Navigating the Landscape of Java Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Iteration
Related Articles: Navigating the Landscape of Java Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Iteration
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Landscape of Java Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Iteration. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Navigating the Landscape of Java Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Iteration
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Navigating the Landscape of Java Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Iteration
- 3.1 The Importance of Iteration: Unveiling the Potential of Maps
- 3.2 Exploring the Iteration Landscape: A Journey Through Key Methods
- 3.3 Choosing the Right Approach: Considerations for Efficient Iteration
- 3.4 Frequently Asked Questions: Addressing Common Concerns
- 3.5 Tips for Effective Iteration: Mastering the Art of Map Traversal
- 3.6 Conclusion: Embracing the Power of Iteration
- 4 Closure
Navigating the Landscape of Java Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Iteration
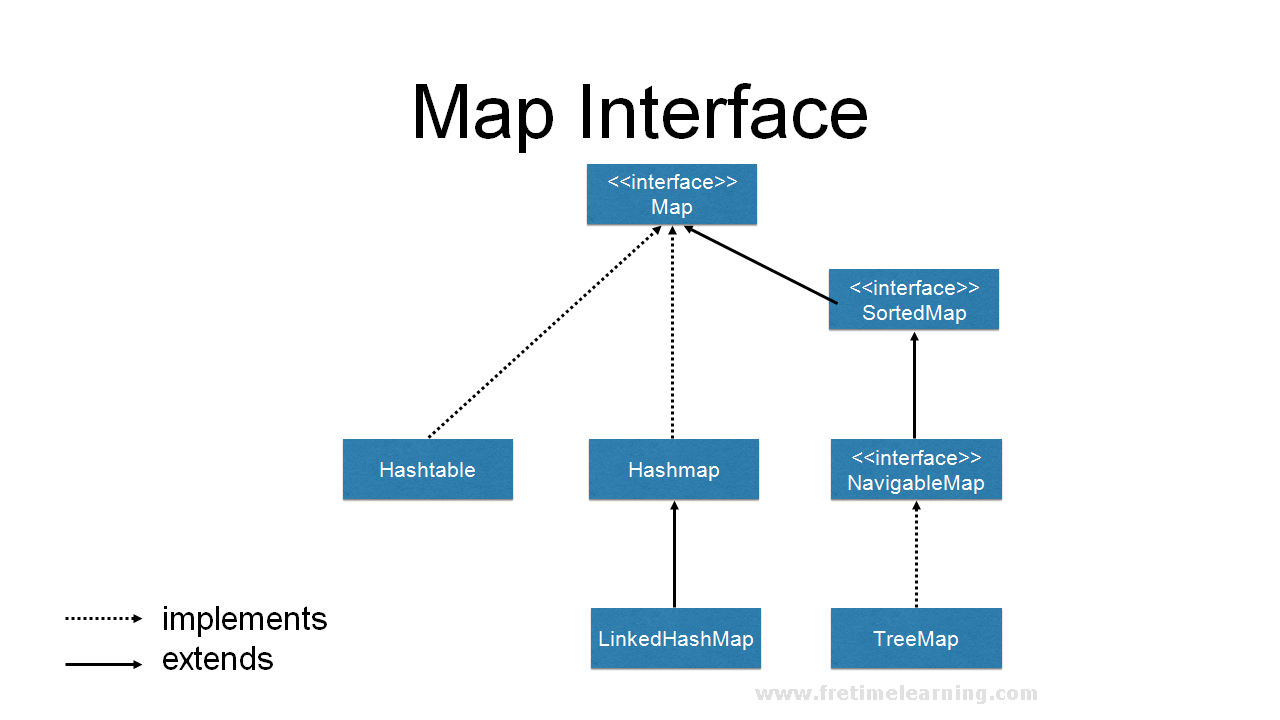
Java maps, a fundamental data structure, offer a powerful way to store and retrieve data based on key-value pairs. Understanding how to iterate through these maps is crucial for effectively manipulating and extracting information. This comprehensive guide delves into the various methods of traversing Java maps, providing insights into their functionalities and practical applications.
The Importance of Iteration: Unveiling the Potential of Maps
Iteration, the process of stepping through each element in a collection, is essential for unlocking the full potential of Java maps. It allows developers to:
- Access and Process Data: Iterate through maps to retrieve specific values based on their corresponding keys, enabling data manipulation and analysis.
- Perform Operations on All Entries: Apply functions or calculations to every key-value pair, facilitating tasks like data aggregation, filtering, or transformation.
- Dynamically Update Maps: Modify map entries during iteration, allowing for dynamic updates based on specific conditions or calculations.
- Efficiently Manage Large Datasets: Iterate through maps to process extensive datasets, ensuring efficient management and manipulation.
Exploring the Iteration Landscape: A Journey Through Key Methods
Java provides several methods for traversing maps, each offering distinct advantages and use cases. This section will explore the most common and effective approaches:
1. Using the keySet() Method
The keySet() method returns a Set containing all the keys present in the map. This Set can then be iterated using a for-each loop, allowing access to individual keys. For each key, the corresponding value can be retrieved using the get() method of the map.
