The Ural Mountains: A Geographic Spine Dividing Europe and Asia
Related Articles: The Ural Mountains: A Geographic Spine Dividing Europe and Asia
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Ural Mountains: A Geographic Spine Dividing Europe and Asia. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: The Ural Mountains: A Geographic Spine Dividing Europe and Asia
- 2 Introduction
- 3 The Ural Mountains: A Geographic Spine Dividing Europe and Asia
- 3.1 Understanding the Ural Mountains on a Map
- 3.2 Beyond the Mountains: Exploring the Significance of the Ural Range
- 3.3 Exploring the Ural Mountains: A Journey Through Time and Landscape
- 3.4 FAQs About the Ural Mountains
- 3.5 Tips for Exploring the Ural Mountains
- 3.6 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
The Ural Mountains: A Geographic Spine Dividing Europe and Asia
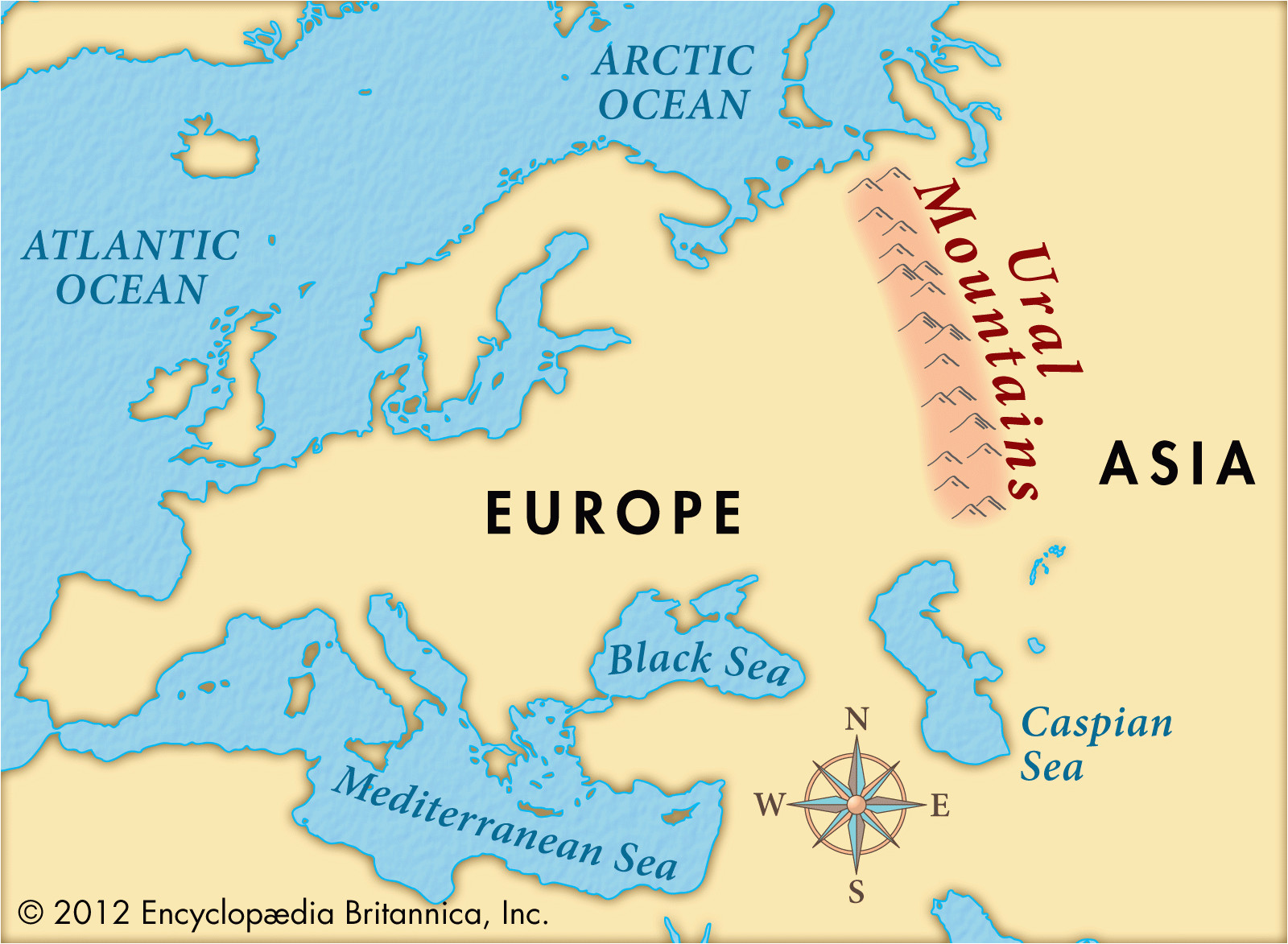
The Ural Mountains, a majestic chain of peaks stretching over 2,500 kilometers, stand as a formidable natural boundary between Europe and Asia. This ancient mountain range, formed over 250 million years ago, plays a crucial role in shaping the geography, climate, and history of the Eurasian continent.
