Navigating the Terrain of Google Maps Data Extraction: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Navigating the Terrain of Google Maps Data Extraction: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Terrain of Google Maps Data Extraction: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Terrain of Google Maps Data Extraction: A Comprehensive Guide
Google Maps has become an indispensable tool for navigating the physical world, offering a vast repository of information about businesses, places, and locations. This wealth of data, however, is not readily accessible in a structured format for analysis and utilization. Herein lies the significance of Google Maps scraping, a process that enables the extraction and organization of this valuable information for various purposes.
Understanding the Essence of Google Maps Scraping
Google Maps scraping involves using automated tools and techniques to gather and organize data from Google Maps. This data can encompass a wide range of information, including:
- Business Information: Name, address, phone number, website URL, opening hours, reviews, ratings, photos, and more.
- Location Data: Coordinates, street addresses, landmarks, nearby points of interest, and geographical features.
- User-Generated Content: Reviews, ratings, photos, videos, and comments contributed by users.
The extracted data can then be processed, analyzed, and utilized for various applications, ranging from market research and competitor analysis to lead generation and customer outreach.
Exploring the Benefits of Google Maps Data Extraction
The benefits of Google Maps scraping extend across diverse domains, empowering businesses and individuals to make informed decisions and achieve specific goals.
1. Market Research and Competitive Analysis:
- Understanding Market Trends: By scraping Google Maps data, businesses can gain insights into the density and distribution of competitors within specific geographic areas. This analysis can reveal market saturation, identify potential growth opportunities, and inform strategic decision-making.
- Identifying Target Demographics: Analyzing reviews and ratings associated with businesses can provide insights into the demographics of customers, their preferences, and the factors influencing their choices. This information can be invaluable for tailoring marketing campaigns and product offerings to specific target audiences.
2. Lead Generation and Customer Outreach:
- Building Targeted Lead Lists: Extracting contact information from Google Maps listings can be used to create targeted lead lists for marketing campaigns. This allows businesses to reach potential customers who are actively searching for products or services relevant to their offerings.
- Personalizing Customer Interactions: By scraping user reviews and comments, businesses can gain a deeper understanding of customer experiences and preferences. This information can be used to personalize marketing messages, improve customer service, and build stronger relationships with customers.
3. Location-Based Services and Navigation:
- Optimizing Delivery Routes: Logistics companies can leverage Google Maps data to optimize delivery routes, minimizing travel time and fuel consumption. This can significantly enhance operational efficiency and reduce delivery costs.
- Developing Location-Based Apps: Developers can utilize scraped Google Maps data to create location-based applications that provide users with relevant information, recommendations, and services based on their current location.
4. Real Estate and Property Analysis:
- Identifying Property Trends: Scraping Google Maps data can provide insights into property values, rental rates, and market trends in specific areas. This information can be invaluable for real estate investors, developers, and property managers.
- Analyzing Neighborhood Characteristics: By scraping data on local businesses, amenities, and points of interest, real estate professionals can gain a comprehensive understanding of neighborhood characteristics, which can inform property valuations and marketing strategies.
5. Tourism and Travel Planning:
- Discovering Hidden Gems: Scraping Google Maps data can reveal hidden gems and local attractions that may not be readily apparent through traditional search engines. This information can enhance travel planning and enrich the overall travel experience.
- Creating Personalized Travel Itineraries: By extracting data on points of interest, restaurants, hotels, and transportation options, travel agencies and online platforms can create personalized travel itineraries tailored to individual traveler preferences.
Technical Aspects of Google Maps Scraping
Google Maps scraping involves a combination of technical skills and tools.
1. Web Scraping Techniques:
- HTTP Requests: Scraping tools send HTTP requests to Google Maps servers to retrieve the desired data.
- HTML Parsing: The retrieved HTML code is parsed to extract the relevant information and organize it into a structured format.
- Data Extraction Libraries: Libraries such as Beautiful Soup, Scrapy, and Selenium are used to automate the process of extracting data from HTML pages.
2. Data Storage and Processing:
- Databases: Extracted data is typically stored in databases such as MySQL, PostgreSQL, or MongoDB for efficient access and analysis.
- Data Cleaning and Transformation: The scraped data may require cleaning and transformation to ensure consistency and accuracy before further processing.
3. Ethical Considerations:
- Google Maps Terms of Service: It is crucial to comply with Google Maps’ Terms of Service and avoid excessive scraping that could overload their servers.
- Respecting Privacy: Scraping user-generated content should be done with respect for user privacy and data protection regulations.
- Responsible Use: The extracted data should be used ethically and responsibly, avoiding any activities that could harm individuals or organizations.
Navigating the Challenges of Google Maps Scraping
While Google Maps scraping offers numerous benefits, it also presents several challenges that require careful consideration.
1. Anti-Scraping Measures: Google employs various anti-scraping measures to protect its servers and prevent data misuse. These measures can include:
- CAPTCHA Challenges: Captcha checks are used to distinguish between human users and automated bots.
