Unlocking the Secrets of Alaska’s Climate: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Temperature Maps
Related Articles: Unlocking the Secrets of Alaska’s Climate: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Temperature Maps
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unlocking the Secrets of Alaska’s Climate: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Temperature Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Unlocking the Secrets of Alaska’s Climate: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Temperature Maps
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unlocking the Secrets of Alaska’s Climate: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Temperature Maps
- 3.1 Unveiling the Dynamics of Alaska’s Temperature Patterns
- 3.2 Navigating the Diverse Regional Climates
- 3.3 The Importance of Alaska’s Temperature Maps
- 3.4 FAQs About Alaska’s Temperature Maps
- 3.5 Tips for Utilizing Alaska’s Temperature Maps
- 3.6 Conclusion: Navigating Alaska’s Climate with Temperature Maps
- 4 Closure
Unlocking the Secrets of Alaska’s Climate: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Temperature Maps
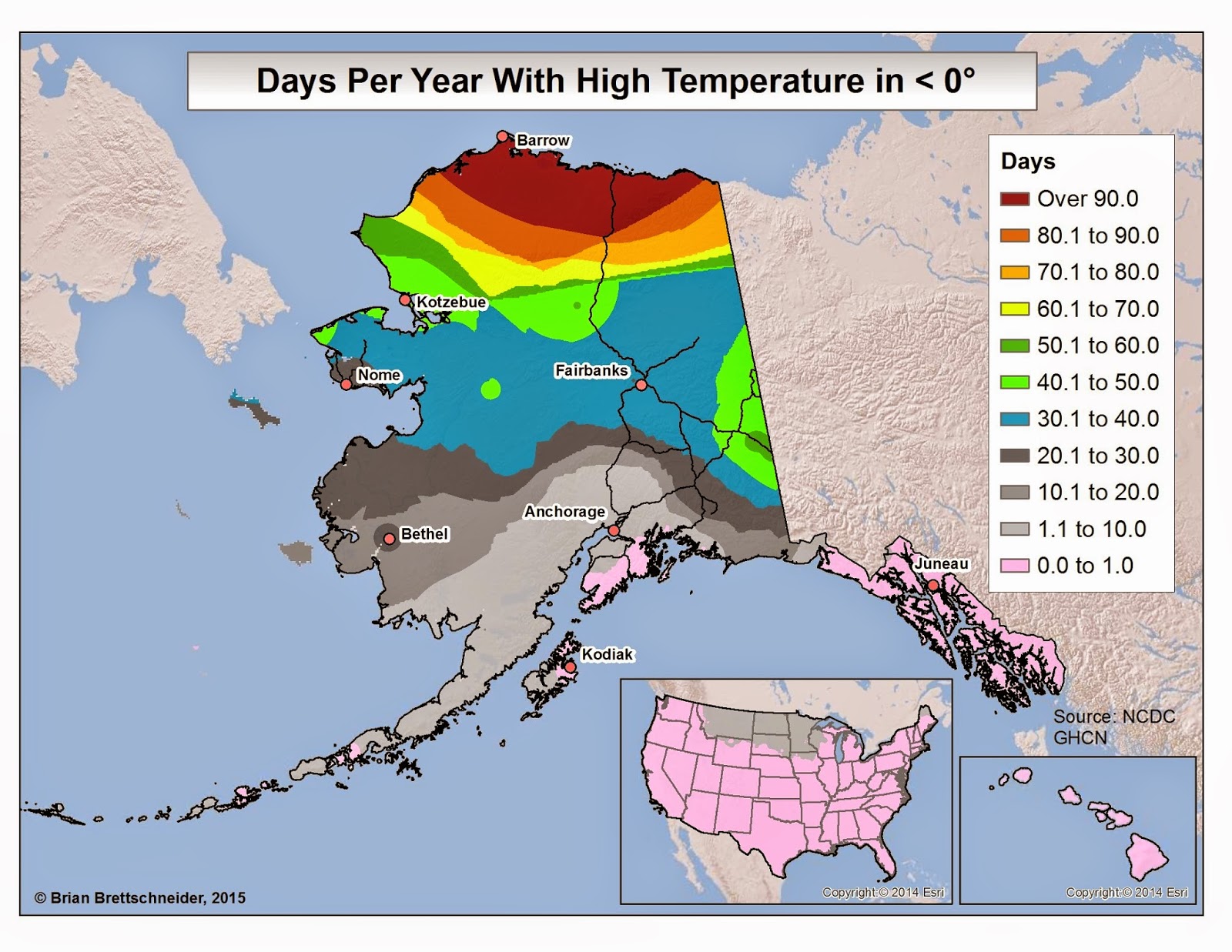
Alaska, the largest state in the United States, is renowned for its breathtaking landscapes and diverse ecosystems. However, beneath its picturesque exterior lies a complex and dynamic climate system. Understanding Alaska’s temperature patterns is crucial for various aspects of life in the state, from planning outdoor activities to managing resources and adapting to the changing environment.