Understanding the Ural Mountains on a Map
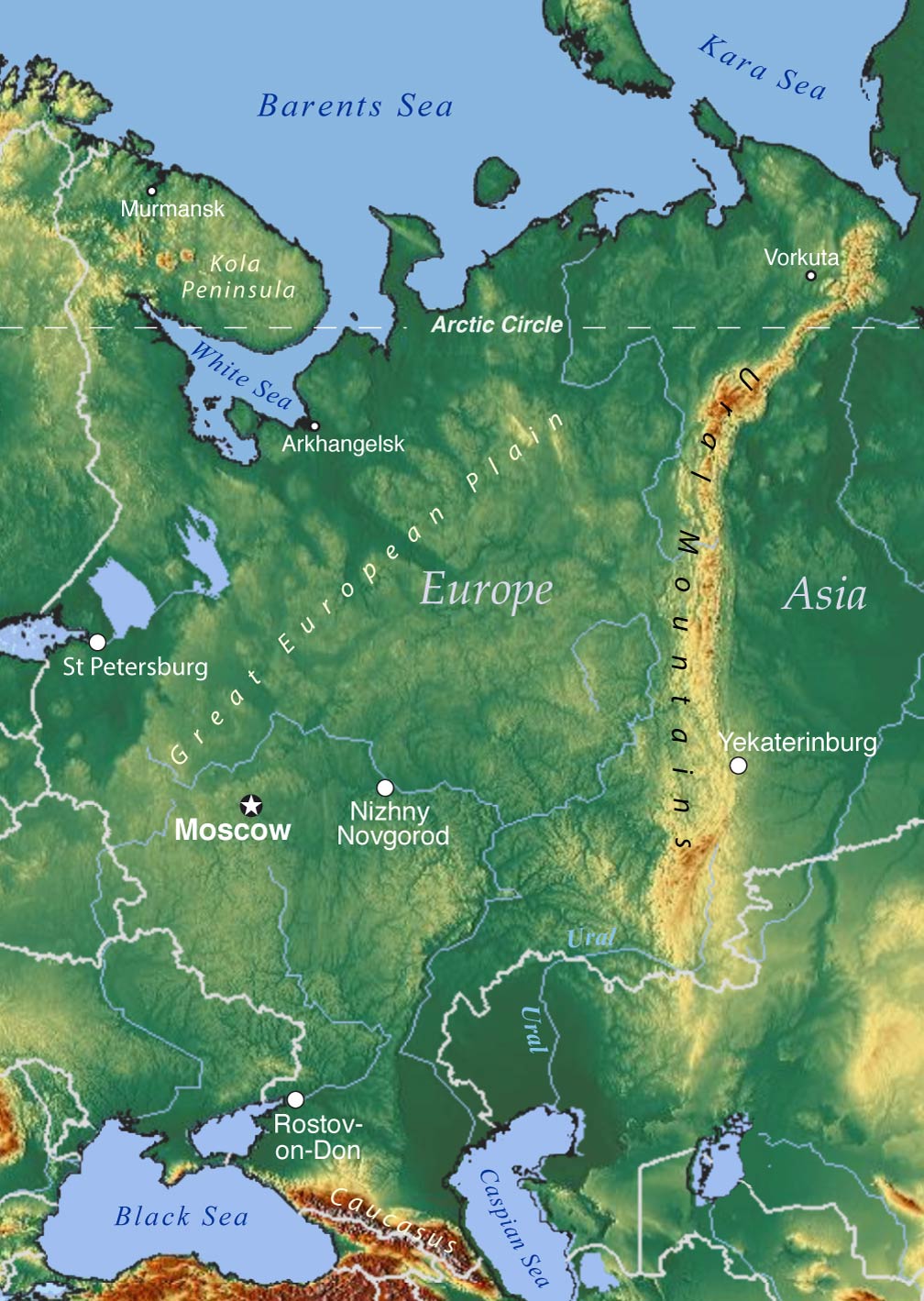
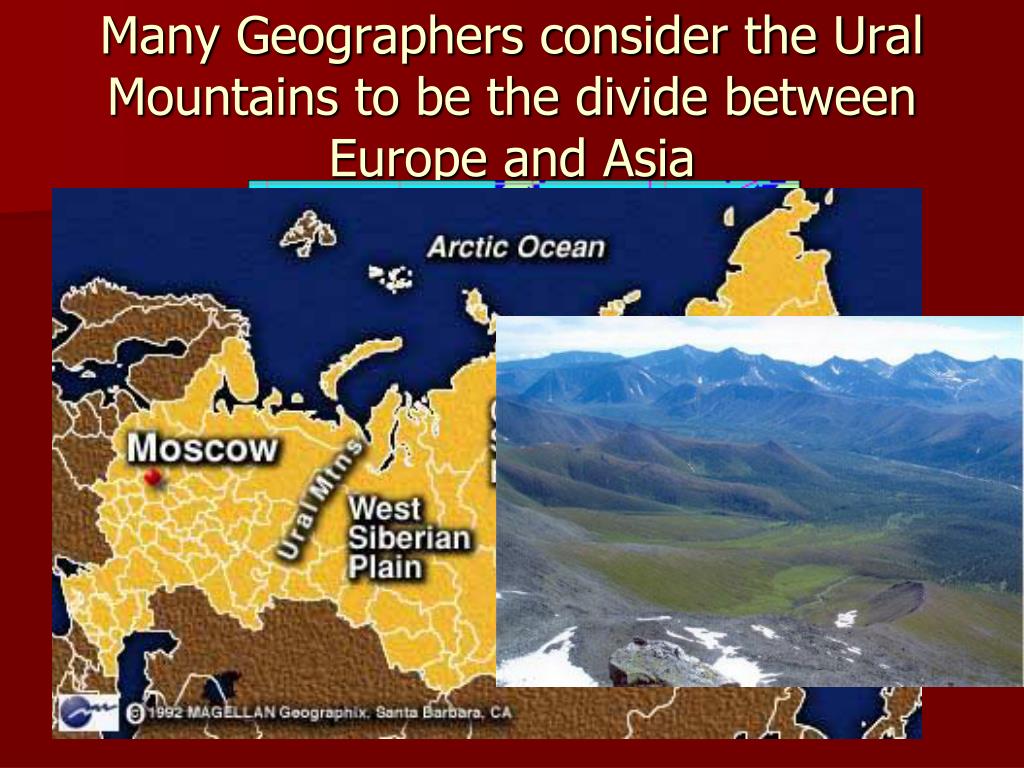
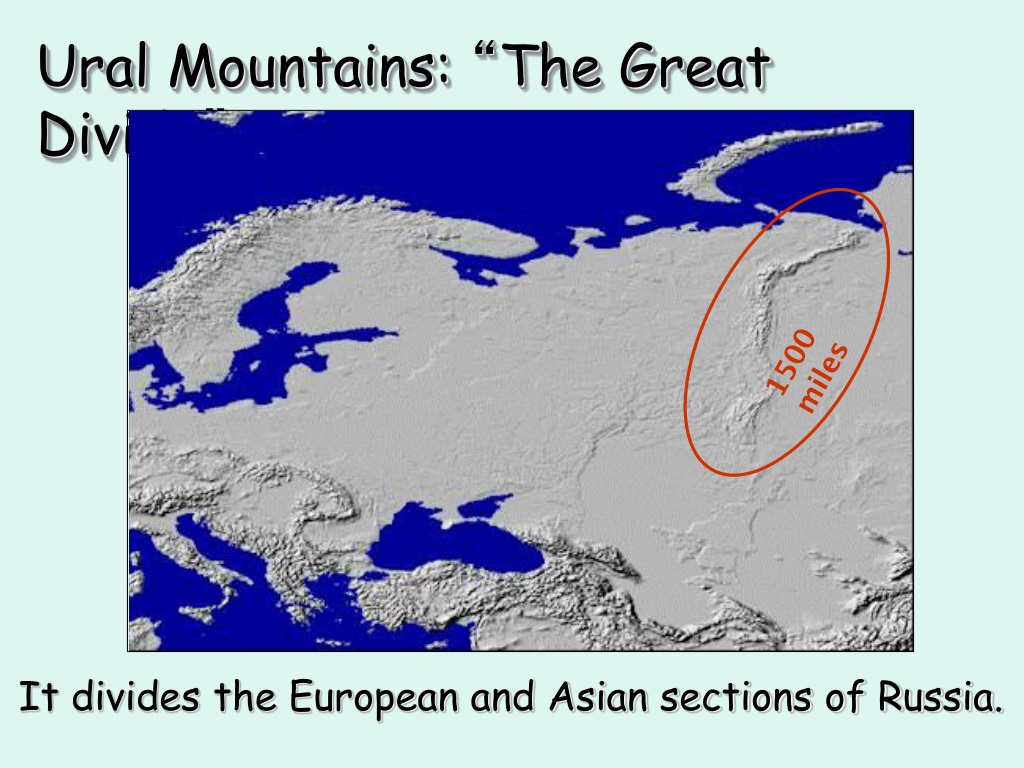
A map of the Ural Mountains reveals a striking feature: a long, sinuous line that runs from the Arctic Ocean in the north, through the heart of Russia, and down to the steppes of Kazakhstan in the south. This geographic backbone, with its diverse landscape, harbors rich natural resources and has been a vital corridor for trade and cultural exchange throughout history.
Key Geographic Features:
- Location: The Ural Mountains are located in western Russia, extending from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Ural River and the steppes of Kazakhstan in the south.
- Length: Stretching over 2,500 kilometers, the Ural Mountains are one of the longest mountain ranges in the world.
- Highest Peak: Mount Narodnaya, reaching 1,895 meters above sea level, is the highest peak in the Ural Mountains.
- Diversity: The Ural Mountains exhibit diverse topography, ranging from low hills and plateaus to rugged peaks and deep valleys.
