The Heart of the Map: Navigating the Complexities of Geographic Information Systems
Related Articles: The Heart of the Map: Navigating the Complexities of Geographic Information Systems
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Heart of the Map: Navigating the Complexities of Geographic Information Systems. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Heart of the Map: Navigating the Complexities of Geographic Information Systems

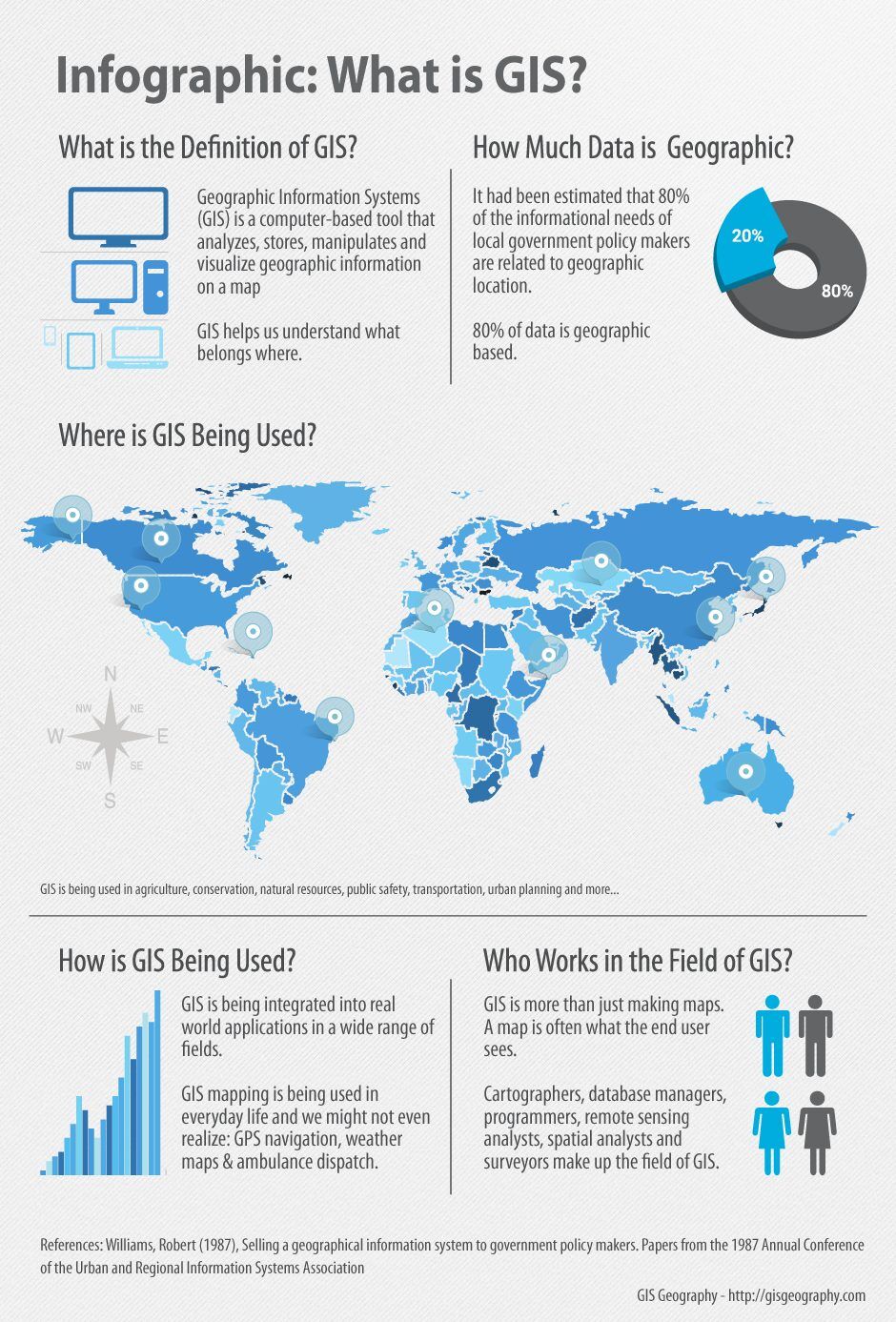
The field of geography is undergoing a revolution, driven by the power of technology. At the core of this revolution lies a critical component: the map. Yet, it’s not just any map; it’s a geographic information system (GIS), a dynamic and multifaceted tool that goes beyond static representations of the world. The GIS acts as the heart of this revolution, pulsing with data, analysis, and insights that are transforming our understanding and management of the planet.
