Unlocking the Insights: A Comprehensive Guide to MAP Testing for Second Graders
Related Articles: Unlocking the Insights: A Comprehensive Guide to MAP Testing for Second Graders
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unlocking the Insights: A Comprehensive Guide to MAP Testing for Second Graders. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unlocking the Insights: A Comprehensive Guide to MAP Testing for Second Graders

The second grade is a pivotal year in a child’s academic journey. It marks a transition from foundational literacy and numeracy skills to more complex concepts and applications. To gauge student progress and identify areas requiring support, many schools utilize standardized assessments, including the Measures of Academic Progress (MAP) test. Understanding the nuances of MAP testing for second graders is crucial for parents, educators, and administrators alike. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of MAP testing, its scoring system, and its significance in shaping educational interventions.
Understanding the MAP Test
The Measures of Academic Progress (MAP) is a computer-adaptive assessment designed to measure student growth in reading, language usage, and mathematics. Unlike traditional standardized tests, MAP tests are not designed to compare students against a national norm. Instead, they focus on individual student growth over time.
How the MAP Test Works
MAP tests are adaptive, meaning the difficulty of the questions adjusts based on the student’s performance. If a student answers a question correctly, the next question will be slightly more challenging. Conversely, if a student answers incorrectly, the next question will be easier. This adaptive nature ensures the test accurately gauges a student’s current skill level and provides valuable insights into their strengths and weaknesses.
The Importance of MAP Testing in Second Grade
MAP testing plays a critical role in second grade for several reasons:
- Individualized Learning: MAP scores provide teachers with a detailed picture of each student’s strengths and areas for improvement. This allows teachers to tailor their instruction to meet the individual needs of each learner.
- Progress Monitoring: By administering MAP tests multiple times throughout the year, educators can track student progress and identify any areas where students may be falling behind. Early intervention can prevent learning gaps from widening.
- Data-Driven Instruction: MAP scores provide educators with valuable data to inform their teaching practices. This data can be used to identify trends in student performance, adjust curriculum, and implement targeted interventions.
- Parent Communication: MAP scores provide parents with valuable insights into their child’s academic progress. This information can help parents support their child’s learning at home.
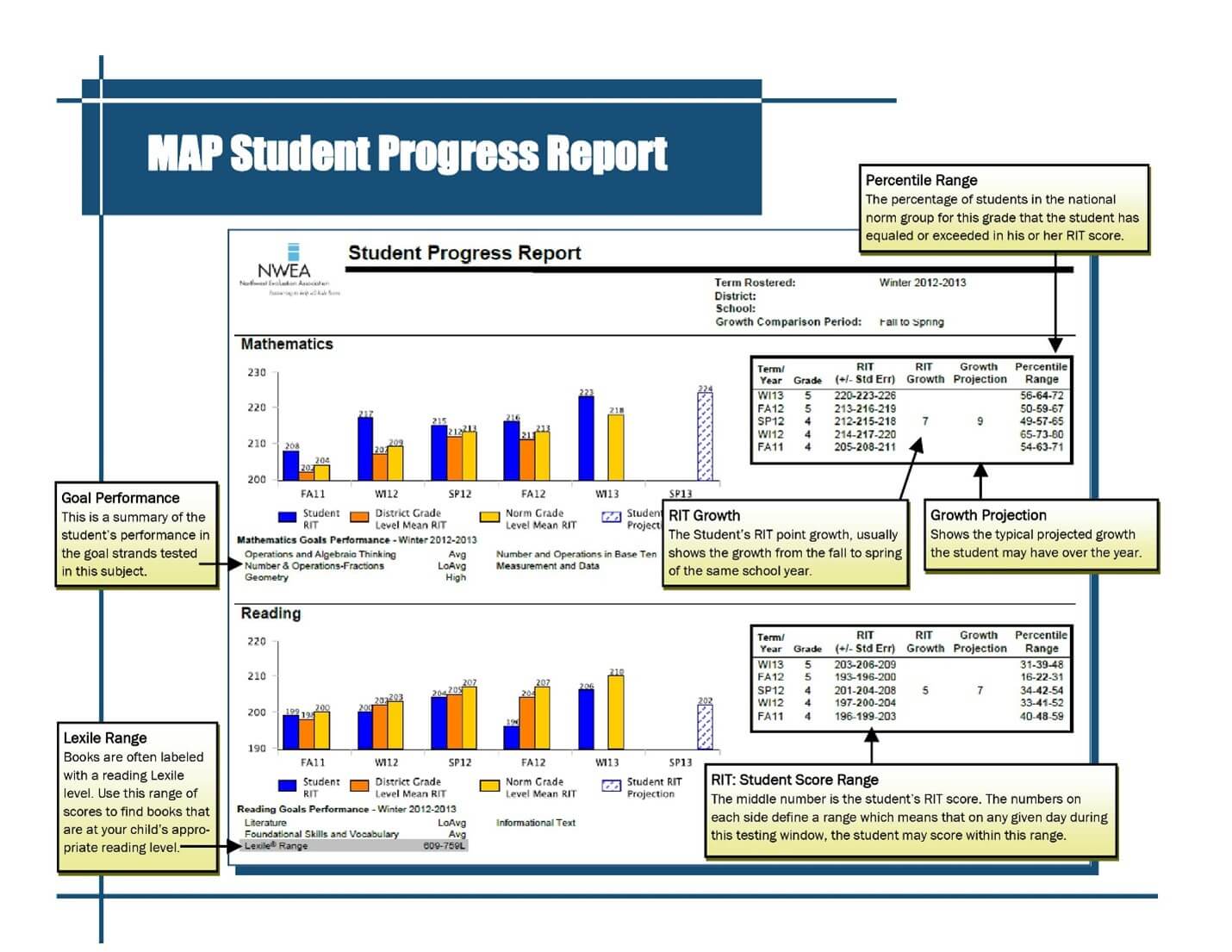
Deciphering the MAP Scores
MAP test scores are reported on a scale called the RIT scale (Rasch Item Difficulty). The RIT scale is a continuous scale, meaning that there are no gaps or breaks between scores. This allows for precise measurement of student growth over time.
Understanding the RIT Scale
- Higher RIT scores indicate higher levels of achievement.
- Each RIT point represents a specific level of skill mastery.
- A student’s RIT score is a measure of their current academic performance, not their potential.
Interpreting the MAP Scores
MAP scores are presented in a variety of ways, including:
- Growth percentile: This metric indicates a student’s growth compared to other students in their grade.
- Growth standard deviation: This metric indicates how much a student’s score has changed from one test administration to the next.
