature maps?
A: Wet bulb temperature maps are based on models and estimations, which may not perfectly capture the complex dynamics of real-world weather patterns. Additionally, they may not account for localized microclimates or variations in individual heat tolerance.
Tips for Using Wet Bulb Temperature Maps
- Consider the context: When interpreting a wet bulb temperature map, it’s crucial to consider the specific region and time period. WBT can vary significantly depending on location, season, and time of day.
- Focus on the highest values: Pay attention to areas with the highest WBT values, as these are the regions most at risk of extreme heat events.
- Integrate with other data: Combine wet bulb temperature maps with other data sources, such as population density, socioeconomic factors, and infrastructure information, to gain a comprehensive understanding of heat vulnerability.
- Take action: Use the information from the map to inform decision-making and implement strategies to mitigate heat-related risks.
Conclusion
Wet bulb temperature maps are essential tools for understanding and preparing for the impacts of climate change. By providing a clear and comprehensive picture of heat stress across different regions, these maps empower individuals, communities, and policymakers to take proactive measures to mitigate the risks of extreme heat. As the world continues to grapple with the consequences of climate change, wet bulb temperature maps will play an increasingly important role in ensuring the health and well-being of all.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unlocking the Secrets of the Wet Bulb Temperature Map: A Comprehensive Guide. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!