The Loop Map: A Powerful Tool for Navigating Complex Systems
Related Articles: The Loop Map: A Powerful Tool for Navigating Complex Systems
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Loop Map: A Powerful Tool for Navigating Complex Systems. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: The Loop Map: A Powerful Tool for Navigating Complex Systems
- 2 Introduction
- 3 The Loop Map: A Powerful Tool for Navigating Complex Systems
- 3.1 What is a Loop Map?
- 3.2 Core Components of a Loop Map
- 3.3 Types of Loops
- 3.4 Benefits of Using a Loop Map
- 3.5 Applications of Loop Map in Various Fields
- 3.6 FAQs about Loop Maps
- 3.7 Tips for Creating Effective Loop Maps
- 3.8 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
The Loop Map: A Powerful Tool for Navigating Complex Systems

In the intricate tapestry of modern systems, understanding the interconnectedness of elements is paramount. Whether it’s a business process, a software architecture, or a social network, complex systems often present a daunting challenge for comprehension and analysis. This is where the loop map emerges as a potent tool, offering a visual and conceptual framework for navigating such complexities.
What is a Loop Map?
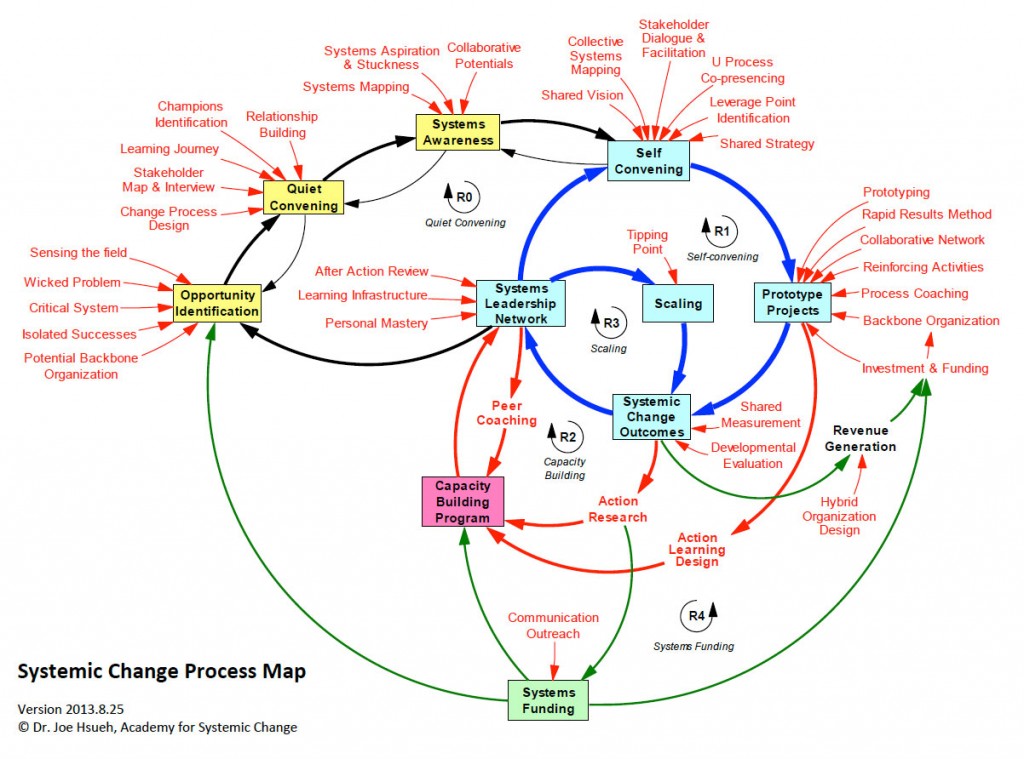
A loop map is a visual representation of a system’s feedback loops. It depicts how various elements within the system influence one another, creating a cyclical chain of cause and effect. These loops can be positive, amplifying change, or negative, dampening it. By visualizing these loops, individuals can gain a deeper understanding of how the system functions, identify potential points of intervention, and anticipate the consequences of various actions.
Core Components of a Loop Map
A loop map typically comprises the following key components:
- Elements: These are the individual components of the system, such as departments, processes, or variables.
- Arrows: These represent the relationships between elements, indicating the direction of influence.
- Signs: These denote the nature of the relationship, whether it is positive (amplifying) or negative (dampening).
- Loop: This is the closed cycle of influence, formed by connecting elements through arrows.