- Rate Limiting: Google limits the number of requests that can be made from a single IP address within a specific time frame.
- Dynamic Content: Google Maps often uses dynamic content that changes with each request, making it difficult to extract consistent data.
2. Data Format and Consistency:
- Data Inconsistency: The format and structure of Google Maps data can vary across different regions and devices.
- Data Duplication: Scraping data from multiple sources can lead to data duplication and inconsistencies.
3. Legal and Ethical Considerations:
- Terms of Service Compliance: It is essential to comply with Google Maps’ Terms of Service and avoid violating any legal restrictions.
- Data Privacy and Security: Scraping user-generated content raises concerns about data privacy and security.
FAQs Regarding Google Maps Scraping
1. Is Google Maps scraping legal?
While Google Maps scraping is generally legal, it is crucial to comply with Google’s Terms of Service and avoid violating any legal restrictions.
2. What are the risks associated with Google Maps scraping?
The risks associated with Google Maps scraping include potential legal action from Google, violation of user privacy, and data security breaches.
3. How can I avoid getting blocked by Google Maps?
To avoid getting blocked, it is recommended to use a proxy server, rotate IP addresses, and adhere to Google’s rate limits.
4. What are the best tools for Google Maps scraping?
Some popular tools for Google Maps scraping include Scrapy, Beautiful Soup, Selenium, and Apify.
5. What are the ethical considerations of Google Maps scraping?
Ethical considerations include respecting user privacy, complying with Google’s Terms of Service, and using the extracted data responsibly.
Tips for Effective Google Maps Scraping
1. Plan Your Scraping Project: Define your scraping goals, identify the specific data you need, and choose the appropriate tools.
2. Respect Google’s Terms of Service: Adhere to Google’s guidelines and avoid excessive scraping that could overload their servers.
3. Use Proxy Servers: Rotate IP addresses and use proxy servers to avoid getting blocked by Google.
4. Handle Dynamic Content: Use tools like Selenium that can handle dynamic content and JavaScript rendering.
5. Clean and Validate Data: Ensure the scraped data is clean, accurate, and consistent before using it for analysis.
Conclusion
Google Maps scraping presents a powerful tool for extracting valuable data from this ubiquitous platform. By understanding the technical aspects, ethical considerations, and challenges associated with this process, businesses and individuals can leverage this data to gain competitive advantages, optimize operations, and make informed decisions. As Google Maps continues to evolve and provide an ever-expanding repository of information, the significance of Google Maps scraping will only grow in the coming years.




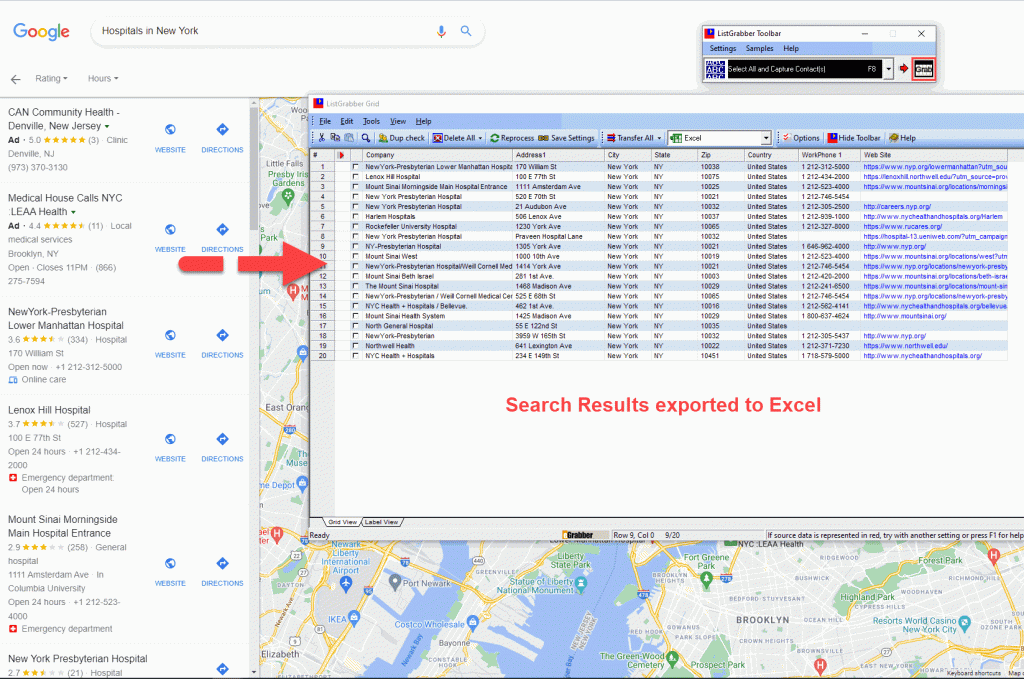

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Terrain of Google Maps Data Extraction: A Comprehensive Guide. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!