Unlocking Efficiency: A Comprehensive Guide to Process Map Creation
Related Articles: Unlocking Efficiency: A Comprehensive Guide to Process Map Creation
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unlocking Efficiency: A Comprehensive Guide to Process Map Creation. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Unlocking Efficiency: A Comprehensive Guide to Process Map Creation
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unlocking Efficiency: A Comprehensive Guide to Process Map Creation
- 3.1 The Essence of Process Mapping: A Visual Blueprint for Efficiency
- 3.2 The Benefits of Process Mapping: Unveiling Opportunities for Growth
- 3.3 The Process of Process Mapping: A Step-by-Step Guide
- 3.4 Methods of Process Mapping: Choosing the Right Tool
- 3.5 Tips for Successful Process Mapping: A Practical Guide
- 3.6 FAQs: Addressing Common Questions about Process Mapping
- 3.7 Conclusion: Empowering Organizations for Growth and Success
- 4 Closure
Unlocking Efficiency: A Comprehensive Guide to Process Map Creation
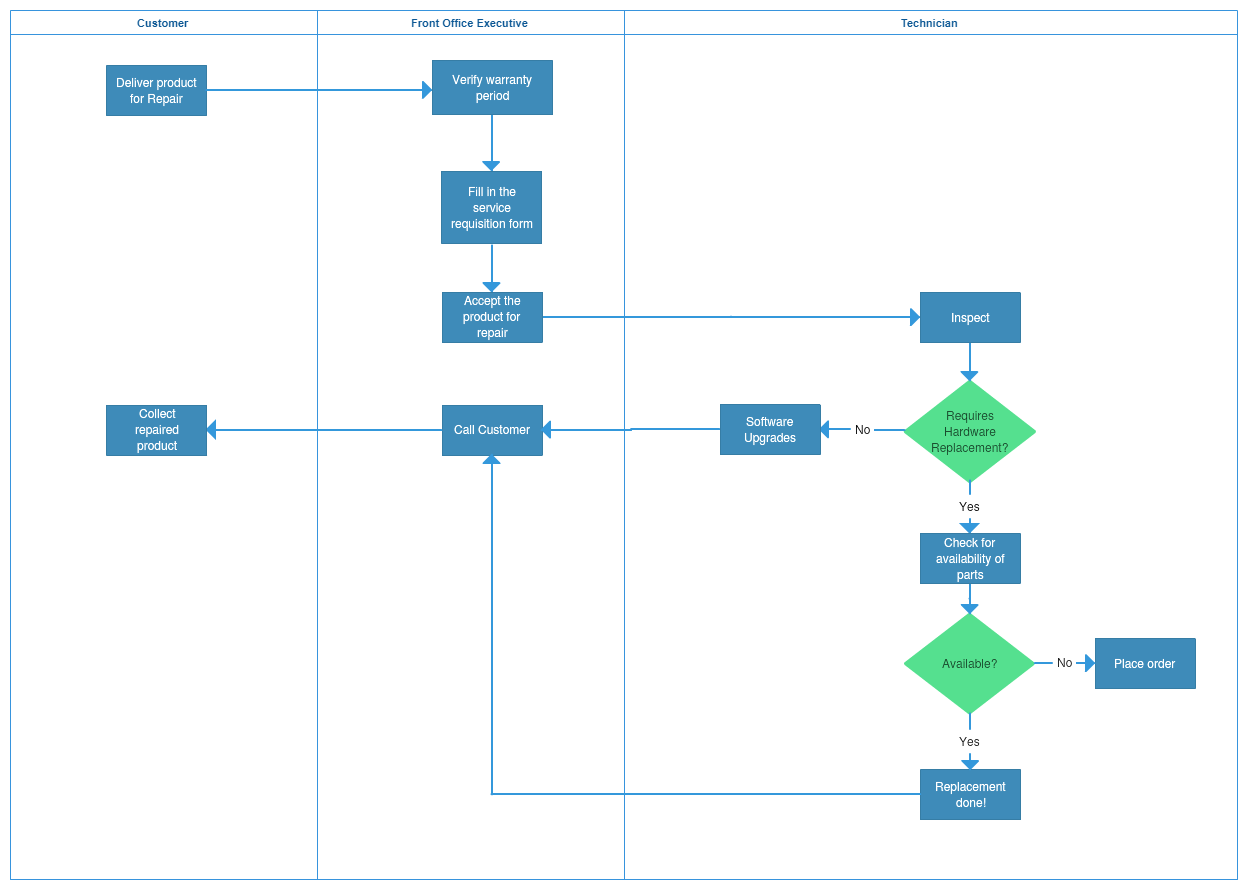
In the modern business landscape, characterized by constant change and increasing complexity, optimizing workflows is paramount. Process mapping emerges as a powerful tool for achieving this goal, offering a visual representation of how tasks and activities are interconnected within an organization. By meticulously documenting and analyzing these processes, businesses gain valuable insights that facilitate improvement, streamline operations, and ultimately drive success.
The Essence of Process Mapping: A Visual Blueprint for Efficiency
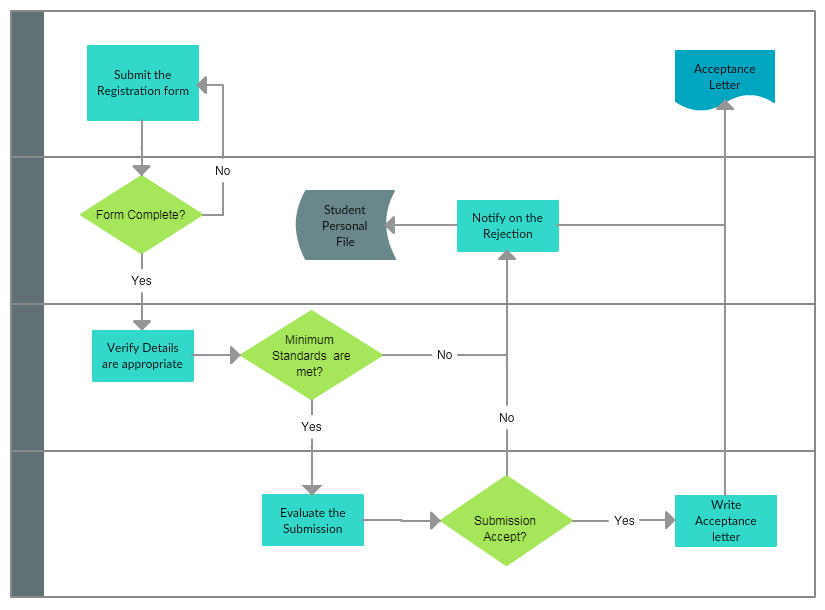
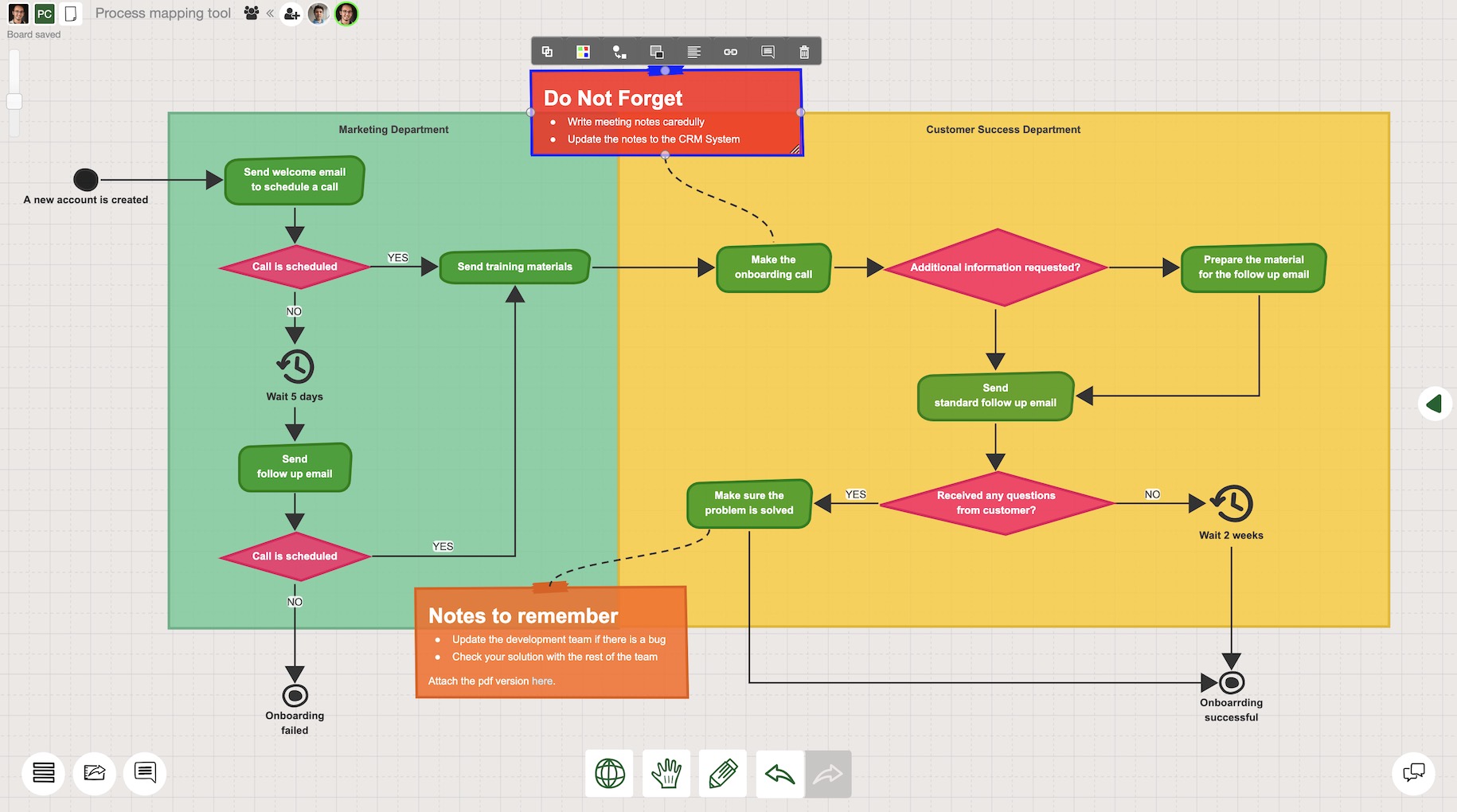
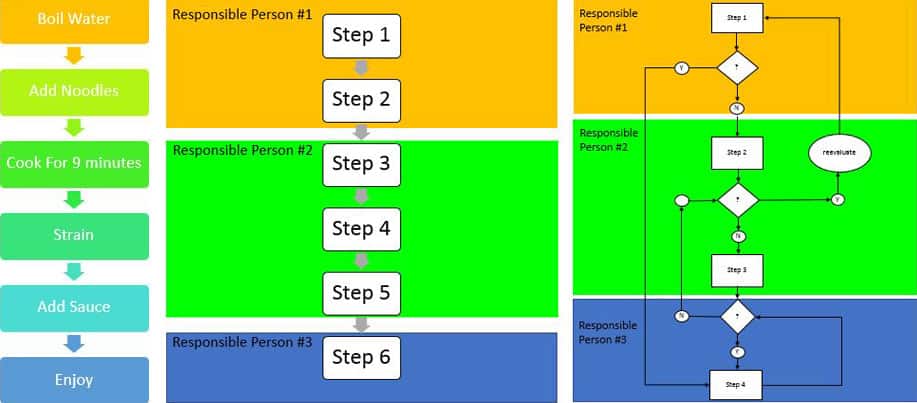
Process mapping, also known as workflow mapping, is a systematic approach to visually representing a process. It involves breaking down a complex sequence of activities into smaller, manageable steps, illustrating their logical flow and dependencies. The resulting map serves as a visual blueprint, providing a clear understanding of the process’s structure, identifying potential bottlenecks, and highlighting areas ripe for optimization.
The Benefits of Process Mapping: Unveiling Opportunities for Growth
Beyond its visual appeal, process mapping offers a multitude of benefits that translate into tangible improvements across various aspects of an organization:
- Enhanced Efficiency: By visualizing the process flow, organizations can identify redundant steps, unnecessary delays, and inefficiencies. This allows for streamlining, reducing waste, and optimizing resource allocation, ultimately leading to increased productivity and cost savings.
- Improved Communication: Process maps act as a common language, facilitating clear and concise communication among team members, stakeholders, and departments. Everyone involved gains a shared understanding of the process, fostering collaboration and minimizing misunderstandings.
- Increased Transparency: Process maps provide a transparent view of how work is performed, making it easier to track progress, identify areas of improvement, and hold individuals accountable for their roles within the process.
- Enhanced Quality Control: By documenting the process, organizations can ensure consistent adherence to established procedures, minimizing errors and enhancing the quality of output.
- Effective Training and Onboarding: Process maps serve as invaluable resources for training new employees, providing a clear and concise guide to the organization’s workflows. This facilitates faster onboarding and reduces the learning curve for new team members.
- Strategic Planning and Innovation: Process mapping provides a foundation for strategic planning, allowing organizations to identify areas for process improvement, automation, or innovation. It enables a proactive approach to optimizing workflows and adapting to changing market demands.
- Risk Mitigation: By mapping out processes, organizations can identify potential risks and develop mitigation strategies. This proactive approach minimizes disruptions, ensures business continuity, and safeguards against unforeseen challenges.
The Process of Process Mapping: A Step-by-Step Guide
Creating a process map requires a systematic approach, involving several key steps:
- Define the Scope: Clearly define the process to be mapped, specifying its starting point, end point, and any relevant boundaries.
- Gather Information: Collect data about the process, including interviews with stakeholders, documentation review, and observation of the process in action.
- Identify the Process Steps: Break down the process into individual steps, ensuring a logical flow and clear understanding of each activity.
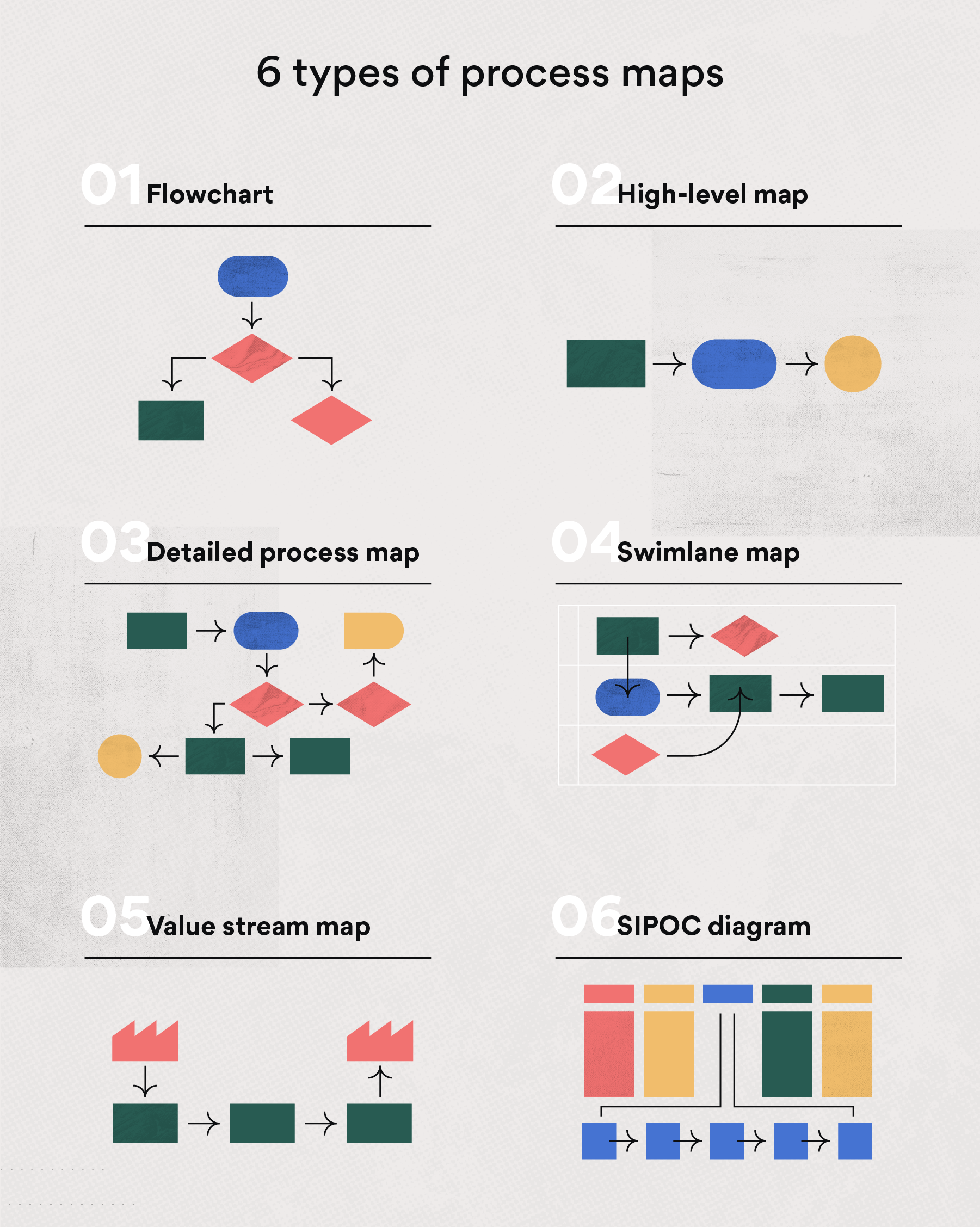
- Develop the Map: Choose a suitable mapping method, such as flowcharting, swimlane diagrams, or value stream mapping, and create a visual representation of the process.
- Validate and Review: Present the map to stakeholders for review and feedback, ensuring accuracy and clarity.
- Implement and Monitor: Implement the process map as a guide for operational workflows, and continuously monitor its effectiveness, identifying areas for further optimization.
Methods of Process Mapping: Choosing the Right Tool
The choice of mapping method depends on the complexity of the process, the desired level of detail, and the intended audience. Some common methods include:
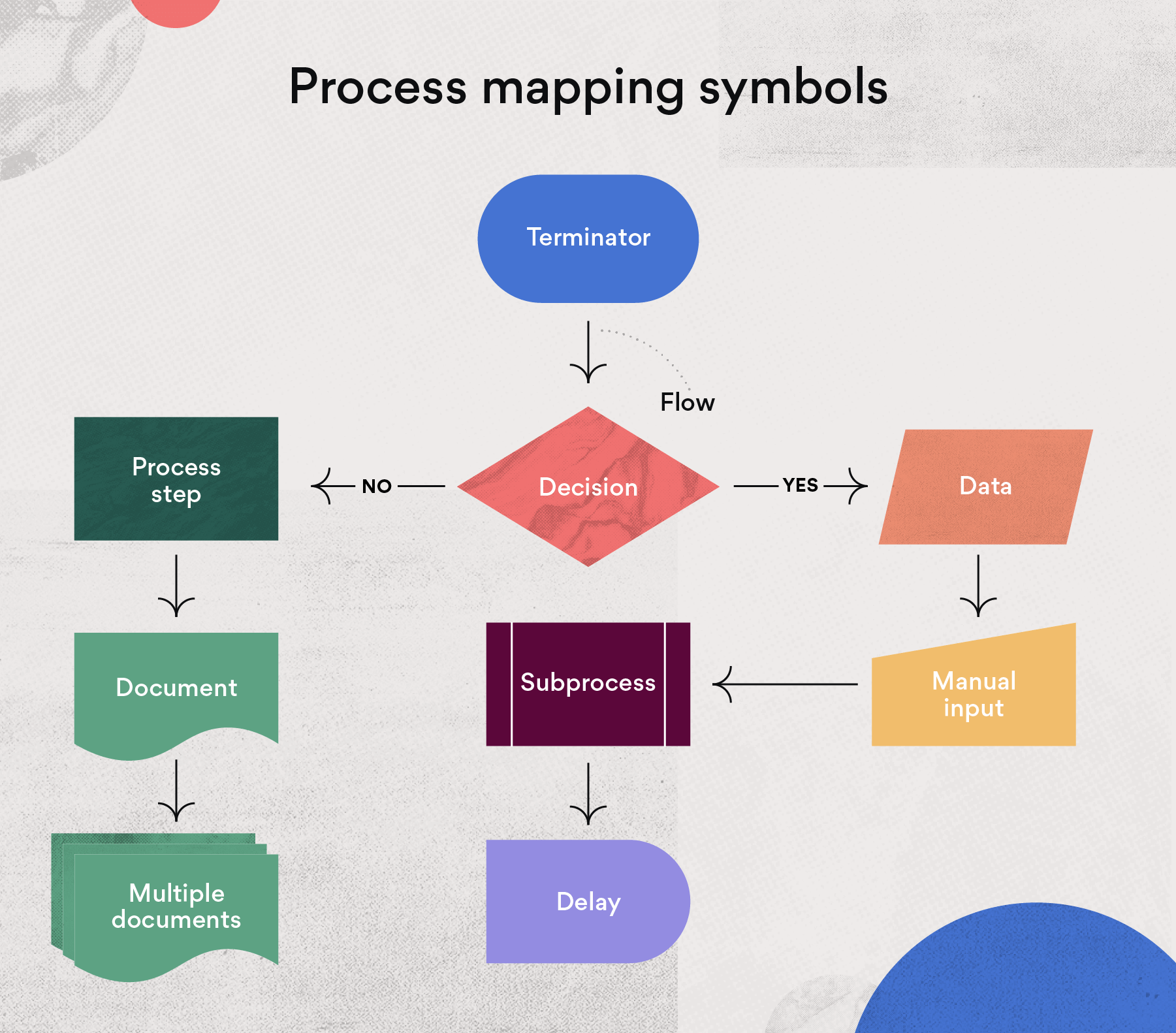
- Flowcharting: A simple and versatile method that uses symbols to represent different activities and their sequence.
- Swimlane Diagrams: Useful for visualizing processes involving multiple departments or roles, with each lane representing a specific function.
- Value Stream Mapping: A comprehensive method that maps the entire value stream, from customer request to product delivery, identifying waste and opportunities for improvement.
- Business Process Modeling Notation (BPMN): A standardized notation for modeling business processes, offering a robust and detailed approach to process mapping.
Tips for Successful Process Mapping: A Practical Guide
Creating effective process maps requires careful planning and execution. Consider these tips for maximizing the impact of your process mapping efforts:
- Start Small: Begin with mapping a simple process before tackling more complex workflows.
- Focus on Value: Prioritize mapping processes that have a significant impact on the organization’s value chain.
- Involve Stakeholders: Engage stakeholders throughout the process, ensuring their input and buy-in.
- Use Clear and Concise Language: Employ simple, understandable language to make the map accessible to everyone.
- Maintain Regular Updates: Regularly review and update the map to reflect changes in the process or organization.
- Utilize Software Tools: Leverage process mapping software to streamline the creation, collaboration, and maintenance of maps.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions about Process Mapping
1. What are some common process mapping errors to avoid?
- Over-complication: Avoid including unnecessary details or using overly complex notation.
- Lack of Clarity: Ensure the map is clear and easy to understand, avoiding ambiguity or jargon.
- Ignoring Feedback: Neglecting to solicit and incorporate stakeholder feedback can lead to inaccuracies and inefficiencies.
- Lack of Regular Updates: Failing to update the map to reflect changes in the process can render it outdated and irrelevant.
2. How can I measure the effectiveness of my process maps?
- Track Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Monitor metrics such as cycle time, cost per unit, and error rates to assess the impact of process improvements.
- Conduct User Surveys: Gather feedback from stakeholders on the usability and effectiveness of the process.
- Compare Before and After Data: Analyze data from before and after the process mapping implementation to identify improvements.
3. What are some examples of processes that can be mapped?
- Sales and Marketing: Lead generation, customer acquisition, product launch, marketing campaigns.
- Operations: Production, inventory management, order fulfillment, customer service.
- Finance: Budgeting, forecasting, expense management, accounts payable/receivable.
- Human Resources: Recruitment, onboarding, training, performance management.
- Information Technology: Software development, system maintenance, network security.
4. What are the limitations of process mapping?
- Static Representation: Process maps represent a snapshot of the process at a specific point in time, and may not capture dynamic changes.
- Oversimplification: Mapping complex processes can lead to oversimplification, omitting crucial details or nuances.
- Limited Scope: Process mapping may not address all aspects of a process, such as cultural factors or employee motivation.
5. How can I make process mapping a continuous improvement initiative?
- Regular Reviews: Schedule periodic reviews of process maps to identify areas for improvement.
- Employee Feedback: Encourage employees to provide feedback on the process and suggest improvements.
- Continuous Improvement Culture: Foster a culture of continuous improvement, where process optimization is an ongoing endeavor.
Conclusion: Empowering Organizations for Growth and Success
Process mapping is not merely a documentation exercise; it is a powerful tool for unlocking efficiency, driving innovation, and achieving organizational goals. By providing a visual blueprint for understanding, analyzing, and improving workflows, process mapping empowers organizations to streamline operations, enhance communication, and foster a culture of continuous improvement. As businesses navigate the complexities of the modern world, embracing process mapping becomes essential for achieving sustainable growth and success.
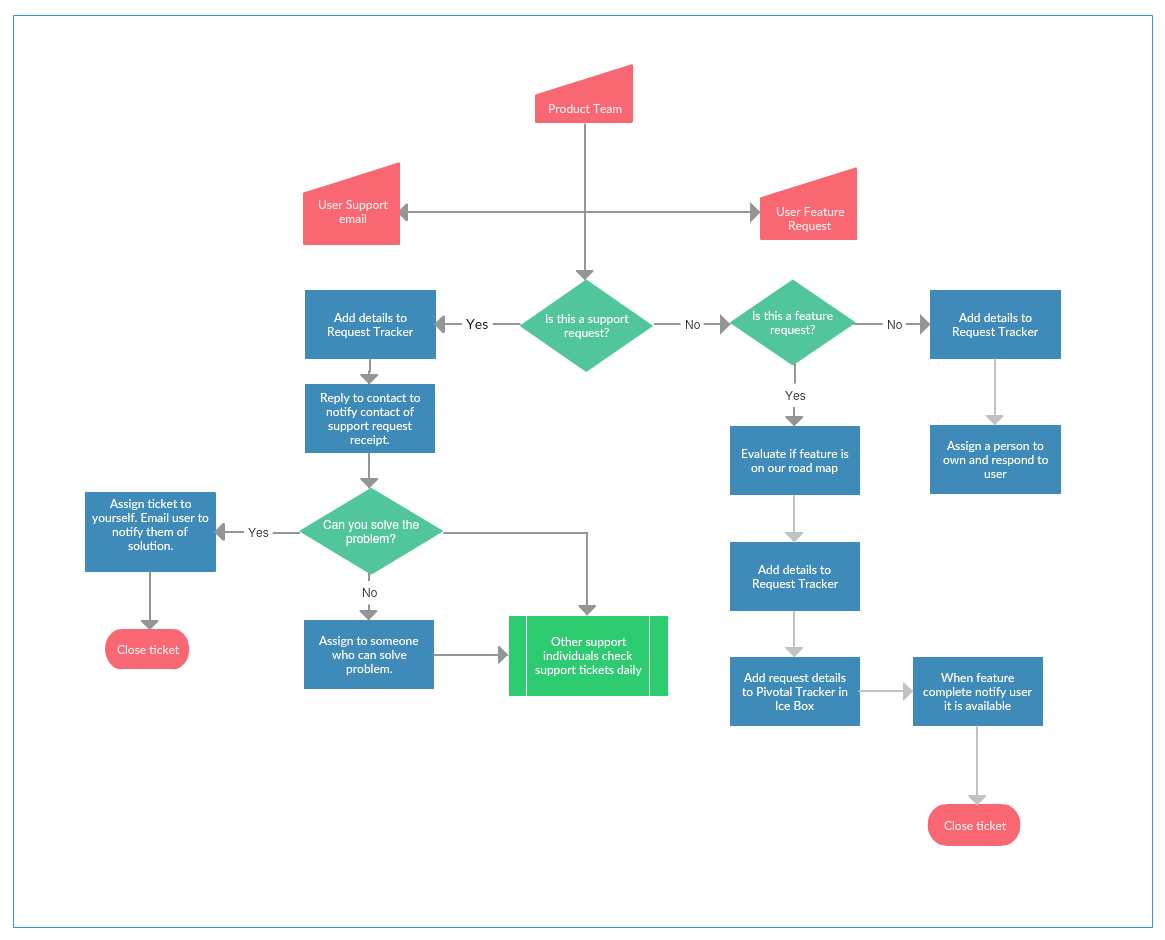


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unlocking Efficiency: A Comprehensive Guide to Process Map Creation. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!