Navigating the Land of Promise: A Comprehensive Look at Israel in Biblical Times
Related Articles: Navigating the Land of Promise: A Comprehensive Look at Israel in Biblical Times
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Land of Promise: A Comprehensive Look at Israel in Biblical Times. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Land of Promise: A Comprehensive Look at Israel in Biblical Times

The land of Israel, as depicted in the Bible, is a tapestry woven with narratives of faith, struggle, and triumph. Its geographical features, from fertile valleys to rugged mountains, played a pivotal role in shaping the lives of its inhabitants and the unfolding of biblical events. Understanding the physical landscape of ancient Israel is crucial for comprehending the historical context, cultural nuances, and theological significance of the biblical narratives.
The Land: A Mosaic of Diverse Terrain
Ancient Israel, encompassing the modern-day state of Israel, the West Bank, and parts of Jordan, was a geographically diverse region. Its landscape, a mixture of mountains, valleys, plains, and deserts, presented both challenges and opportunities for its inhabitants.
-
The Coastal Plain: This fertile strip of land, stretching along the Mediterranean Sea, provided access to trade routes and supported agriculture. Cities like Jaffa, Ashdod, and Ashkelon flourished along this coastal plain, serving as important maritime centers.
-
The Shephelah: This hilly region, situated between the coastal plain and the Judean Mountains, offered a transition zone with a mix of agricultural land and pasture. It was home to numerous towns and villages, including the important city of Gath.
-
The Judean Mountains: This rugged mountain range, rising to over 3,000 feet, provided natural defenses and served as a stronghold for the Israelites. Jerusalem, the capital city, was strategically located in this region, dominating the surrounding landscape.
-
The Jordan Valley: This fertile rift valley, running along the eastern side of the Judean Mountains, was a vital agricultural region, watered by the Jordan River. The Dead Sea, with its unique salt content, marked the southern end of the valley.
-
The Transjordan: This region, east of the Jordan River, comprised a variety of terrains, including the Gilead plateau, the Moabite Plateau, and the Edomite highlands. These areas were inhabited by various tribes, including the Ammonites, Moabites, and Edomites.
-
The Negev Desert: This arid region, south of the Judean Mountains, was sparsely populated but held strategic importance for its trade routes and natural resources.
The People: A Tapestry of Tribes and Nations
The land of Israel in biblical times was not a monolithic entity. It was inhabited by a diverse array of tribes and nations, each with its own distinct culture, language, and religious beliefs.
-
The Israelites: The biblical narrative centers around the Israelites, a group of tribes descended from Abraham, Isaac, and Jacob. They were united by their shared faith in the God of Israel and their covenant with him.
-
The Canaanites: This group of people, inhabiting the land before the arrival of the Israelites, were known for their advanced agricultural practices, urban settlements, and religious beliefs.
-
The Philistines: These seafaring people, originating from the Aegean region, settled along the southern coastal plain. They were known for their military prowess and their cultural influence.
-
The Ammonites and Moabites: These Semitic tribes, residing east of the Jordan River, were closely related to the Israelites but often engaged in conflict with them.
-
The Edomites: These people, inhabiting the Edomite highlands, were considered to be descendants of Esau, Jacob’s brother. They had a complex relationship with the Israelites, marked by both hostility and alliances.
The Importance of the Land: A Sacred Space and a Crossroads of Cultures
The land of Israel held immense cultural and religious significance for its inhabitants. It was considered a sacred space, where God had revealed himself to his people and established his covenant with them. The land was also a crossroads of cultures, where diverse peoples interacted and exchanged ideas, goods, and beliefs.
-
The Promised Land: For the Israelites, the land of Canaan was a promised land, bestowed upon them by God as a reward for their faithfulness. It was a place of refuge, abundance, and spiritual renewal.
-
The Center of the Covenant: The land of Israel was the stage for the unfolding of the covenant between God and his people. It was here that God gave his law, established his temple, and sent his prophets.
-
A Land of Struggle and Triumph: The history of ancient Israel was marked by both struggle and triumph. The Israelites faced numerous challenges, including wars, famines, and internal divisions. Yet, they also experienced moments of great victory and spiritual renewal.
