Understanding the Grid: Delving into the Map of Gulf of Mexico Blocks
Related Articles: Understanding the Grid: Delving into the Map of Gulf of Mexico Blocks
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Grid: Delving into the Map of Gulf of Mexico Blocks. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding the Grid: Delving into the Map of Gulf of Mexico Blocks
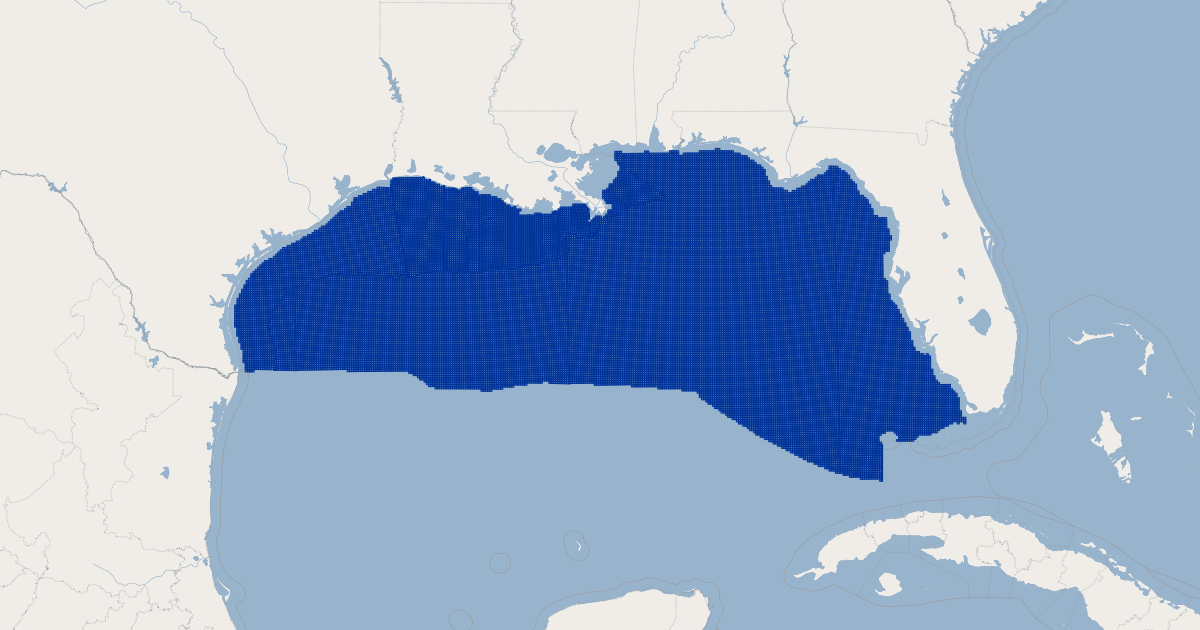
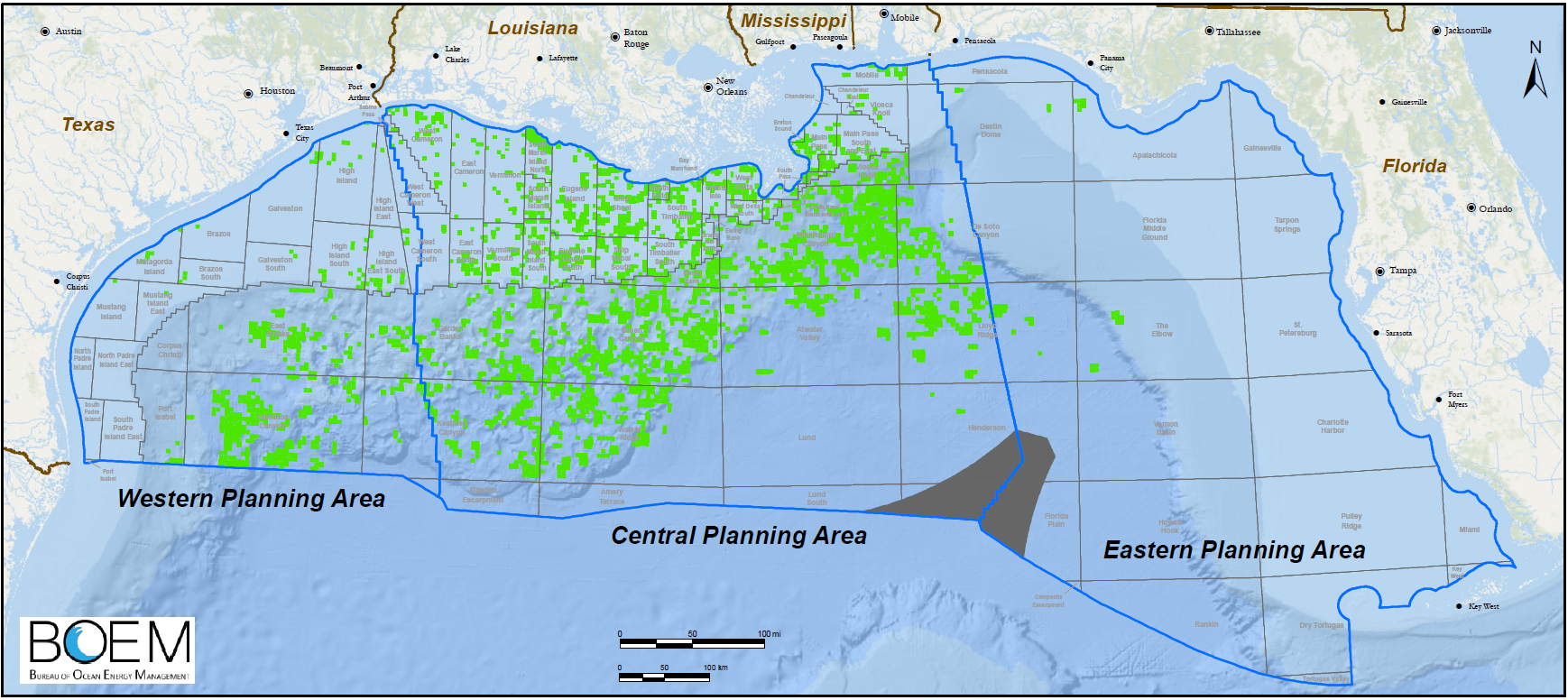
The Gulf of Mexico, a vast expanse of water teeming with natural resources, is meticulously divided into a grid system known as "blocks." This system, a crucial tool for managing offshore oil and gas exploration and production, provides a framework for understanding the distribution of these resources and facilitating their responsible extraction.
The Grid System: A Foundation for Offshore Exploration
The Gulf of Mexico block map, a visual representation of this grid system, serves as a fundamental tool for navigating the complexities of offshore oil and gas activities. Each block, typically square in shape, represents a specific geographic area within the Gulf. These blocks are identified by a combination of letters and numbers, forming a unique identifier for each location.
The map’s grid structure facilitates several key functions:
- Lease Allocation: Blocks serve as units for leasing rights to explore and extract oil and gas resources. The Bureau of Ocean Energy Management (BOEM), a federal agency, oversees the leasing process, awarding rights to companies through competitive bids.
- Exploration and Production Planning: The block system provides a clear framework for planning exploration and production activities. Companies can precisely define their exploration targets within specific blocks, allowing for efficient resource management and environmental impact assessment.
- Data Management: The grid system simplifies data collection and analysis related to offshore activities. Geological, geophysical, and environmental data are organized based on block boundaries, enabling easier access and interpretation.
- Environmental Monitoring: The block system plays a crucial role in environmental monitoring and protection. By defining specific areas, it facilitates the assessment of potential impacts from oil and gas activities and the implementation of appropriate mitigation measures.
Beyond the Grid: Understanding the Importance of Block Maps