- Rivers and Lakes: The Urals are home to numerous rivers, including the Ural River, which flows southwards into the Caspian Sea, and numerous lakes, some of which are important sources of water for the region.
Beyond the Mountains: Exploring the Significance of the Ural Range
The Ural Mountains hold immense significance, extending beyond their geographic importance to encompass a range of cultural, economic, and environmental implications.
1. A Natural Divide and Cultural Bridge:
The Ural Mountains have historically served as a natural boundary between Europe and Asia. This geographical separation has influenced the development of distinct cultures, languages, and traditions on either side of the range. However, the mountains also served as a bridge for interaction and cultural exchange. The movement of people, goods, and ideas across the Urals has led to a rich tapestry of cultural influences in the region.
2. A Rich Reservoir of Natural Resources:
The Ural Mountains are renowned for their abundant mineral wealth. Deposits of iron ore, copper, nickel, platinum, and diamonds have fueled industrial development in the region. The mountains also hold significant reserves of oil and natural gas, further contributing to their economic importance.
3. A Vital Corridor for Trade and Transportation:
Throughout history, the Ural Mountains have served as a crucial trade route connecting Europe and Asia. The Trans-Siberian Railway, one of the longest railways in the world, traverses the Urals, facilitating the movement of goods and people across the continent.
4. A Haven of Biodiversity:
The diverse topography and climate of the Ural Mountains support a rich ecosystem. From the taiga forests of the north to the steppe grasslands of the south, the range is home to a wide variety of flora and fauna, including endangered species like the Siberian tiger and the snow leopard.
5. A Source of Inspiration and Cultural Identity:
The Ural Mountains have inspired artists, writers, and musicians for centuries. Their rugged beauty and historical significance have been captured in literature, music, and art, contributing to the cultural identity of the region.
Exploring the Ural Mountains: A Journey Through Time and Landscape
A journey through the Ural Mountains is a journey through time and landscape. From the ancient forests of the north to the rolling steppes of the south, the range offers a diverse range of experiences.
1. The Northern Urals:
- Arctic Landscapes: The northernmost part of the Ural Mountains is characterized by rugged, Arctic landscapes. Glaciers, tundra, and snow-capped peaks dominate the region, offering breathtaking views and challenging hiking trails.
- Reindeer Herding: The indigenous Nenets people have traditionally relied on reindeer herding in this harsh environment.
- Mining: The northern Urals are rich in mineral resources, including platinum and diamonds. Mining has played a significant role in the region’s economic development.
2. The Middle Urals:
- Forests and Mountains: The middle Urals are dominated by dense forests, including coniferous taiga and mixed deciduous forests. The region is also home to numerous peaks, including Mount Narodnaya, the highest point in the Urals.
- Industrial Centers: The middle Urals are a major industrial center, with cities like Yekaterinburg and Chelyabinsk housing factories, steel mills, and other industrial facilities.
- Tourism: The middle Urals offer opportunities for hiking, skiing, and other outdoor activities. The region is also home to several historical and cultural sites, including the Hermitage Museum in Yekaterinburg.
3. The Southern Urals:
- Steppes and Hills: The southern Urals are characterized by rolling hills and steppes, with a more arid climate than the north. The region is home to a variety of flora and fauna, including wild horses, wolves, and gazelles.
- Mineral Resources: The southern Urals are rich in mineral resources, including copper, nickel, and iron ore. Mining has played a significant role in the region’s economic development.
- Cultural Heritage: The southern Urals are home to a variety of cultures, including the Bashkir people, known for their traditional music, dance, and crafts.
FAQs About the Ural Mountains
1. Why are the Ural Mountains important?
The Ural Mountains are important for a variety of reasons, including their role as a natural boundary between Europe and Asia, their rich mineral resources, their importance for trade and transportation, their diverse ecosystem, and their cultural significance.
2. What are the Ural Mountains made of?
The Ural Mountains are primarily composed of metamorphic rocks, including schist, gneiss, and quartzite. These rocks were formed over millions of years through the process of mountain building.
3. Are the Ural Mountains still growing?
The Ural Mountains are not actively growing today. They have reached a state of geological stability, although erosion and weathering continue to shape their landscape.
4. What are the major cities in the Ural region?
Some of the major cities in the Ural region include Yekaterinburg, Chelyabinsk, Perm, Magnitogorsk, and Nizhny Tagil. These cities are important centers of industry, culture, and education.
5. What is the best time to visit the Ural Mountains?
The best time to visit the Ural Mountains depends on your interests. For hiking and outdoor activities, the summer months (June to August) are ideal. For skiing and winter sports, the winter months (December to February) are best.
Tips for Exploring the Ural Mountains
- Plan your trip carefully: The Ural Mountains are a vast region with diverse landscapes. Research your destination and choose activities that align with your interests and fitness level.
- Pack appropriately: The weather in the Ural Mountains can be unpredictable, so pack layers of clothing and appropriate footwear.
- Respect the environment: The Ural Mountains are a fragile ecosystem. Stay on designated trails, pack out all trash, and avoid disturbing wildlife.
- Learn about the local culture: The Ural region is home to a variety of cultures and traditions. Take the opportunity to learn about the history and customs of the people who live in this area.
- Enjoy the journey: The Ural Mountains offer a unique and unforgettable travel experience. Take the time to appreciate the beauty of the landscape, the rich history, and the diverse cultures of this remarkable region.
Conclusion
The Ural Mountains, a majestic chain of peaks spanning over 2,500 kilometers, stand as a testament to the power of geological forces and the enduring influence of nature on human history. From their role as a natural boundary between Europe and Asia to their rich mineral resources and diverse ecosystem, the Urals continue to shape the geography, economy, and culture of the Eurasian continent. Exploring this remarkable mountain range offers a journey through time and landscape, revealing the beauty, history, and cultural richness of this unique region.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Ural Mountains: A Geographic Spine Dividing Europe and Asia. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!