Map<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("Apple", 1);
map.put("Banana", 2);
map.put("Orange", 3);
// Iterate through the keys
for (String key : map.keySet())
// Retrieve the value associated with the key
Integer value = map.get(key);
System.out.println("Key: " + key + ", Value: " + value);
2. Leveraging the entrySet() Method
The entrySet() method returns a Set of Map.Entry objects, where each entry represents a key-value pair. Iterating through this Set provides direct access to both the key and value within each entry.
Map<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("Apple", 1);
map.put("Banana", 2);
map.put("Orange", 3);
// Iterate through the entries
for (Map.Entry<String, Integer> entry : map.entrySet())
// Access the key and value directly
String key = entry.getKey();
Integer value = entry.getValue();
System.out.println("Key: " + key + ", Value: " + value);
3. Employing the forEach() Method (Java 8 and Above)
Java 8 introduced the forEach() method for collections, simplifying iteration. This method takes a Consumer object, which defines the action to be performed for each entry.
Map<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("Apple", 1);
map.put("Banana", 2);
map.put("Orange", 3);
// Iterate through the entries
map.forEach((key, value) ->
System.out.println("Key: " + key + ", Value: " + value);
);4. Iterating with an Iterator
The iterator() method returns an Iterator object, which allows sequential access to the elements of the map. The hasNext() method checks if there are more elements to iterate, and the next() method retrieves the next element, which is a Map.Entry object.
Map<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("Apple", 1);
map.put("Banana", 2);
map.put("Orange", 3);
// Get an iterator for the entries
Iterator<Map.Entry<String, Integer>> iterator = map.entrySet().iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext())
// Retrieve the next entry
Map.Entry<String, Integer> entry = iterator.next();
// Access the key and value
String key = entry.getKey();
Integer value = entry.getValue();
System.out.println("Key: " + key + ", Value: " + value);
Choosing the Right Approach: Considerations for Efficient Iteration
Selecting the appropriate iteration method depends on the specific requirements and context. Here are some key considerations:
-
Readability and Simplicity: The
forEach()method (Java 8 and above) offers the most concise and readable syntax, making it ideal for straightforward iteration. -
Direct Access to Key and Value: The
entrySet()method provides direct access to both the key and value within each entry, making it suitable when both are needed. -
Customization and Control: The
iterator()method offers greater control over the iteration process, allowing for complex operations and custom logic. -
Performance: The
keySet()method, while less intuitive, can be slightly more efficient for specific scenarios, especially when only the keys are required.
Frequently Asked Questions: Addressing Common Concerns
1. Can I modify the map while iterating through it?
Modifying a map while iterating using the keySet() or entrySet() methods can lead to unpredictable behavior due to potential changes in the map’s internal structure. The iterator() method offers better control, allowing modification through its remove() method. However, it’s generally advisable to avoid modifying a map during iteration unless absolutely necessary.
2. Is there a specific order in which map entries are iterated?
The order of iteration in maps is not guaranteed to be consistent. While some implementations might maintain insertion order, others might not. Relying on a specific iteration order can lead to unexpected results and should be avoided.
3. What happens if a key is removed from the map during iteration?
Removing a key during iteration can lead to unpredictable results, depending on the chosen method. The iterator() method allows removing the current entry using the remove() method, but attempting to remove an entry not returned by the next() method can result in an exception.
4. How can I iterate through a map in reverse order?
The entrySet() method returns a Set, which doesn’t inherently guarantee order. To achieve reverse iteration, you can use a List implementation that maintains insertion order, such as LinkedList, and iterate through it in reverse using a for loop with a decreasing index.
5. Can I iterate through a map using a traditional for loop?
While possible, iterating through a map using a traditional for loop is generally not recommended due to its complexity. The methods discussed above offer more efficient and readable alternatives.
Tips for Effective Iteration: Mastering the Art of Map Traversal
- Choose the appropriate method: Carefully select the most suitable iteration method based on the specific requirements and context.
- Understand the order of iteration: Be aware that the order of iteration in maps is not guaranteed to be consistent.
- Avoid modifying the map during iteration: Modifying a map while iterating can lead to unpredictable behavior.
-
Utilize the
remove()method with caution: Use theremove()method from theiterator()carefully to avoid unexpected results. -
Consider using a
Listfor guaranteed order: If a specific iteration order is required, use aListimplementation that maintains insertion order.
Conclusion: Embracing the Power of Iteration
Iteration is a fundamental aspect of Java map manipulation. By understanding the various methods and their nuances, developers can effectively access, process, and manage data stored in maps. Choosing the right method based on specific requirements and adhering to best practices ensures efficient and predictable map traversal, unlocking the full potential of this powerful data structure.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Landscape of Java Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Iteration. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!