This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of Alaska’s temperature maps, providing a clear and informative explanation of their significance and utility. We will explore the factors influencing temperature variations, the diverse regional climates, and the valuable insights these maps offer for various stakeholders.
Unveiling the Dynamics of Alaska’s Temperature Patterns
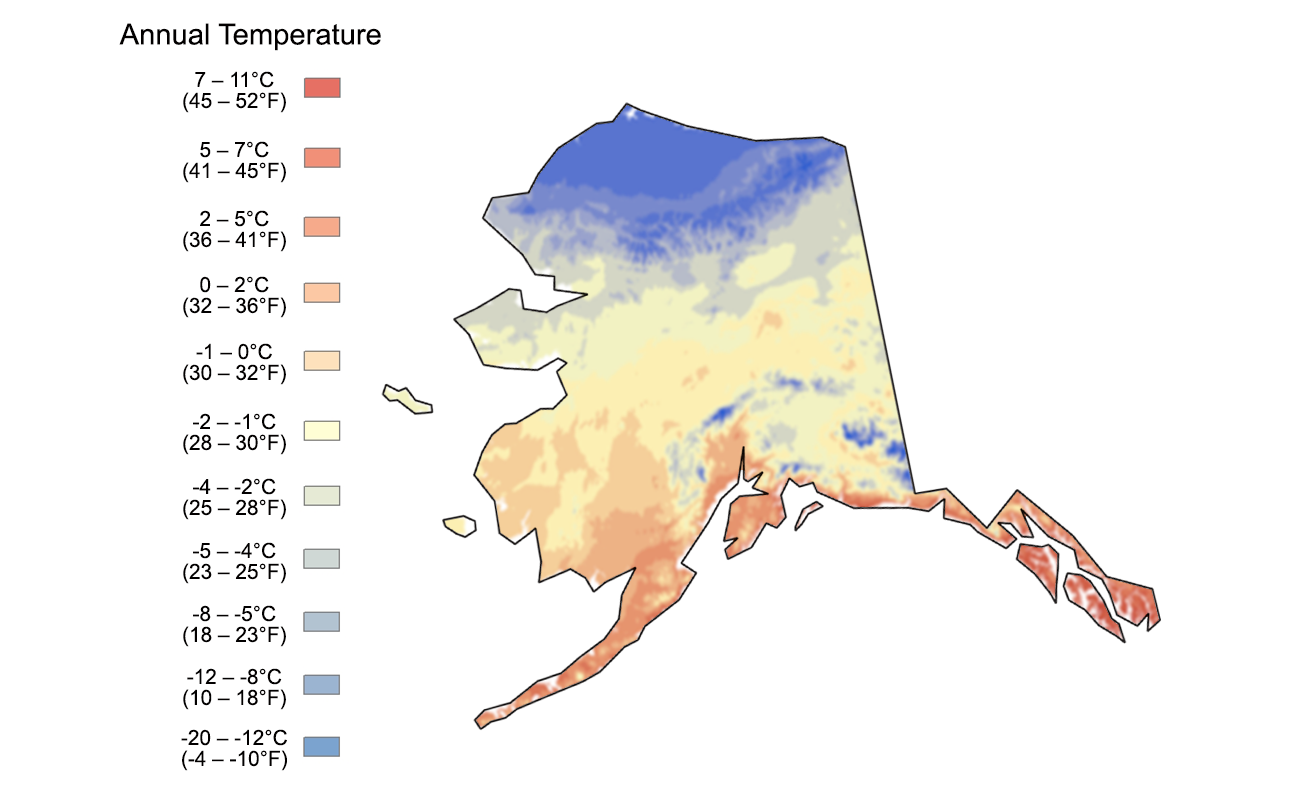
Alaska’s vast size and unique geographic features contribute to a wide range of temperature variations across the state. The temperature map serves as a visual representation of these differences, providing a snapshot of the thermal landscape at a given time.
Key Factors Influencing Alaska’s Temperatures:
- Latitude: Alaska’s high latitude position results in long periods of darkness during winter and extended daylight hours in summer, significantly impacting temperature variations.
- Ocean Currents: The influence of the Pacific Ocean, particularly the warm Alaska Current and the cold Bering Sea Current, plays a crucial role in moderating coastal temperatures.
- Topography: The state’s mountainous terrain creates distinct microclimates, with higher elevations experiencing colder temperatures due to the decrease in air pressure and the impact of the orographic effect.
