Understanding the Geographic Distribution of the Water Moccasin: A Guide to the Species’ Range
Related Articles: Understanding the Geographic Distribution of the Water Moccasin: A Guide to the Species’ Range
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Geographic Distribution of the Water Moccasin: A Guide to the Species’ Range. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Understanding the Geographic Distribution of the Water Moccasin: A Guide to the Species’ Range
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Understanding the Geographic Distribution of the Water Moccasin: A Guide to the Species’ Range
- 3.1 The Water Moccasin’s Range: A Detailed Look
- 3.2 Factors Influencing the Water Moccasin’s Range
- 3.3 Understanding the Range Map: A Visual Representation
- 3.4 Importance of Range Map Accuracy: A Focus on Conservation
- 3.5 FAQs Regarding the Water Moccasin’s Range
- 3.6 Tips for Avoiding Encounters with Water Moccasins
- 3.7 Conclusion: The Importance of Understanding the Water Moccasin’s Range
- 4 Closure
Understanding the Geographic Distribution of the Water Moccasin: A Guide to the Species’ Range
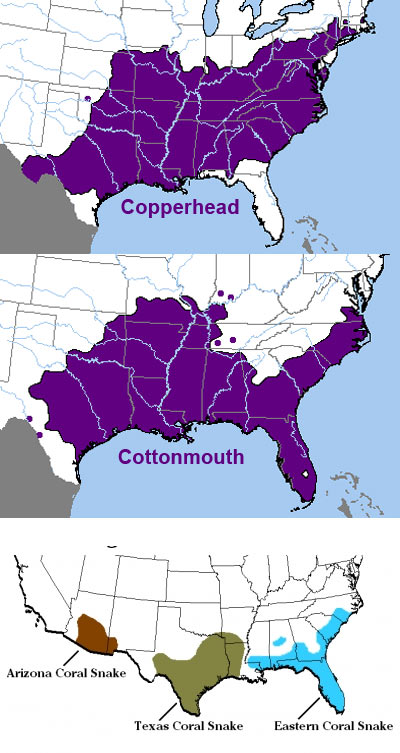
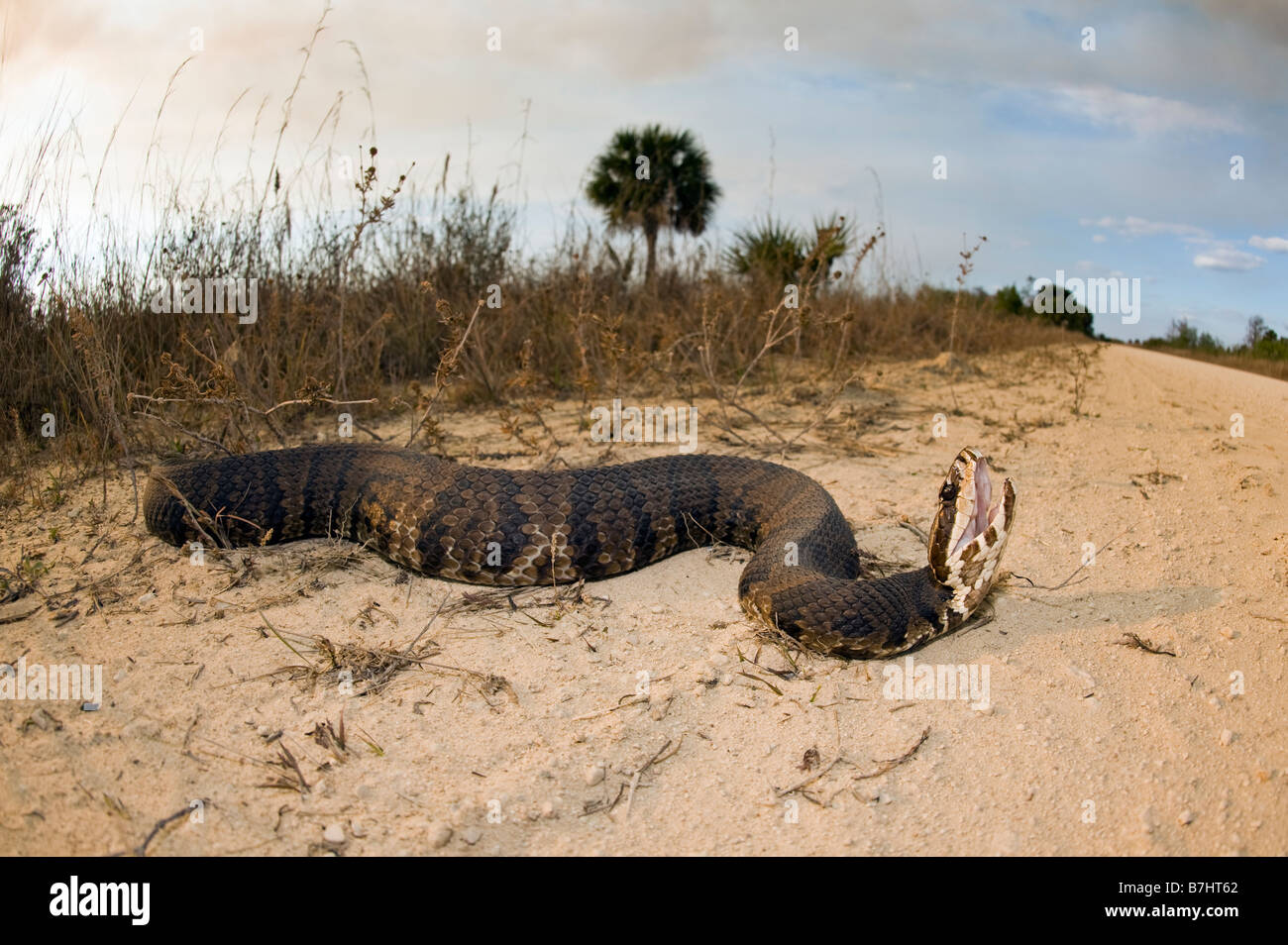
The water moccasin, also known as the cottonmouth, is a venomous snake native to the southeastern United States. Its distinctive appearance and potentially dangerous venom make it a subject of both fascination and fear. Understanding the geographic distribution of this species, often visualized through a range map, is crucial for several reasons, including:
- Public Safety: Knowledge of the water moccasin’s range allows individuals to be more aware of potential encounters, especially in areas where the snake is prevalent. This awareness can lead to proactive measures like avoiding known habitats and taking precautions when engaging in outdoor activities.
- Conservation Efforts: Mapping the species’ range provides valuable data for conservationists working to protect the water moccasin and its habitat. Understanding population distribution helps identify areas where conservation efforts are most needed and allows for the monitoring of population trends.
- Scientific Research: The range map serves as a foundation for scientific research on the water moccasin, including studies on its ecology, behavior, and evolution. It provides insights into factors influencing the species’ distribution and helps researchers understand the potential impact of environmental changes on the snake’s population.