Navigating the Biblical Landscape: Tools and Resources
To navigate the complex landscape of ancient Israel, several tools and resources are available:
-
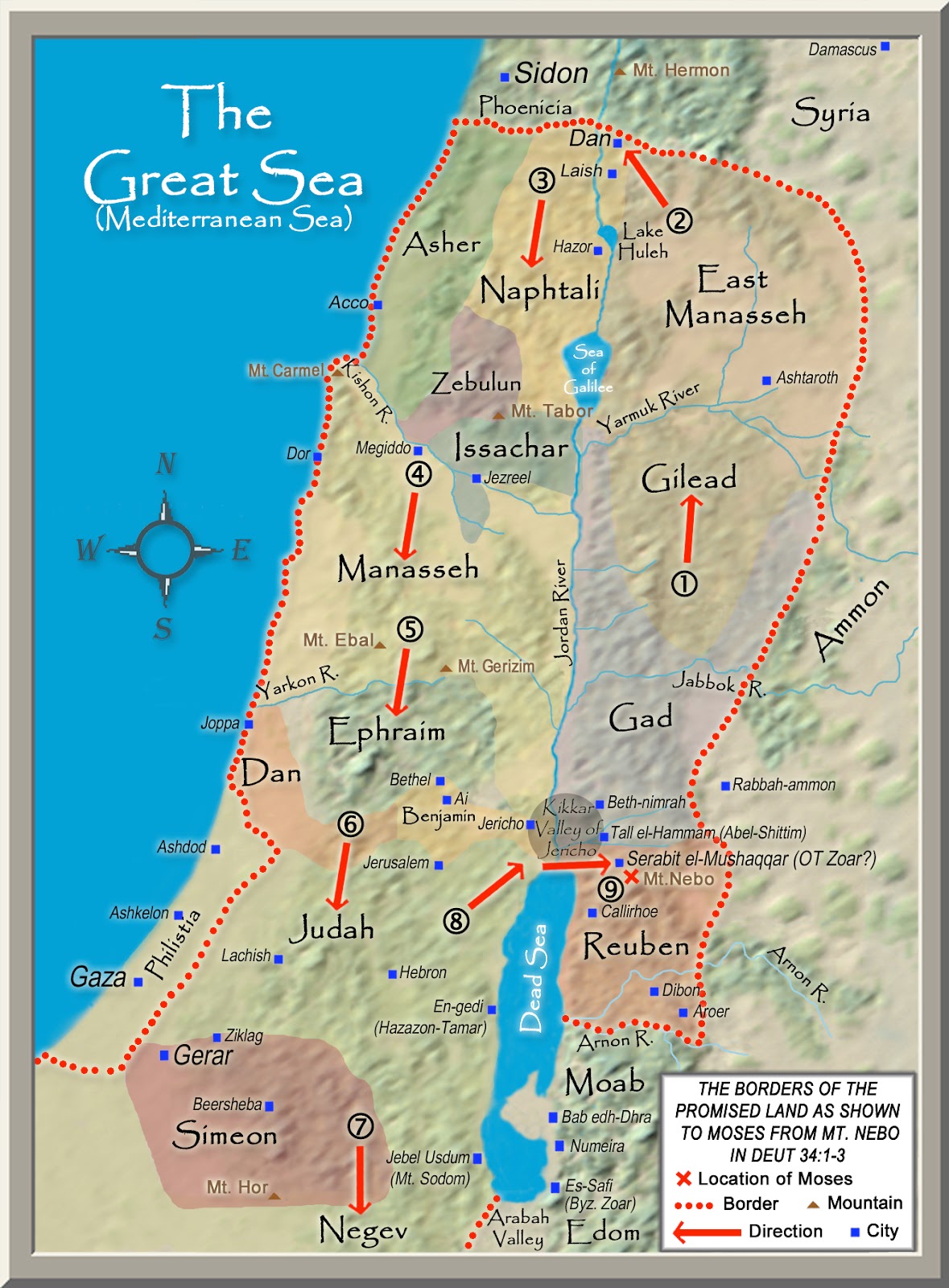
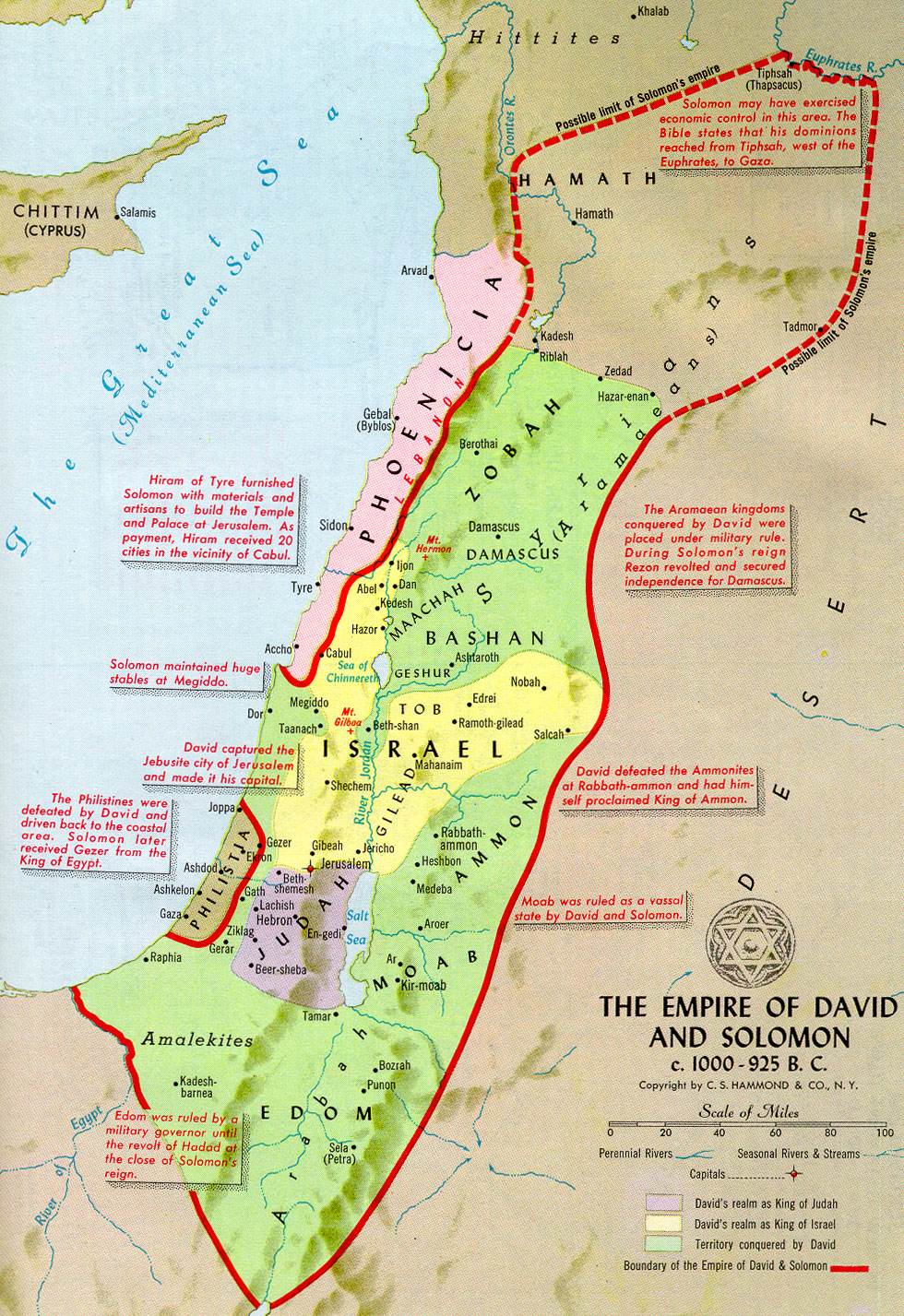
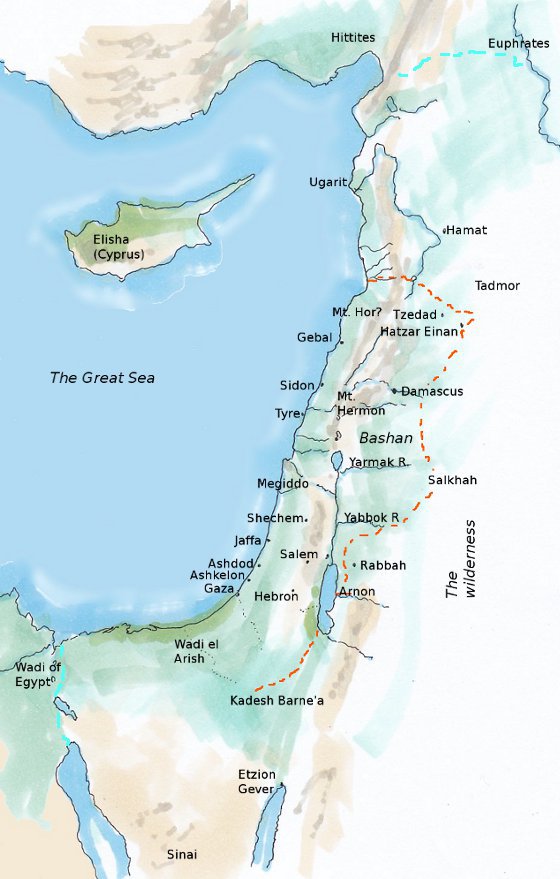
Biblical Maps: These maps, found in various Bible editions and online resources, provide a visual representation of the geographical features and locations mentioned in the Bible.
-
Historical Atlases: These atlases offer detailed maps of the ancient world, including ancient Israel, and provide historical context for the events described in the Bible.
-
Archaeological Evidence: Archaeological discoveries have shed light on the material culture, social practices, and religious beliefs of ancient Israel.
-
Scholarly Works: Numerous books and articles by biblical scholars and historians offer in-depth analyses of the history, geography, and culture of ancient Israel.
FAQs about Israel in Biblical Times
Q: What is the significance of Jerusalem in biblical times?
A: Jerusalem was a strategically important city, located at the crossroads of trade routes and natural defenses. It was also the religious center of the Israelites, housing the Temple of Solomon, a place of worship and pilgrimage.