Understanding the Power of GIS
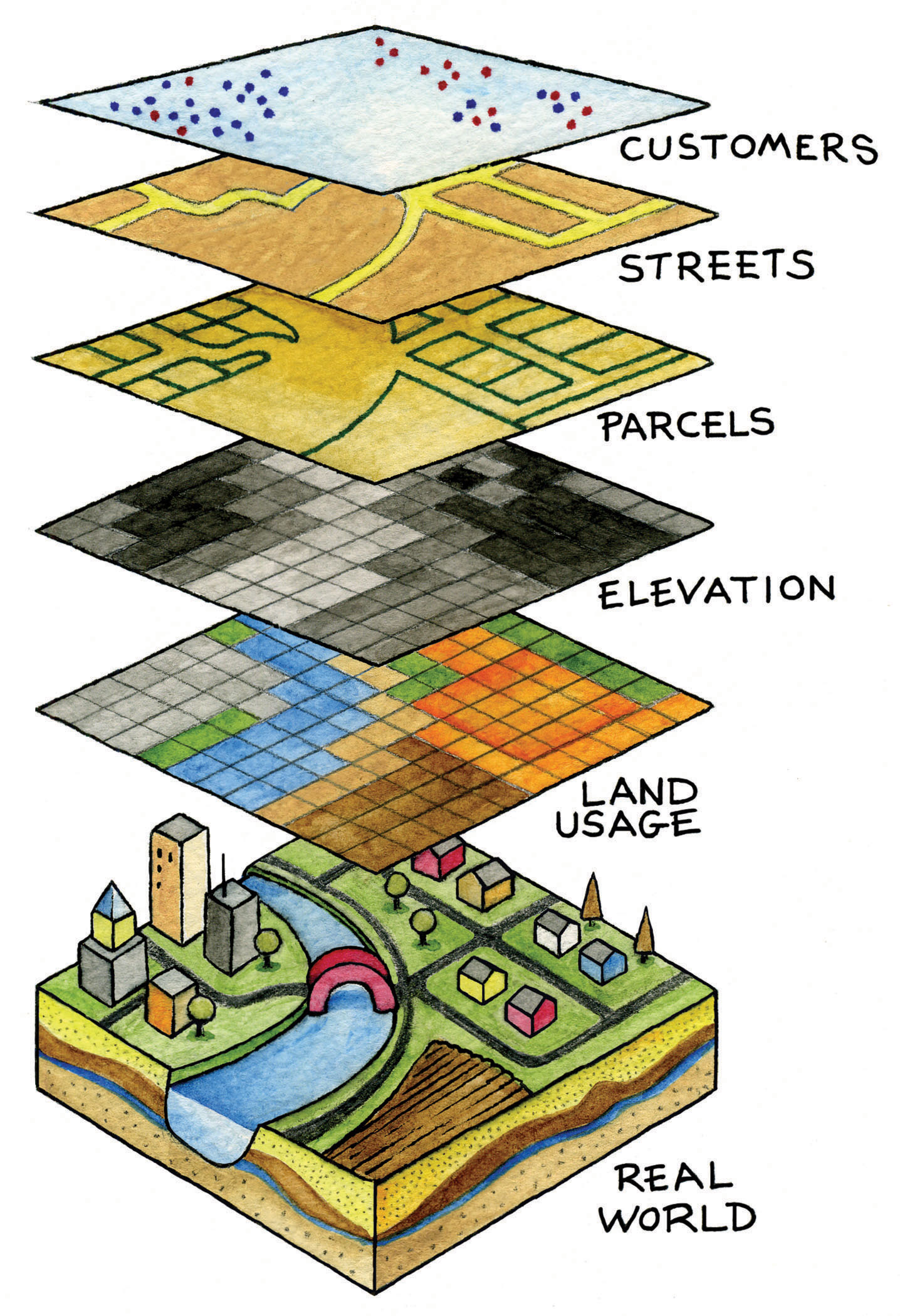
A GIS is more than just a digital map. It’s a sophisticated platform that integrates, analyzes, and visualizes geographic data. This data can encompass diverse elements, from physical features like elevation and land cover to social and economic indicators like population density and infrastructure.