- National percentile: This metric compares a student’s score to the performance of other students nationwide.
Analyzing the MAP Scores
While the RIT scale provides a precise measurement of student performance, it is important to consider the context of the scores. Factors such as the student’s prior academic history, learning style, and classroom environment can influence their performance on the MAP test.
Using MAP Scores to Enhance Learning
MAP scores provide valuable insights into student performance and can be used to guide instructional decisions.
- Targeted Interventions: Educators can use MAP scores to identify students who may need additional support in specific areas.
- Differentiated Instruction: Teachers can use MAP scores to differentiate instruction and provide each student with appropriate learning challenges.
- Curriculum Adjustments: Schools can use MAP scores to evaluate the effectiveness of their curriculum and make adjustments as needed.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What are the benefits of MAP testing?
A: MAP testing offers several benefits, including:
- Individualized learning: MAP scores help educators tailor instruction to meet the specific needs of each student.
- Progress monitoring: MAP tests allow educators to track student growth over time and identify areas where students may be falling behind.
- Data-driven instruction: MAP scores provide valuable data that can inform instructional decisions.
- Parent communication: MAP scores provide parents with insights into their child’s academic progress.
Q: How often should students take the MAP test?
A: The frequency of MAP testing varies depending on the school district and the individual needs of the students. Generally, students take the MAP test three times per year: fall, winter, and spring.
Q: How can parents help their children prepare for the MAP test?
A: Parents can help their children prepare for the MAP test by:
- Encouraging reading: Encourage your child to read regularly and engage in conversations about what they are reading.
- Developing math skills: Play math games with your child and help them with their homework.
- Creating a positive learning environment: Provide your child with a quiet place to study and show them that you value their education.
Q: What are some tips for students taking the MAP test?
A: Students can improve their performance on the MAP test by:
- Getting a good night’s sleep: A well-rested student is more likely to focus and perform their best.
- Eating a healthy breakfast: Fueling your brain with a healthy meal can improve concentration.
- Reading the directions carefully: Make sure you understand the instructions before you begin the test.
- Taking your time: Don’t rush through the test. Read each question carefully and think about your answer.
- Guessing is okay: If you don’t know the answer to a question, make your best guess.
Conclusion
MAP testing plays a significant role in second grade, providing valuable insights into student performance and guiding instructional decisions. By understanding the nuances of the MAP test, its scoring system, and its importance in shaping educational interventions, parents, educators, and administrators can work together to ensure that all students have the opportunity to reach their full academic potential. While MAP testing provides a snapshot of student progress, it’s important to remember that it is just one piece of the educational puzzle. Combining MAP scores with other assessments, classroom observations, and student portfolios creates a more holistic picture of each child’s learning journey.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unlocking the Insights: A Comprehensive Guide to MAP Testing for Second Graders. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!