The Gulf of Mexico block map transcends its role as a simple grid system. It represents a complex interplay of economic, environmental, and political factors that influence the future of offshore energy development.
- Economic Development: The map highlights the vast potential of the Gulf of Mexico for oil and gas production, contributing significantly to the US economy. Revenue generated from lease sales and production royalties fuels economic growth and supports job creation in coastal communities.
- Energy Security: The Gulf of Mexico is a crucial source of domestic energy, providing a significant portion of the nation’s oil and gas supply. The block map facilitates the development of these resources, bolstering energy security and reducing reliance on foreign imports.
- Environmental Stewardship: The map’s framework enables responsible resource management and environmental protection. The BOEM employs strict regulations and oversight to minimize the environmental impact of oil and gas activities, ensuring the long-term sustainability of the Gulf ecosystem.
- International Collaboration: The block map also plays a role in fostering international collaboration. The Gulf of Mexico is shared by the United States, Mexico, and Cuba, requiring coordinated efforts to manage resources and ensure environmental integrity.
Navigating the Complexities: FAQs on the Gulf of Mexico Block Map
1. What is the size of a typical Gulf of Mexico block?
The size of a block varies depending on its location, but typically ranges from 5,760 to 6,400 acres.
2. How are blocks assigned for oil and gas exploration?
The BOEM conducts lease sales, offering blocks to companies through competitive bidding. The highest bidder receives the lease rights for a specific block.
3. What are the environmental considerations associated with oil and gas exploration in the Gulf of Mexico?
Environmental considerations include potential impacts on marine life, habitat destruction, oil spills, and greenhouse gas emissions. The BOEM implements stringent environmental regulations and monitoring programs to mitigate these risks.
4. How does the block system contribute to energy security?
The block map facilitates the development of domestic oil and gas resources, reducing reliance on foreign imports and strengthening energy independence.
5. Are there any plans to expand the Gulf of Mexico block system?
The BOEM regularly reviews and updates the block system based on resource potential, environmental considerations, and technological advancements.