Q: What were the major cities in ancient Israel?
A: Besides Jerusalem, other major cities included:
- Hebron: A significant city in the Judean Mountains, associated with the patriarchs Abraham, Isaac, and Jacob.
- Bethlehem: The birthplace of King David and Jesus Christ.
- Nazareth: The hometown of Jesus Christ.
- Jericho: An ancient city located near the Dead Sea, known for its strategic importance and its role in the Israelite conquest of Canaan.
Q: What were the main agricultural products in ancient Israel?
A: The fertile land of Israel supported a variety of agricultural products, including:
- Grains: Wheat, barley, and millet were staple crops.
- Fruits: Grapes, olives, figs, and pomegranates were common fruits.
- Livestock: Sheep, goats, cattle, and donkeys were raised for meat, milk, and transportation.
Q: What were the main religious practices in ancient Israel?
A: The Israelites practiced a monotheistic religion, worshipping the God of Israel. Their religious practices included:
- Temple worship: Offering sacrifices and prayers at the Temple in Jerusalem.
- Festivals: Observing religious holidays like Passover, Pentecost, and Sukkot.
- Observance of the Law: Following the commandments and laws given by God.
Tips for Understanding Israel in Biblical Times
- Visualize the landscape: Use maps and online resources to visualize the geography of ancient Israel and how it impacted the lives of its inhabitants.
- Consider the historical context: Understand the political, social, and religious context of the time period to gain a deeper understanding of biblical narratives.
- Engage with archaeological evidence: Explore archaeological discoveries to gain insights into the material culture and daily life of ancient Israel.
- Consult scholarly works: Read books and articles by biblical scholars and historians to gain a comprehensive perspective on the history, geography, and culture of ancient Israel.
Conclusion: A Legacy that Endures
The land of Israel, as depicted in the Bible, remains a source of fascination and inspiration for people around the world. Understanding its geography, its people, and its significance helps us to appreciate the rich tapestry of biblical narratives and the enduring legacy of faith, struggle, and triumph that continues to shape the world today. By navigating the landscape of ancient Israel, we can gain a deeper understanding of the human experience and the enduring power of faith.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Land of Promise: A Comprehensive Look at Israel in Biblical Times. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!