Navigating the Labyrinth of Headaches: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Managing Different Types
Related Articles: Navigating the Labyrinth of Headaches: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Managing Different Types
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Labyrinth of Headaches: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Managing Different Types. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Labyrinth of Headaches: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Managing Different Types
Headaches are a ubiquitous experience, affecting nearly everyone at some point in their lives. While most headaches are benign and resolve on their own, some can be debilitating and require medical attention. Understanding the different types of headaches is crucial for effective management and seeking appropriate treatment. This comprehensive guide provides a detailed overview of various headache types, their characteristics, causes, and potential treatments.
A Visual Map of Headache Types
Imagine a map with different regions representing distinct headache types. Each region has its unique topography, reflecting the characteristics and causes of the headache.
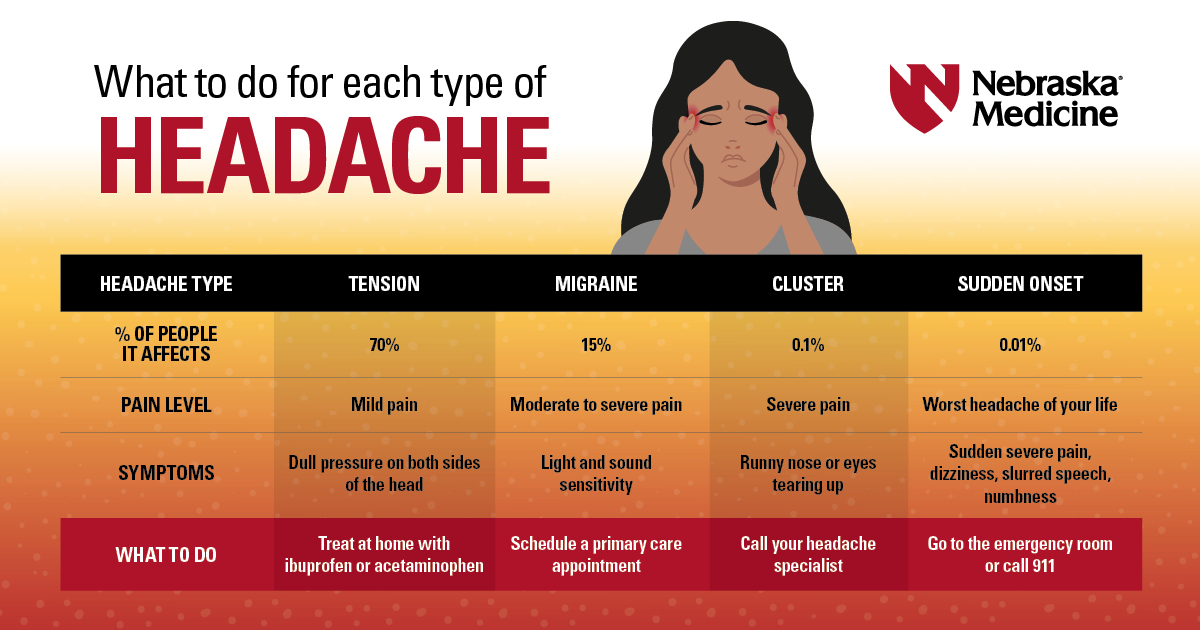
1. Primary Headaches
This region encompasses headaches that are not caused by an underlying medical condition. They are the most common type and include:
- Tension Headaches: These are the most frequent type, often described as a tight band or pressure around the head. They can be mild to moderate in intensity and typically last for 30 minutes to several hours.
- Migraines: Migraines are characterized by intense, throbbing pain, often on one side of the head. They can be accompanied by nausea, vomiting, and sensitivity to light and sound. Migraines can last for hours or even days.
- Cluster Headaches: Cluster headaches are severe, excruciating headaches that occur in clusters, meaning several headaches happen in a short period, followed by a period of remission. They are often described as a burning, piercing pain behind one eye.
2. Secondary Headaches
This region represents headaches that are caused by an underlying medical condition. These headaches can be a symptom of a more serious problem, such as:
- Sinus Headaches: These headaches are caused by inflammation or infection of the sinuses, often accompanied by facial pain and pressure.
- Cervicogenic Headaches: These headaches originate from the neck muscles and joints, often triggered by poor posture or muscle strain.
- Post-Traumatic Headaches: These headaches develop after a head injury, such as a concussion.
- Medication-Overuse Headaches: These headaches develop due to overuse of pain relievers, often leading to a vicious cycle of pain and medication reliance.