6. What are the challenges associated with oil and gas exploration in the Gulf of Mexico?
Challenges include deepwater drilling risks, hurricanes, environmental concerns, and fluctuating oil and gas prices.
7. How does the block system promote economic development?
The block system drives investment in offshore energy infrastructure, creating jobs, boosting local economies, and generating tax revenue.
8. What are the potential benefits of renewable energy development in the Gulf of Mexico?
Renewable energy sources like wind and solar power offer a cleaner alternative to fossil fuels, reducing greenhouse gas emissions and promoting sustainable development.
9. How does the block system impact coastal communities?
The block system can both benefit and impact coastal communities. It creates jobs and economic opportunities but also raises concerns about environmental risks and potential disruptions to marine ecosystems.
10. What are the future prospects for oil and gas exploration in the Gulf of Mexico?
The future of oil and gas exploration in the Gulf of Mexico is uncertain, influenced by factors like global energy demand, environmental regulations, and the transition to renewable energy sources.
Tips for Understanding the Gulf of Mexico Block Map
- Utilize online resources: Numerous websites, including those of the BOEM and the US Geological Survey, provide detailed information on the Gulf of Mexico block system, including maps, data, and reports.
- Consult with experts: Experts in offshore energy, geology, and environmental science can provide valuable insights and guidance on the complexities of the block map.
- Stay informed about industry trends: Keep abreast of developments in the oil and gas industry, including technological advancements, environmental regulations, and market dynamics.
- Engage in public dialogue: Participate in discussions and forums related to offshore energy development, promoting informed decision-making and responsible resource management.
Conclusion: A Framework for Responsible Resource Management
The Gulf of Mexico block map serves as a crucial tool for navigating the complexities of offshore oil and gas exploration and production. It provides a framework for responsible resource management, balancing economic development with environmental stewardship. Understanding the intricacies of this grid system is essential for informed decision-making, fostering sustainable energy development, and ensuring the long-term health of the Gulf of Mexico ecosystem.
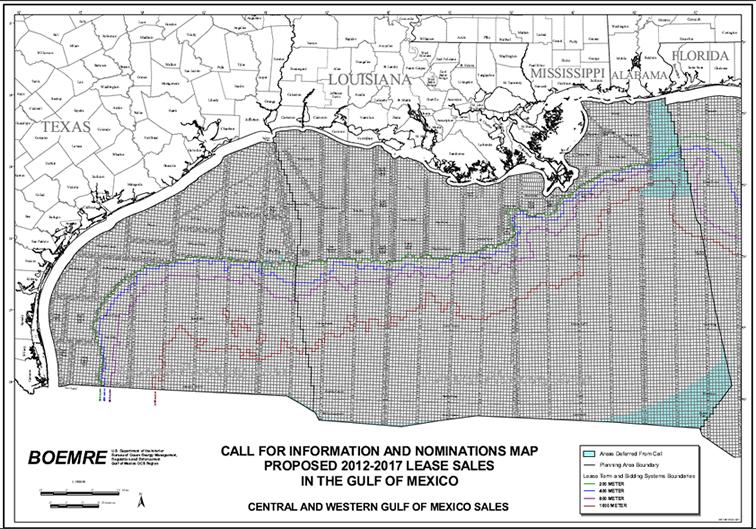
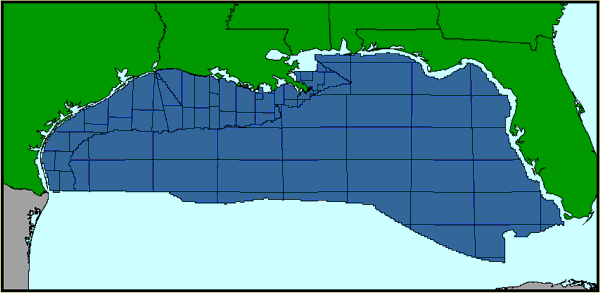




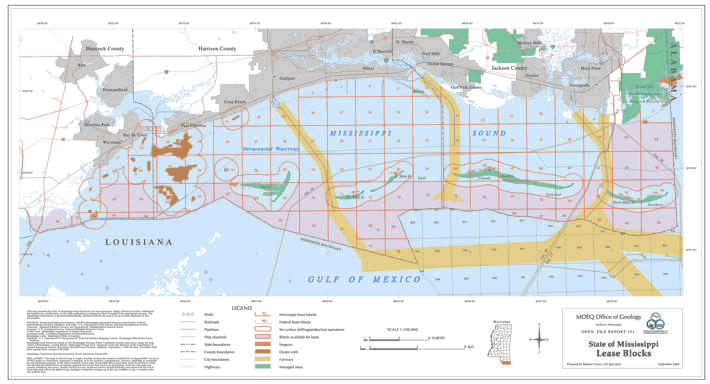
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Grid: Delving into the Map of Gulf of Mexico Blocks. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!