The Water Moccasin’s Range: A Detailed Look
The water moccasin’s range encompasses a significant portion of the southeastern United States, extending from southern Virginia and North Carolina down to Florida and west to eastern Texas. This extensive range can be broadly divided into four distinct areas:
- Coastal Plain: This region, characterized by low-lying areas and abundant waterways, is the primary habitat for the water moccasin. It includes the coastal areas of Virginia, North Carolina, South Carolina, Georgia, Florida, Alabama, Mississippi, Louisiana, and Texas.
- Piedmont: While less common than in the Coastal Plain, water moccasins are found in the Piedmont region, which encompasses the foothills of the Appalachian Mountains. This region includes portions of Virginia, North Carolina, South Carolina, Georgia, and Alabama.
- Appalachian Mountains: The water moccasin’s presence in the Appalachian Mountains is limited, with only scattered populations found in isolated areas with suitable habitat. These populations are typically found along streams and rivers within the mountains.
- Mississippi River Valley: The Mississippi River Valley, with its extensive network of waterways, provides a suitable habitat for water moccasins. The species is found along the river and its tributaries, extending north into Illinois and Missouri.
Factors Influencing the Water Moccasin’s Range
Several factors play a crucial role in determining the geographic distribution of the water moccasin. These factors include:
- Climate: Water moccasins thrive in warm, humid climates with ample water sources. Their range coincides with the southeastern United States, known for its subtropical and temperate climate.
- Habitat: The presence of suitable habitat is essential for the water moccasin’s survival. They prefer areas with slow-moving water, such as swamps, marshes, lakes, and rivers. They also require access to vegetation for shelter and basking sites.
- Prey Availability: Water moccasins are opportunistic predators, feeding primarily on fish, frogs, and other small animals. The availability of these prey species influences their distribution.
- Competition: Competition with other snake species, such as the copperhead and the eastern cottonmouth, can also influence the water moccasin’s range.
- Human Impact: Human activities, such as habitat destruction and fragmentation, can negatively impact the water moccasin’s range.