Understanding the Landscape: A Closer Look at Headache Types
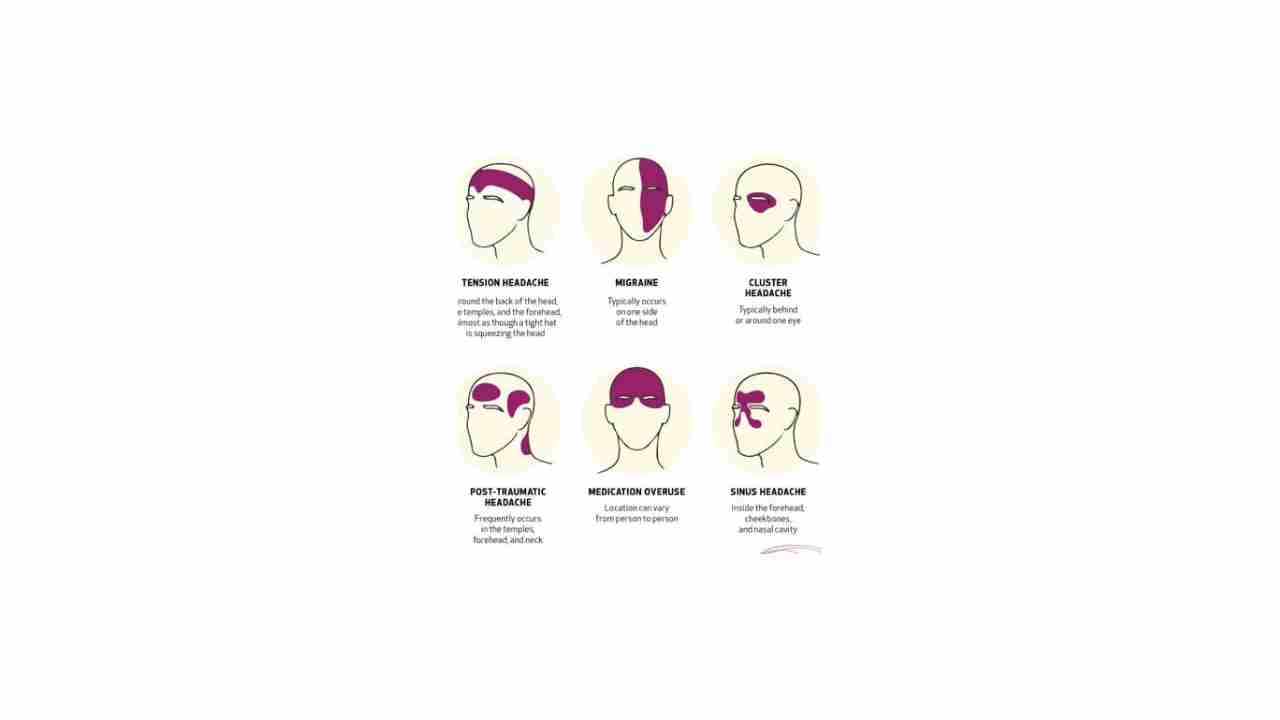
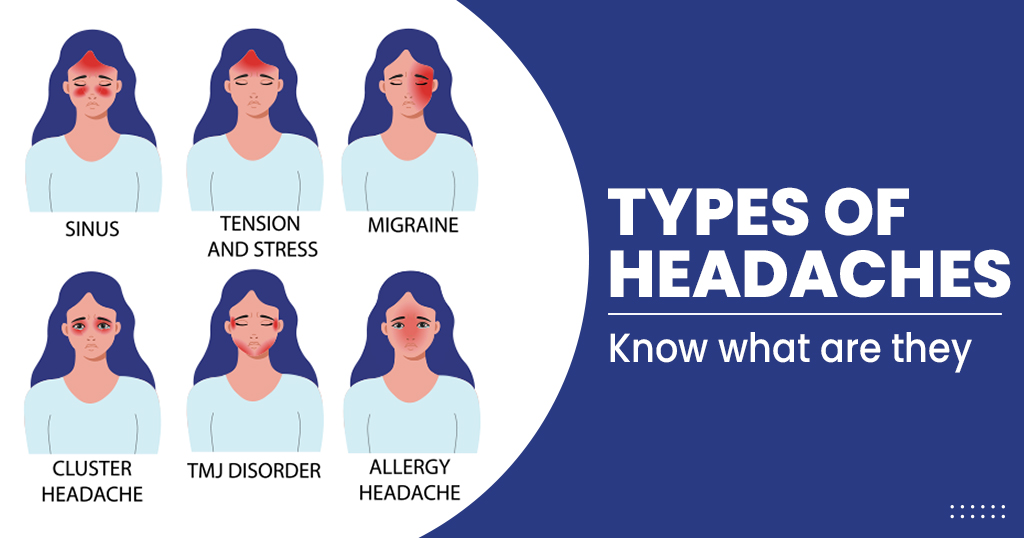
1. Tension Headaches
- Characteristics: A tight band or pressure around the head, often described as a feeling of tightness or squeezing.
- Causes: Stress, anxiety, muscle tension, poor posture, lack of sleep, dehydration, and caffeine withdrawal.
- Treatment: Over-the-counter pain relievers, relaxation techniques, massage therapy, and stress management strategies.