Types of Loops
Loop maps can be classified into different types based on the nature of the feedback they represent:
- Reinforcing Loops: These are positive feedback loops, where changes in one element amplify changes in others, creating a snowball effect. For instance, increased demand for a product can lead to higher production, which further increases demand.
- Balancing Loops: These are negative feedback loops, where changes in one element counteract changes in others, maintaining a state of equilibrium. For example, a thermostat regulates temperature by turning the heating system on when the temperature drops and off when it rises.
Benefits of Using a Loop Map
Employing a loop map offers numerous advantages in analyzing and managing complex systems:
- Enhanced Understanding: By visualizing the interconnectedness of elements, loop maps provide a clear and concise representation of how the system functions. This facilitates a deeper understanding of cause-and-effect relationships and the potential consequences of various actions.
- Identification of Leverage Points: Loop maps can pinpoint critical elements within a system that exert significant influence on the overall behavior. Identifying these leverage points allows for targeted interventions to optimize system performance.
- Improved Decision-Making: Understanding the dynamics of feedback loops empowers individuals to make more informed decisions. By considering the potential consequences of various actions on the entire system, decision-makers can minimize unintended consequences and maximize desired outcomes.
- Collaboration and Communication: Loop maps serve as a powerful tool for facilitating communication and collaboration among stakeholders. The visual representation allows for shared understanding and fosters a common ground for discussion and analysis.
- Problem Solving and Innovation: By revealing the underlying mechanisms driving system behavior, loop maps can aid in identifying root causes of problems and developing innovative solutions. Understanding the interplay of feedback loops provides a framework for addressing challenges from a systemic perspective.
Applications of Loop Map in Various Fields
The loop map’s versatility extends across numerous fields:
- Business: Loop maps can analyze supply chains, market dynamics, customer relationships, and organizational structures, optimizing business processes and fostering sustainable growth.
- Software Development: They can model software systems, identify potential bottlenecks, and facilitate the design of robust and efficient architectures.
- Social Systems: Loop maps can illuminate the complex interactions within social networks, understanding the spread of information, the formation of opinions, and the dynamics of social change.
- Environmental Systems: They can analyze ecological systems, understanding the impact of human activities on the environment and devising strategies for sustainable development.
- Healthcare: Loop maps can model disease progression, identify key factors influencing patient outcomes, and optimize treatment strategies.
FAQs about Loop Maps
Q: What are the limitations of loop maps?
A: Loop maps are simplified representations of complex systems, and they may not capture all the nuances of real-world interactions. Additionally, constructing accurate and comprehensive loop maps can be time-consuming and require a deep understanding of the system under analysis.
Q: How can I create a loop map?
A: There are various software tools available for creating loop maps, such as Vensim, Stella, and iThink. Alternatively, you can create a loop map manually using pen and paper or a whiteboard.
Q: How do I use a loop map to solve problems?
A: Once you have created a loop map, you can analyze it to identify the root causes of problems and potential solutions. By understanding the interplay of feedback loops, you can develop strategies that target the key leverage points within the system.
Q: How do I know if my loop map is accurate?
A: The accuracy of a loop map depends on the quality of data and the depth of understanding of the system. It is essential to validate the loop map by comparing its predictions with real-world observations and seeking feedback from stakeholders.
Tips for Creating Effective Loop Maps
- Start with a Clear Objective: Define the specific purpose of the loop map, whether it is to understand a particular process, identify leverage points, or develop solutions to a problem.
- Identify the Key Elements: Determine the most relevant elements within the system and their relationships to each other.
- Focus on Feedback Loops: Pay attention to the cyclical nature of influence within the system, identifying the key feedback loops that drive its behavior.
- Keep it Simple: Start with a basic loop map and gradually add complexity as needed. Avoid overwhelming the audience with too much detail.
- Use Visual Aids: Employ clear and concise visuals, such as arrows, signs, and colors, to enhance readability and understanding.
- Test and Iterate: Validate the loop map by comparing its predictions with real-world observations and refining it based on feedback.
Conclusion
The loop map serves as a powerful tool for navigating the complexities of modern systems. By visualizing the interconnectedness of elements and the dynamics of feedback loops, individuals can gain a deeper understanding of system behavior, identify leverage points for intervention, and make more informed decisions. As the complexity of our world continues to grow, the ability to effectively model and analyze systems through loop maps will become increasingly essential for navigating challenges and achieving desired outcomes.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Loop Map: A Powerful Tool for Navigating Complex Systems. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!