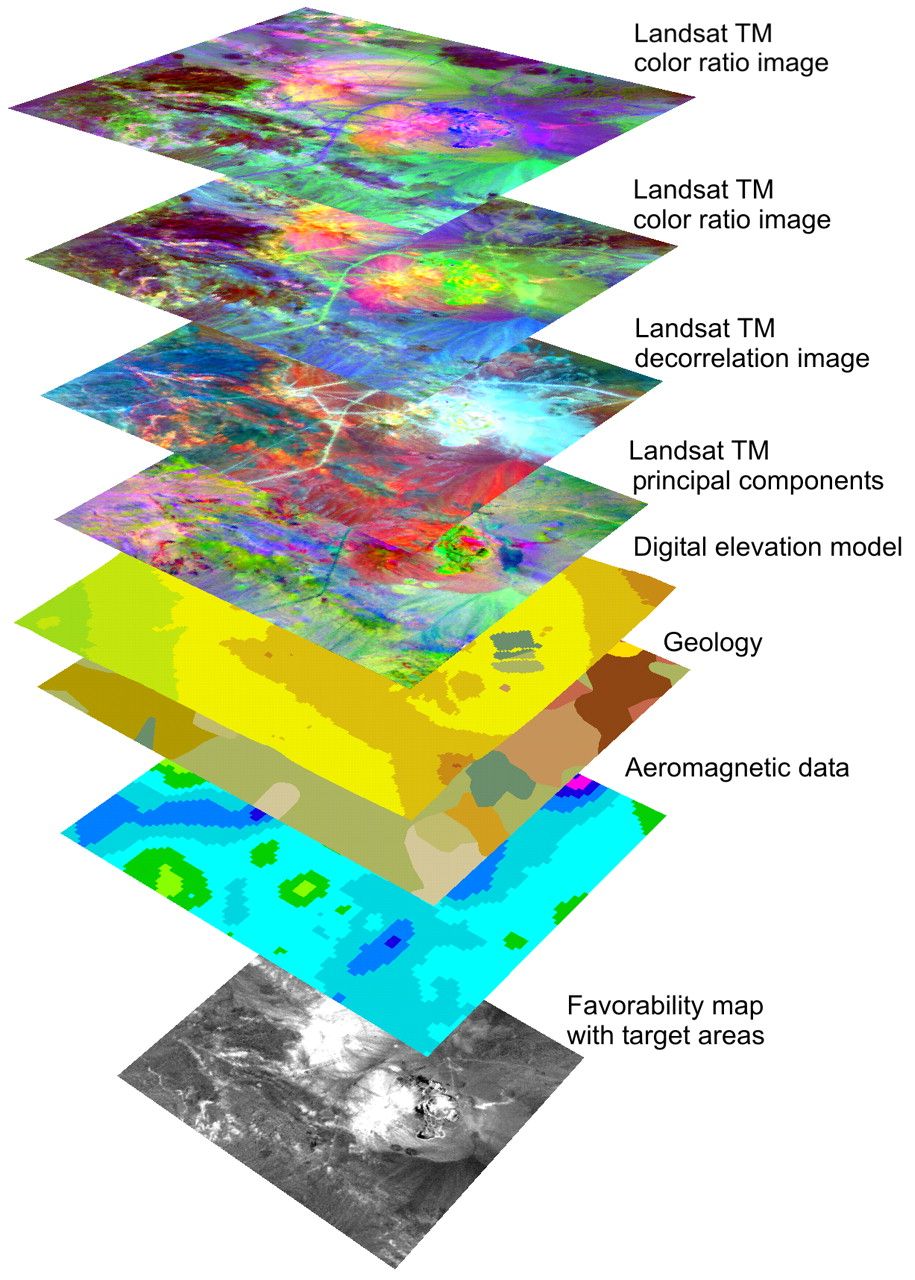
The key to the GIS lies in its ability to link these data layers. By overlaying information, analysts can reveal complex relationships and patterns, uncovering insights that would be impossible to discern through traditional methods. This capability unlocks a wide range of applications across various fields, including:
- Environmental Management: GIS helps identify areas vulnerable to natural disasters, monitor deforestation, and manage water resources.
- Urban Planning: It facilitates the development of efficient transportation systems, optimizes land use, and analyzes population growth patterns.
- Resource Management: GIS aids in identifying and managing natural resources, like minerals, oil, and gas, while ensuring sustainable practices.