2. Migraines
- Characteristics: Intense, throbbing pain, often on one side of the head, accompanied by nausea, vomiting, and sensitivity to light and sound.
- Causes: Hormonal fluctuations, stress, food triggers, lack of sleep, and environmental factors.
- Treatment: Triptans (medications specifically designed for migraines), over-the-counter pain relievers, anti-nausea medications, and preventive medications.
3. Cluster Headaches
- Characteristics: Severe, excruciating headaches that occur in clusters, with multiple headaches happening in a short period, followed by a period of remission.
- Causes: The exact cause is unknown, but genetics, environmental factors, and changes in brain chemistry are suspected.
- Treatment: Triptans, oxygen therapy, and preventive medications.
4. Sinus Headaches
- Characteristics: Pain and pressure in the forehead, cheeks, and around the eyes, often accompanied by nasal congestion and discharge.
- Causes: Inflammation or infection of the sinuses, often due to allergies, colds, or sinusitis.
- Treatment: Decongestants, nasal sprays, antibiotics (if bacterial infection is present), and pain relievers.
5. Cervicogenic Headaches
- Characteristics: Pain in the back of the head, neck, and shoulders, often accompanied by stiffness and limited neck movement.
- Causes: Muscle strain, poor posture, whiplash, and neck injuries.
- Treatment: Physical therapy, massage therapy, pain relievers, and neck exercises.
6. Post-Traumatic Headaches
- Characteristics: Headaches that develop after a head injury, often characterized by throbbing pain, dizziness, and sensitivity to light and sound.
- Causes: Traumatic brain injury, concussion, and whiplash.
- Treatment: Pain relievers, physical therapy, cognitive behavioral therapy, and stress management techniques.
7. Medication-Overuse Headaches
- Characteristics: Headaches that occur more frequently and become more severe due to overuse of pain relievers.
- Causes: Frequent use of over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen, aspirin, and acetaminophen.
- Treatment: Gradual withdrawal from pain relievers under medical supervision, alternative pain management strategies, and lifestyle modifications.
Navigating the Headache Landscape: FAQs
1. When should I see a doctor for a headache?
- If headaches are severe, persistent, or accompanied by other symptoms, such as fever, stiff neck, vision changes, weakness, or numbness, it is crucial to seek medical attention promptly.
- If headaches are interfering with daily activities or causing significant distress, it is also advisable to consult a healthcare professional.
2. How can I prevent headaches?
- Lifestyle modifications: Maintaining a regular sleep schedule, managing stress, staying hydrated, eating a balanced diet, and engaging in regular exercise can help prevent headaches.
- Avoiding triggers: Identifying and avoiding triggers, such as certain foods, drinks, or environmental factors, can also be beneficial.
- Preventive medications: In some cases, preventive medications may be prescribed by a doctor to reduce the frequency and severity of headaches.
3. What are the potential complications of headaches?
- While most headaches are benign, some can be associated with serious underlying conditions, such as brain tumors, meningitis, or stroke.
- It is crucial to seek medical attention if headaches are accompanied by alarming symptoms, such as fever, stiff neck, vision changes, weakness, or numbness.
4. Are there any home remedies for headaches?
- Relaxation techniques: Techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, and yoga can help reduce stress and muscle tension, which can contribute to headaches.
- Cold or hot compress: Applying a cold or hot compress to the forehead or neck can provide temporary relief from headache pain.
- Hydration: Dehydration can trigger headaches, so staying hydrated is important.
5. What are the latest advancements in headache treatment?
- Neuromodulation therapies: Non-invasive treatments, such as transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) and vagus nerve stimulation (VNS), are showing promise in treating chronic migraines.
- Biofeedback therapy: This technique teaches patients to control their physiological responses, such as heart rate and muscle tension, which can help reduce headache frequency.
- Personalized medicine: Tailoring treatment plans based on individual patient characteristics and triggers is becoming increasingly important in headache management.
Tips for Managing Headaches
- Keep a headache diary: Record the frequency, duration, intensity, and associated symptoms of headaches to help identify triggers and patterns.
- Practice relaxation techniques: Techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, and yoga can help reduce stress and muscle tension.
- Get enough sleep: Aim for 7-8 hours of quality sleep each night.
- Stay hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day.
- Eat a balanced diet: Avoid skipping meals and consuming processed foods.
- Avoid caffeine and alcohol: These substances can trigger headaches.
- Exercise regularly: Physical activity can help reduce stress and improve overall health.
Conclusion
Understanding the different types of headaches and their characteristics is essential for effective management and seeking appropriate treatment. While most headaches are benign and resolve on their own, some can be debilitating and require medical attention. By recognizing the signs and symptoms of different headache types, individuals can make informed decisions about seeking medical advice and exploring available treatment options. Implementing lifestyle modifications, practicing relaxation techniques, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle can play a significant role in preventing and managing headaches, ultimately improving overall well-being.




.jpg)

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Labyrinth of Headaches: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Managing Different Types. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!