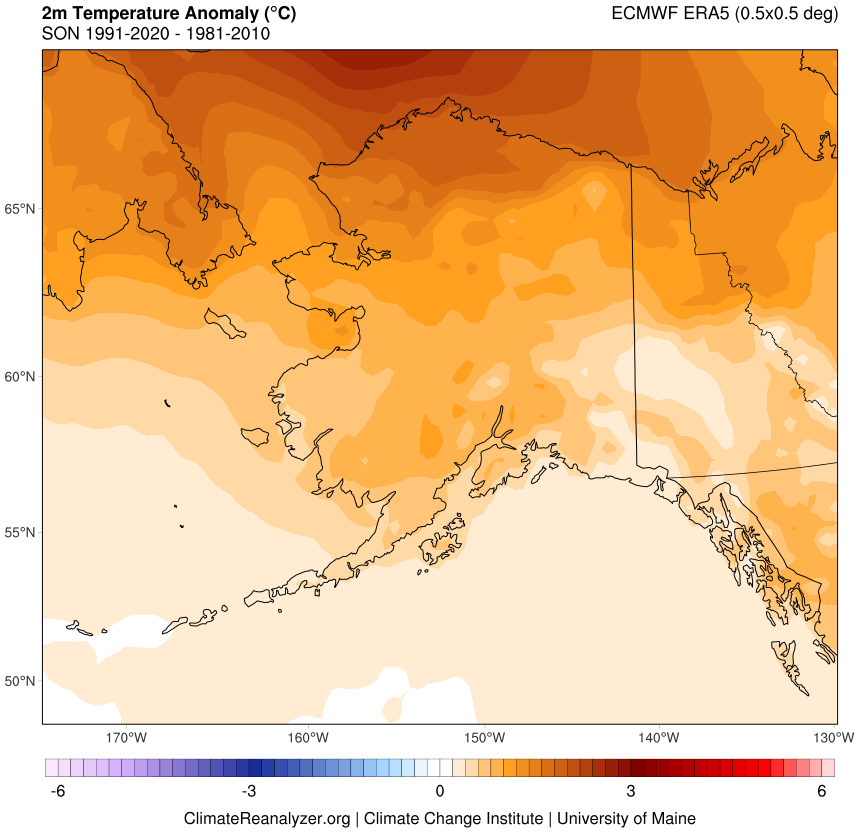
- Arctic Oscillation and Pacific Decadal Oscillation: These large-scale climate patterns influence atmospheric circulation and precipitation, impacting Alaska’s temperature patterns in the long term.
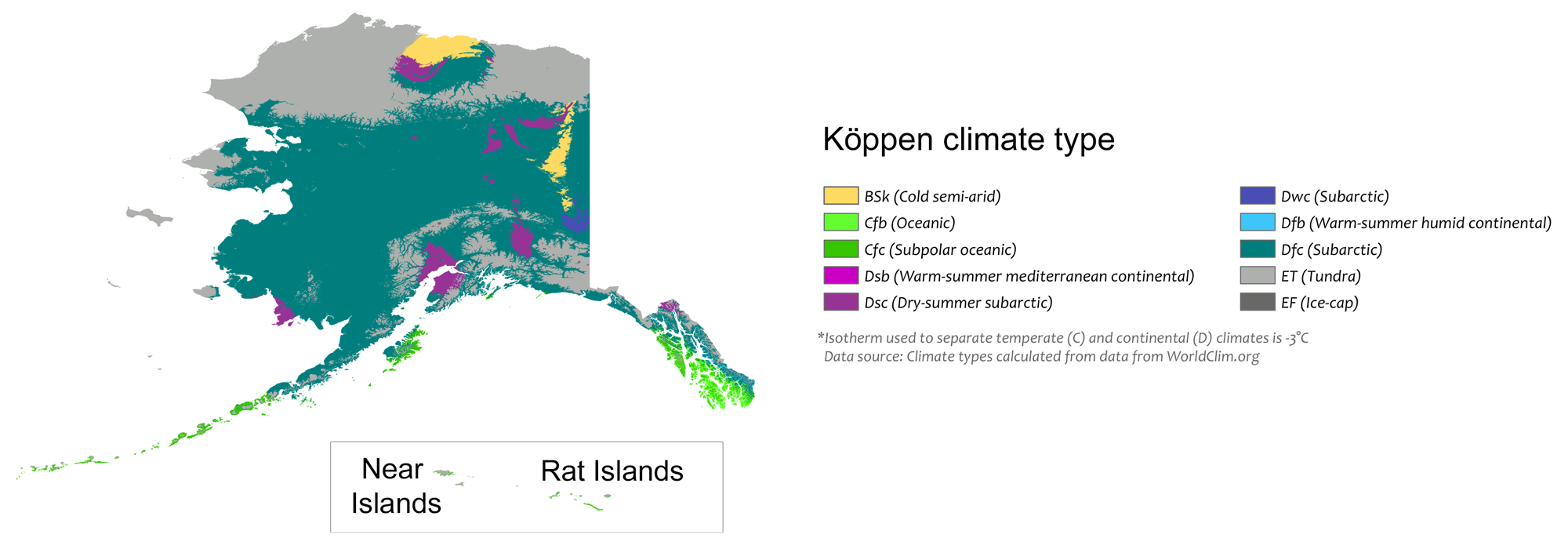
Navigating the Diverse Regional Climates
Alaska’s temperature map reveals a mosaic of regional climates, each with its unique characteristics:
- South-Central Alaska: This region experiences a maritime climate with relatively mild winters and cool, wet summers. The influence of the Alaska Current keeps temperatures moderate, particularly along the coast.
