Mapping the Landscape of Mathematics: A Comprehensive Exploration
Related Articles: Mapping the Landscape of Mathematics: A Comprehensive Exploration
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Mapping the Landscape of Mathematics: A Comprehensive Exploration. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Mapping the Landscape of Mathematics: A Comprehensive Exploration

Mathematics, a fundamental pillar of human knowledge, transcends the boundaries of disciplines, permeating every aspect of our lives. From the intricate patterns in nature to the complex algorithms powering our digital world, mathematics underpins our understanding and shapes our reality.
The Importance of Mapping Mathematics
Visualizing mathematical concepts is crucial for fostering deeper comprehension and unlocking new avenues of exploration. Mapping mathematics, in its various forms, serves as a powerful tool for:
- Conceptualization: By representing abstract mathematical ideas visually, maps facilitate understanding and promote intuitive reasoning. They transform complex equations and theorems into tangible representations, making them more accessible to diverse learners.
- Exploration: Maps provide a framework for exploring relationships between different mathematical concepts. They allow us to identify patterns, discover connections, and uncover hidden insights that might otherwise remain obscured.
- Communication: Maps serve as a common language for communicating mathematical ideas. They enable effective collaboration, fostering dialogue and knowledge sharing amongst mathematicians, researchers, and educators.
- Application: Maps find practical applications in various fields, including data analysis, computer science, engineering, and even art. They provide visual tools for interpreting data, modeling systems, and solving problems.
Types of Mathematical Maps
The world of mathematical maps is diverse, encompassing a wide range of approaches and applications. Here are some notable examples:
1. Number Line Maps:
- Description: These maps represent the real number system as a continuous line, with points corresponding to specific numbers. They are fundamental tools for visualizing basic arithmetic operations, inequalities, and intervals.
- Applications: Number line maps are widely used in elementary and secondary education to introduce students to fundamental mathematical concepts. They also find applications in advanced mathematics, such as real analysis and topology.
2. Coordinate Plane Maps:
- Description: These maps use two perpendicular axes (x and y) to represent points in two-dimensional space. Each point is defined by its coordinates, providing a visual representation of relationships between variables.
- Applications: Coordinate plane maps are essential for understanding functions, graphs, and geometric shapes. They are also used in various applications, including physics, engineering, and computer graphics.
3. Venn Diagrams:
- Description: These diagrams use overlapping circles to represent sets and their relationships. They are particularly useful for visualizing set operations, such as union, intersection, and complement.
- Applications: Venn diagrams are widely used in logic, probability, and statistics to illustrate relationships between different sets of data. They are also helpful in teaching basic set theory concepts.
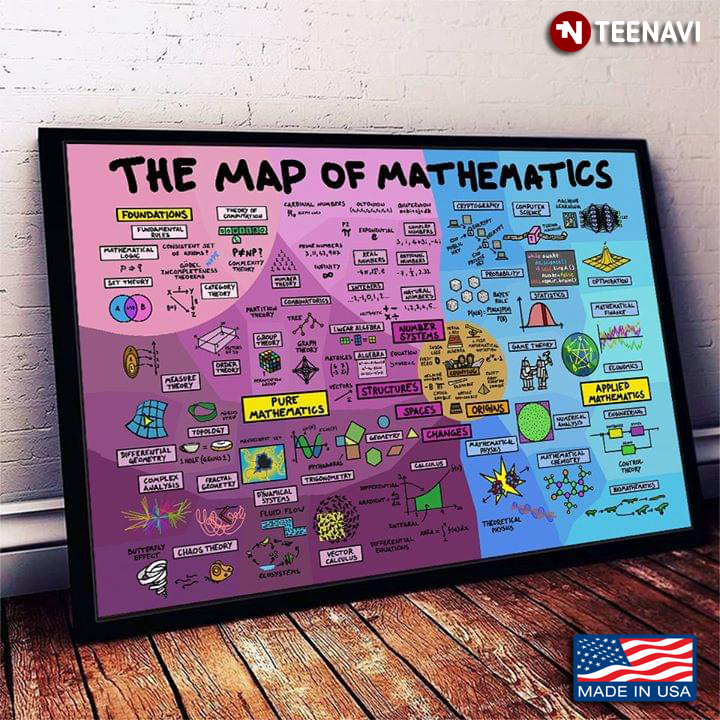
4. Concept Maps:
- Description: These maps use nodes and connecting lines to represent concepts and their relationships. They are particularly useful for visualizing complex ideas and organizing information.
- Applications: Concept maps are used in education, research, and knowledge management to facilitate understanding, recall, and knowledge transfer. They are also helpful for brainstorming and problem-solving.
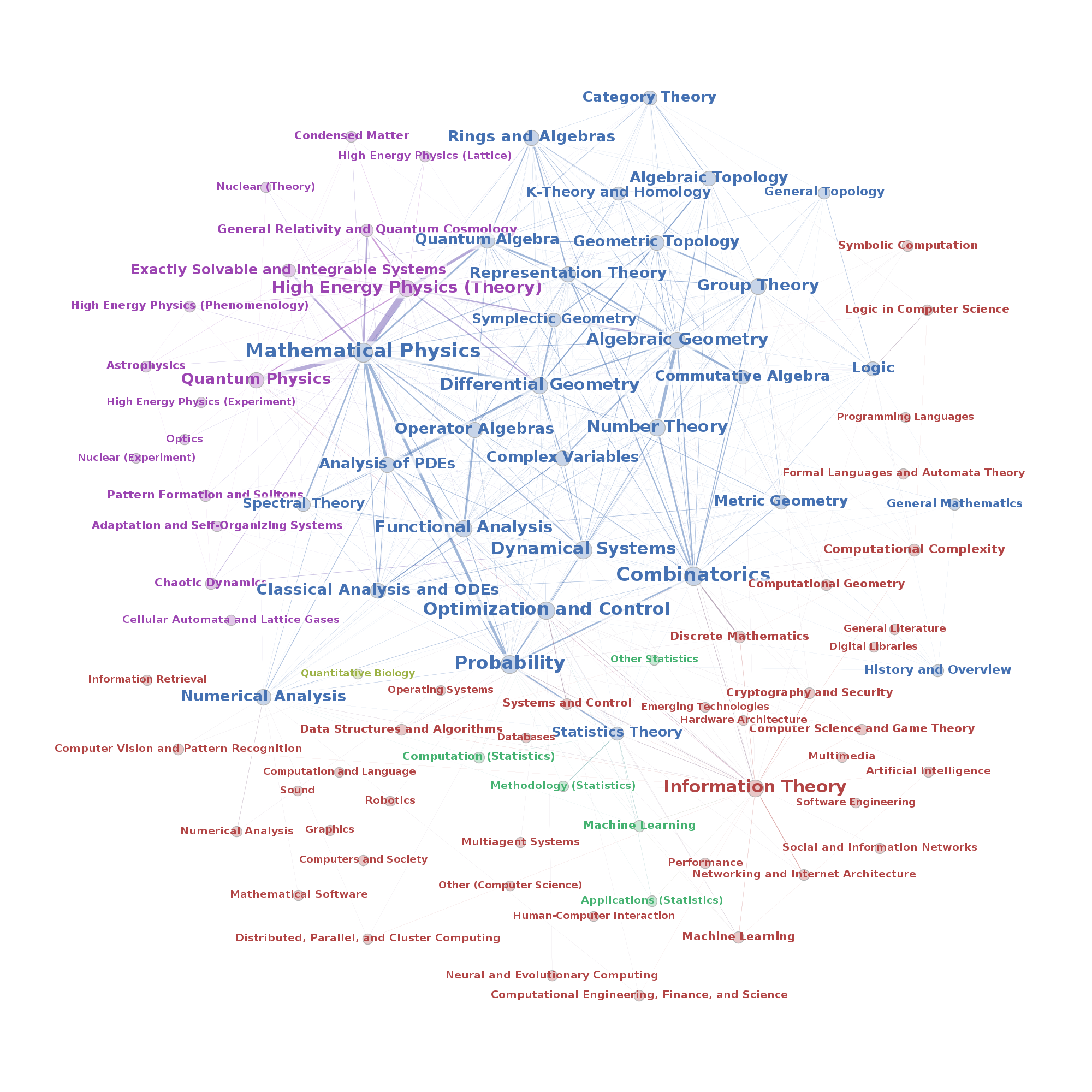
5. Network Maps:
- Description: These maps represent relationships between objects as a network of interconnected nodes. They are particularly useful for visualizing data with complex relationships, such as social networks, transportation systems, and communication networks.
- Applications: Network maps are used in various fields, including social science, computer science, and engineering, to analyze data, model systems, and understand complex interactions.
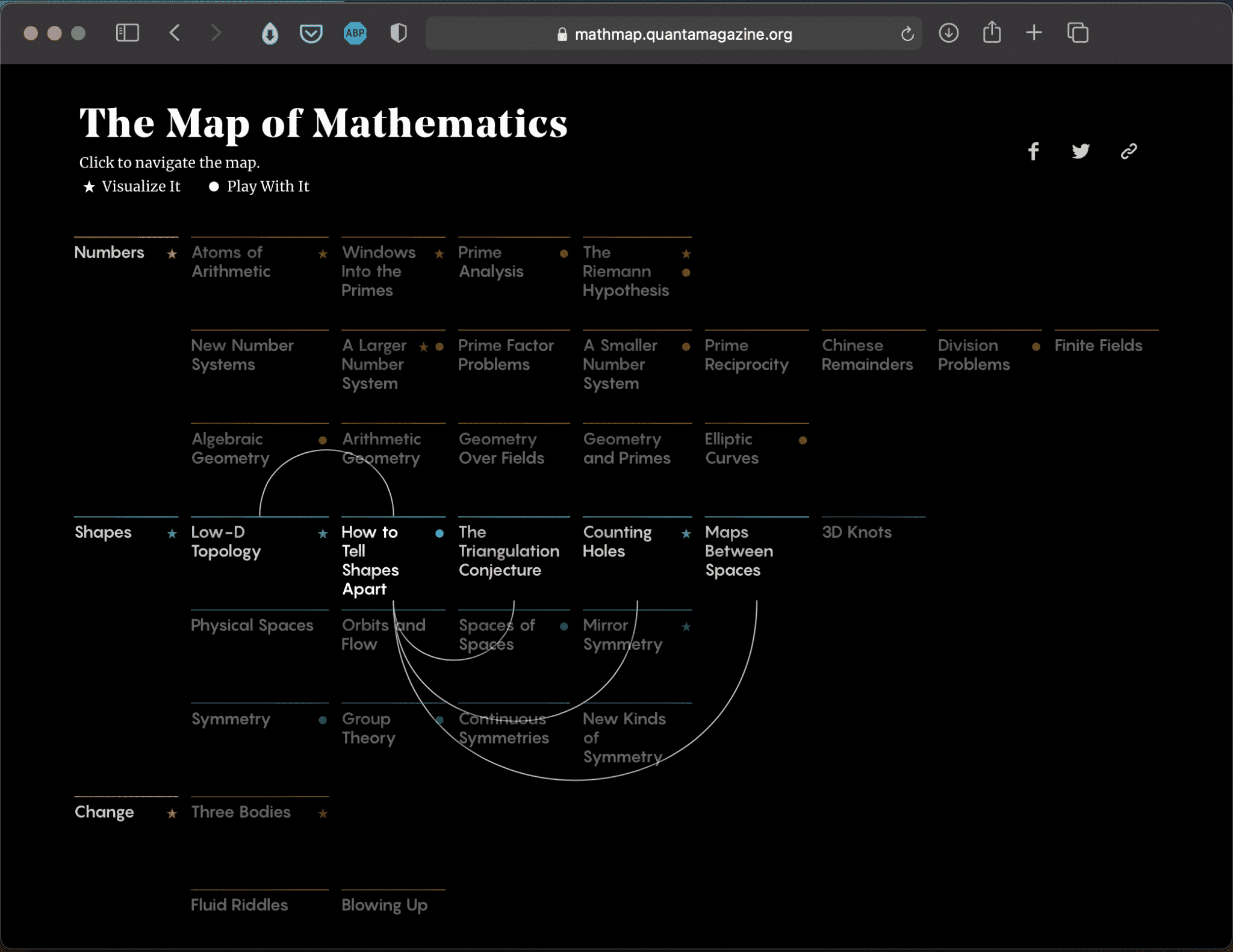
6. Topological Maps:
- