Understanding Virginia’s House Districts: A Guide to Representation and Redistricting
Related Articles: Understanding Virginia’s House Districts: A Guide to Representation and Redistricting
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Understanding Virginia’s House Districts: A Guide to Representation and Redistricting. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Understanding Virginia’s House Districts: A Guide to Representation and Redistricting
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Understanding Virginia’s House Districts: A Guide to Representation and Redistricting
- 3.1 The Importance of District Maps
- 3.2 Redistricting: The Process of Drawing New Districts
- 3.3 Understanding the Dynamics of Virginia’s House Districts
- 3.4 The Impact of Gerrymandering
- 3.5 Challenges and Solutions for Fair Redistricting
- 3.6 FAQs about Virginia’s House Districts
- 3.7 Tips for Engaging with Virginia’s House Districts
- 3.8 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Understanding Virginia’s House Districts: A Guide to Representation and Redistricting

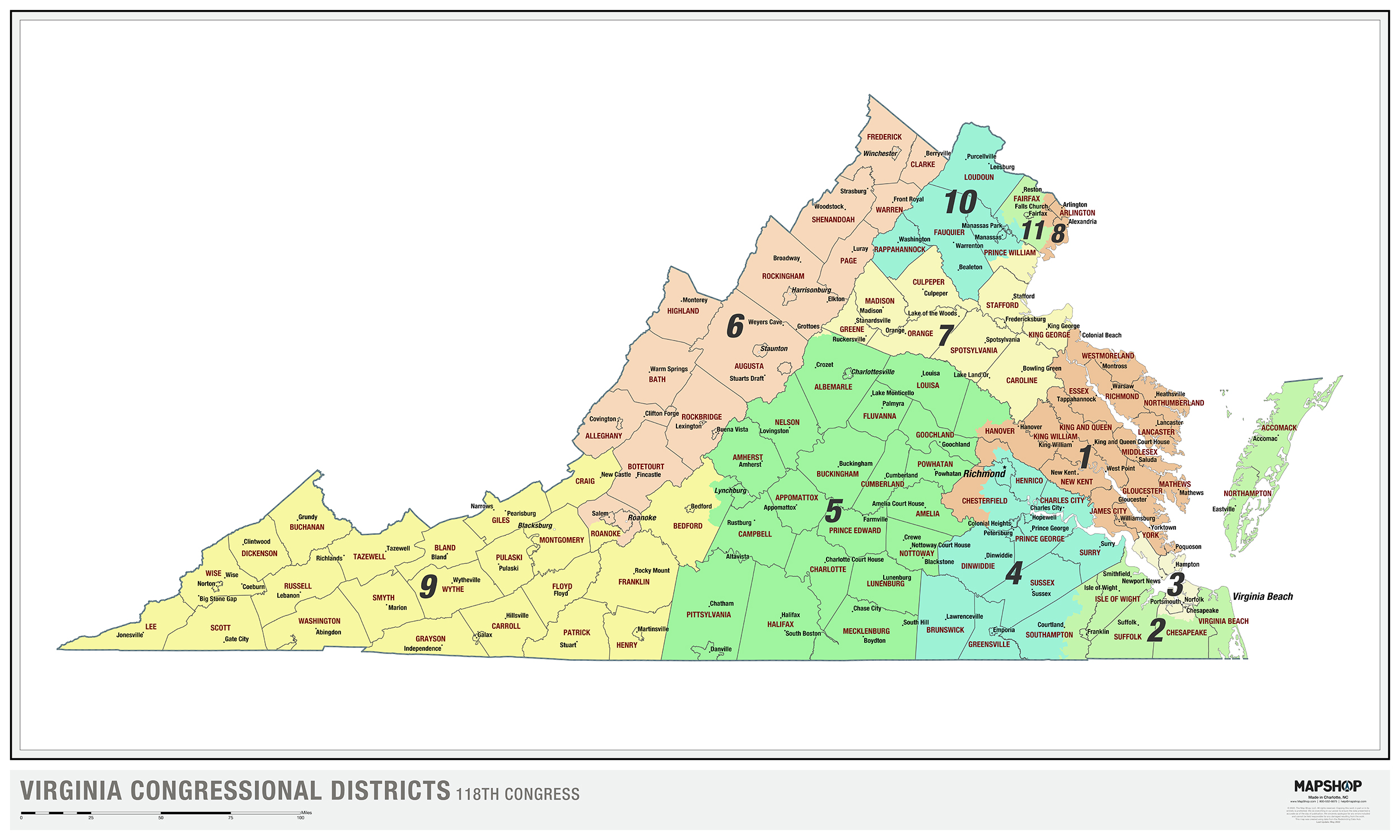
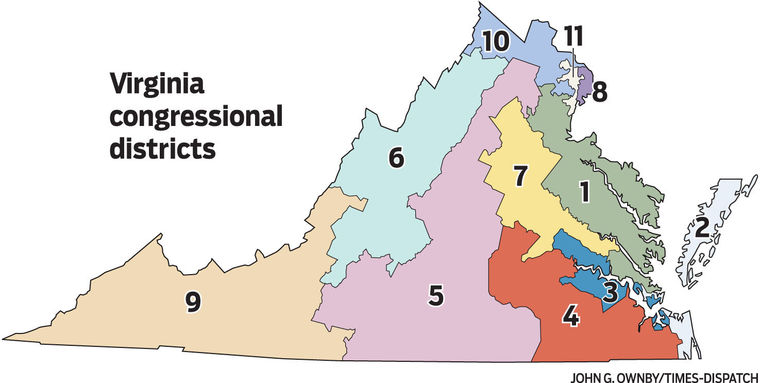
Virginia’s House of Delegates, the lower chamber of the state legislature, is comprised of 100 members, each representing a specific geographic area known as a district. These districts are crucial for ensuring fair and equitable representation of the state’s diverse population. Understanding the boundaries and dynamics of these districts is essential for comprehending the political landscape of Virginia.
The Importance of District Maps
The map of Virginia’s House districts is not merely a visual representation of geographic boundaries. It is a fundamental tool for defining the political landscape of the state. The way districts are drawn can significantly impact the outcome of elections, influencing the political balance of power within the House of Delegates.
Here are some key reasons why understanding Virginia’s House district map is crucial:
- Representation: Districts serve as the building blocks of representative democracy. They ensure that each citizen’s voice is heard and that their interests are represented in the legislative process.
- Fairness: Ideally, districts should be drawn in a way that ensures equal representation for all citizens, regardless of their location or demographic characteristics.
- Accountability: By knowing the boundaries of their district, voters can hold their elected representatives accountable for their actions and decisions.
- Political Power: The way districts are drawn can significantly impact the political balance of power within the House of Delegates, potentially giving one party an advantage over another.
Redistricting: The Process of Drawing New Districts
The process of redrawing district boundaries is known as redistricting. This occurs every ten years following the decennial census, which provides updated population data for the state. Redistricting aims to ensure that each district has roughly the same population, maintaining equal representation.
The redistricting process in Virginia involves the following key steps:
- Census Data: The U.S. Census Bureau conducts a nationwide census every ten years, providing population data for each state and its subdivisions.
- Data Analysis: The data is analyzed by state officials to determine population shifts and growth patterns within Virginia.
- Districting Plan: Based on the data analysis, a proposed plan for new district boundaries is developed.
- Public Input: The proposed plan is made public, allowing citizens to provide feedback and raise concerns.
- Legislative Approval: The proposed plan is reviewed and approved by the state legislature.
- Implementation: Once approved, the new district boundaries are implemented, impacting the upcoming elections.
Understanding the Dynamics of Virginia’s House Districts
Virginia’s House districts exhibit a diverse range of characteristics, reflecting the state’s diverse geography and demographics. Understanding these dynamics is essential for comprehending the political landscape and the challenges of redistricting.
Here are some key factors that influence the dynamics of Virginia’s House districts:
- Population Density: Districts in urban areas tend to have higher population densities compared to rural districts. This can impact the representation of different groups and the relative influence of different regions within the legislature.
- Demographic Makeup: The racial, ethnic, and socioeconomic makeup of districts can influence the priorities and perspectives of elected representatives.
- Political Leanings: Districts can be classified based on their historical voting patterns and the dominant political ideology of their residents.
- Economic Factors: The economic conditions and industries within a district can impact the legislative priorities of elected representatives.
The Impact of Gerrymandering
Gerrymandering, the practice of manipulating district boundaries for partisan advantage, is a significant challenge in Virginia and across the country. It can lead to unfair elections, where one party has an undue advantage, and can undermine the principle of equal representation.
The following are some of the common techniques used in gerrymandering:
- Packing: Concentrating voters of a specific party into a few districts to minimize their impact in other districts.
- Cracking: Spreading voters of a specific party across multiple districts to dilute their voting power.
- Stacking: Combining politically diverse areas into a single district to create a less competitive race.
Challenges and Solutions for Fair Redistricting
Ensuring fair and equitable representation through redistricting is a complex process with ongoing challenges.
Here are some of the key challenges and potential solutions:
- Partisan Influence: The redistricting process is often influenced by partisan interests, leading to gerrymandering and unfair elections. To address this, there have been calls for independent commissions or non-partisan processes for drawing district boundaries.
- Data Transparency: Access to accurate and comprehensive data is crucial for fair redistricting. Ensuring transparency in data collection and analysis can help prevent manipulation and ensure accountability.
- Public Engagement: Public input and participation are essential for ensuring that redistricting plans reflect the diverse needs and concerns of the community.
FAQs about Virginia’s House Districts
1. How are Virginia’s House districts determined?
Virginia’s House districts are determined through a process called redistricting, which occurs every ten years following the decennial census. The process involves analyzing population data, drawing new district boundaries, and obtaining legislative approval.
2. What is the purpose of redistricting?
Redistricting aims to ensure that each district has roughly the same population, maintaining equal representation and ensuring that all citizens have an equal voice in the legislative process.
3. How can I find my Virginia House district?
You can find your Virginia House district by entering your address on the Virginia Department of Elections website or using online mapping tools provided by various organizations.
4. What are the challenges associated with redistricting?
Redistricting is a complex process that is often influenced by partisan interests, leading to gerrymandering and unfair elections. Other challenges include ensuring data transparency, public engagement, and addressing the needs of diverse communities.
5. How can I get involved in the redistricting process?
You can get involved in the redistricting process by attending public hearings, submitting written testimony, contacting your elected representatives, and supporting organizations advocating for fair redistricting.
Tips for Engaging with Virginia’s House Districts
- Stay Informed: Keep up-to-date on redistricting developments, understand the proposed plans, and follow the legislative process.
- Participate in Public Hearings: Attend public hearings and provide feedback on proposed district boundaries.
- Contact Your Representatives: Reach out to your elected representatives to voice your concerns and advocate for fair redistricting.
- Support Advocacy Organizations: Support organizations that are working to ensure fair and equitable representation through redistricting.
Conclusion
The map of Virginia’s House districts plays a vital role in shaping the state’s political landscape. Understanding its significance, the dynamics of district boundaries, and the challenges of redistricting is essential for ensuring fair and equitable representation. By engaging with the process, advocating for transparency and accountability, and supporting organizations working for fair redistricting, citizens can contribute to a more representative and democratic Virginia.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding Virginia’s House Districts: A Guide to Representation and Redistricting. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!