- Interior Alaska: Known for its continental climate, this region experiences extreme temperature fluctuations, with cold, dry winters and warm, sunny summers. The absence of significant moderating influences from the ocean leads to greater temperature swings.
- Southeast Alaska: This region boasts a temperate rainforest climate, characterized by mild temperatures year-round and abundant rainfall. The proximity to the Pacific Ocean provides a moderating influence, keeping temperatures relatively stable.
- Arctic Alaska: This region is dominated by a polar climate, with long, cold winters and short, cool summers. Temperatures can drop significantly below freezing for extended periods, particularly in the interior.
The Importance of Alaska’s Temperature Maps
Understanding Alaska’s temperature patterns is crucial for various stakeholders, including:
- Outdoor Enthusiasts: Hikers, skiers, climbers, and other outdoor enthusiasts rely on accurate temperature information to plan their activities safely and effectively. Understanding the temperature variations across different regions and elevations is essential for ensuring their well-being.
- Resource Managers: Understanding temperature patterns is crucial for managing Alaska’s natural resources, including fisheries, forestry, and wildlife. Temperature fluctuations can impact the health and distribution of various species, requiring informed management strategies.
- Infrastructure Planners: Engineers and architects designing infrastructure projects, such as roads, bridges, and buildings, need to consider the impact of temperature fluctuations on materials and construction processes. Temperature maps provide valuable insights for making informed decisions.
- Climate Scientists: Researchers studying climate change rely on temperature data to monitor trends, understand the impact of warming temperatures, and develop mitigation strategies.
FAQs About Alaska’s Temperature Maps
1. What is the average temperature in Alaska?
Alaska’s average temperature varies significantly across the state, ranging from the mild temperatures of Southeast Alaska to the frigid conditions of Arctic Alaska. The average annual temperature for the entire state is approximately 28 degrees Fahrenheit (-2 degrees Celsius).
2. What is the warmest month in Alaska?
The warmest month in Alaska is typically July, although temperatures can vary significantly depending on the region. South-Central Alaska experiences the warmest temperatures, with average highs in the 60s and 70s Fahrenheit (15-20 degrees Celsius).
3. What is the coldest month in Alaska?
January is generally the coldest month in Alaska, with temperatures dropping below freezing across most of the state. Interior Alaska experiences the most extreme cold, with average lows reaching well below -20 degrees Fahrenheit (-29 degrees Celsius).
4. What are the temperature records for Alaska?
The highest temperature ever recorded in Alaska was 100 degrees Fahrenheit (38 degrees Celsius) in Fort Yukon on June 27, 1915. The lowest temperature ever recorded was -80 degrees Fahrenheit (-62 degrees Celsius) in Prospect Creek on January 23, 1971.
5. How are temperature maps created?
Temperature maps are created using data collected from various sources, including weather stations, satellites, and climate models. This data is analyzed and processed to create a visual representation of temperature variations across the state.
Tips for Utilizing Alaska’s Temperature Maps
- Choose the Right Map: Ensure the map you are using is relevant to your needs, considering factors like time of year, region, and specific data points.
- Understand the Scale: Pay attention to the temperature scale used on the map to interpret the data accurately.
- Consider Elevation: Remember that temperatures decrease with altitude, so elevation is a critical factor to consider when planning activities.
- Check for Updates: Temperature patterns are constantly changing, so it is essential to check for updated maps and data.
Conclusion: Navigating Alaska’s Climate with Temperature Maps
Alaska’s temperature maps provide a powerful tool for understanding the state’s diverse and dynamic climate system. By providing a visual representation of temperature variations, these maps empower individuals and organizations to make informed decisions regarding outdoor activities, resource management, infrastructure planning, and climate research. As Alaska continues to adapt to a changing climate, these maps will play an increasingly crucial role in navigating the state’s unique thermal landscape.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unlocking the Secrets of Alaska’s Climate: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Temperature Maps. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!