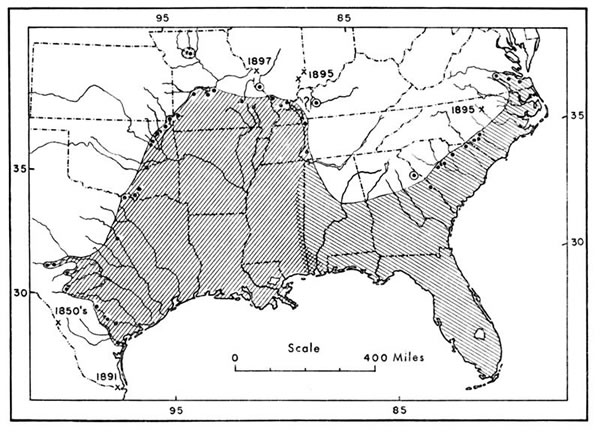
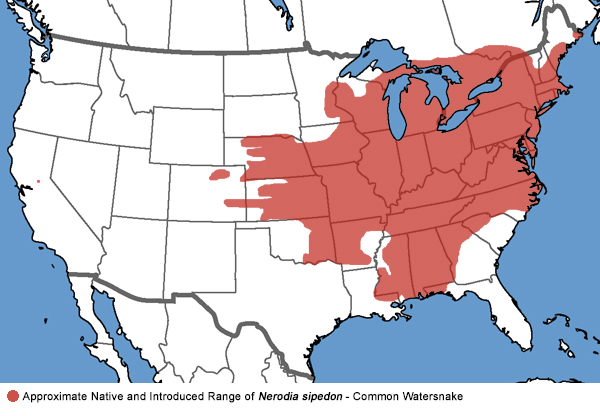
Understanding the Range Map: A Visual Representation
The water moccasin’s range map is a powerful tool for visualizing the species’ geographic distribution. It typically depicts the areas where the species is known to occur, often using colors or patterns to differentiate between different levels of abundance or presence.
The map can provide valuable information, such as:
- Geographic Boundaries: The map clearly defines the boundaries of the species’ range, indicating the areas where water moccasins are commonly found and those where they are absent.
- Population Density: The map can show areas with higher or lower densities of water moccasins, reflecting factors like habitat availability and prey abundance.
- Habitat Preferences: The map can highlight the specific habitats favored by the species, such as wetlands, rivers, and forests.
- Geographic Variations: The map can reveal differences in the species’ range across different regions, highlighting potential adaptations to local environmental conditions.
Importance of Range Map Accuracy: A Focus on Conservation
Maintaining accurate and up-to-date range maps is crucial for effective conservation efforts. Accurate information allows conservationists to:
- Prioritize Conservation Areas: By identifying areas with high water moccasin populations, conservationists can focus resources on protecting those critical habitats.
- Monitor Population Trends: Tracking changes in the species’ range over time can provide insights into population trends and identify potential threats.
- Develop Effective Management Strategies: Understanding the factors influencing the water moccasin’s range allows conservationists to develop effective management strategies, such as habitat restoration and mitigation of human impacts.
FAQs Regarding the Water Moccasin’s Range
Q: Are water moccasins found in all states bordering the Gulf of Mexico?
A: While water moccasins are found in several states bordering the Gulf of Mexico, they are not present in all of them. Their range extends to Texas, Louisiana, Mississippi, Alabama, and Florida, but not to the northernmost Gulf states like Texas, Louisiana, and Mississippi.
Q: Is the water moccasin’s range expanding or shrinking?
A: The water moccasin’s range is generally considered stable, but there are localized areas where populations may be expanding or shrinking due to factors such as habitat loss, climate change, and human activities.
Q: Do water moccasins prefer freshwater or saltwater?
A: Water moccasins are primarily freshwater snakes and are not found in saltwater environments. They are adapted to living in slow-moving freshwater bodies like swamps, marshes, and rivers.
Q: What are the most common threats to the water moccasin’s range?
A: The most common threats to the water moccasin’s range include habitat loss due to urbanization and agriculture, pollution of waterways, and climate change.
Q: Are water moccasins protected by law?
A: The water moccasin is not currently listed as a federally endangered or threatened species, but it is protected in some states under local laws.
Tips for Avoiding Encounters with Water Moccasins
- Be Aware of Their Habitat: Recognize areas known to be inhabited by water moccasins, such as swamps, marshes, and rivers.
- Wear Appropriate Footwear: When hiking or walking in areas with potential water moccasin habitat, wear closed-toe shoes or boots to protect your feet.
- Avoid Disturbance: Do not disturb vegetation or rocks near water bodies, as this could disturb a water moccasin.
- Stay on Marked Trails: When hiking, stay on marked trails to avoid venturing into areas where water moccasins may be present.
- Be Cautious During Dusk and Dawn: Water moccasins are more active during dusk and dawn, so exercise extra caution during these times.
- Keep a Safe Distance: If you encounter a water moccasin, observe it from a safe distance and do not attempt to approach or handle it.
Conclusion: The Importance of Understanding the Water Moccasin’s Range
The water moccasin’s range map is a valuable tool for understanding the geographic distribution of this venomous snake. It provides crucial information for public safety, conservation efforts, and scientific research. By recognizing the factors influencing the species’ range and understanding the importance of accurate mapping, individuals can contribute to the protection and conservation of this fascinating creature.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Geographic Distribution of the Water Moccasin: A Guide to the Species’ Range. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!