- Public Health: It assists in mapping disease outbreaks, identifying high-risk areas, and implementing targeted interventions.
- Emergency Response: GIS provides real-time information for disaster response, allowing for efficient resource allocation and communication.
- Business Analysis: GIS enables businesses to understand customer demographics, optimize supply chains, and analyze market trends.
Key Components of a GIS
The heart of a GIS is comprised of several interconnected components:
- Hardware: The physical infrastructure, including computers, servers, and data storage devices.
- Software: The applications that enable data collection, analysis, and visualization, such as ArcGIS, QGIS, and MapInfo.
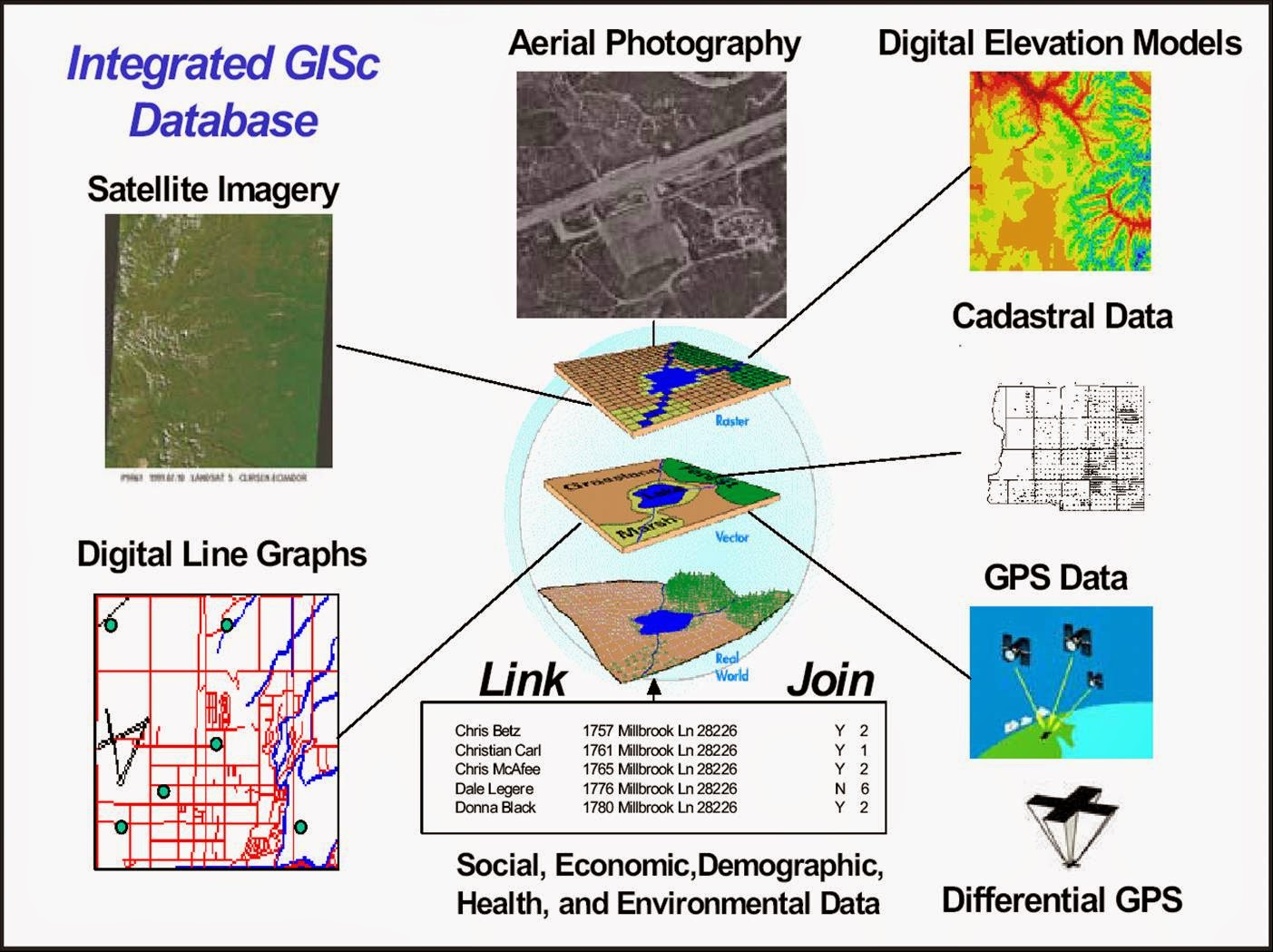
- Data: The core of the GIS, encompassing geographic information in various formats, including maps, aerial photographs, satellite imagery, and tabular data.
- People: The individuals who collect, analyze, and interpret data, ultimately transforming information into actionable insights.
The Importance of Data in GIS
The quality and diversity of data are crucial for a GIS to function effectively. Data can be collected through various methods, including:
- Remote Sensing: Utilizing satellites and aerial platforms to capture images and other data.
- Global Positioning System (GPS): Determining location coordinates using satellites.
- Field Surveys: Gathering data directly on the ground through measurements and observations.
- Existing Databases: Accessing and integrating data from public and private sources.
Data accuracy, consistency, and timeliness are paramount for ensuring the reliability of GIS outputs. The ability to manage and integrate data from multiple sources is a key strength of the GIS, enabling comprehensive analyses and robust decision-making.
The Role of Spatial Analysis
GIS goes beyond simply visualizing data; it allows for powerful spatial analysis. This involves applying various analytical techniques to geographic data, including:
- Buffering: Creating zones around specific locations, such as schools or hospitals, to analyze accessibility or impact.
- Overlaying: Combining multiple data layers to identify areas with specific characteristics, like areas with high population density and low access to healthcare.
- Network Analysis: Evaluating the efficiency of transportation networks, identifying shortest routes, and analyzing traffic flow.
- Proximity Analysis: Determining the distance between features, such as finding the nearest fire station to a potential wildfire.
- Spatial Statistics: Analyzing spatial patterns and trends to identify clusters, outliers, and other significant features.
These analyses generate valuable insights, enabling informed decision-making in various sectors.
Benefits of Utilizing GIS
The adoption of GIS offers numerous benefits, contributing to:
- Improved Decision-Making: By providing comprehensive insights and supporting data-driven analysis, GIS helps make more informed and effective decisions.
- Enhanced Efficiency: GIS streamlines processes, optimizes resource allocation, and improves overall operational efficiency.
- Increased Accuracy: GIS provides precise spatial information, leading to more accurate assessments and predictions.
- Better Communication: GIS facilitates clear and concise communication of complex information through maps, charts, and other visualizations.
- Greater Collaboration: GIS enables collaboration among stakeholders, fostering shared understanding and facilitating collective decision-making.
FAQs about GIS
1. What is the difference between a map and a GIS?
A map is a static representation of geographic information, while a GIS is a dynamic system that integrates, analyzes, and visualizes data. A GIS allows for interactive exploration and analysis, going beyond the limitations of traditional maps.
2. How can I learn more about GIS?
Numerous resources are available for learning about GIS, including online courses, tutorials, and books. Many universities offer degree programs in GIS, and professional organizations provide certification programs.
3. What are some real-world applications of GIS?
GIS is used in a wide range of applications, including environmental management, urban planning, resource management, public health, emergency response, and business analysis.
4. How does GIS relate to other technologies?
GIS integrates with other technologies, such as remote sensing, GPS, and cloud computing, enhancing its capabilities and expanding its applications.
5. What are the challenges of using GIS?
Challenges include data availability, accuracy, and consistency, as well as the need for technical expertise and specialized software.
Tips for Utilizing GIS Effectively
- Clearly define your goals: Identify the specific questions you want to answer or problems you want to solve using GIS.
- Choose the right data: Select data that is relevant, accurate, and appropriate for your analysis.
- Use appropriate tools: Select the GIS software and analytical techniques that best suit your needs.
- Visualize your results: Create clear and informative maps, charts, and other visualizations to communicate your findings.
- Share your results: Disseminate your findings to stakeholders and decision-makers to promote informed decision-making.
Conclusion
The GIS acts as the heart of a geographic revolution, empowering us to understand and manage our planet more effectively. Its ability to integrate, analyze, and visualize geographic data unlocks a wealth of insights, transforming how we approach environmental challenges, plan our cities, manage resources, and respond to emergencies. As technology continues to evolve, the GIS will undoubtedly play an even more critical role in shaping our future. By harnessing the power of GIS, we can unlock the potential of geographic information to create a more sustainable, equitable, and prosperous world.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Heart of the Map: Navigating the Complexities of Geographic Information Systems. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
%20Components.PNG)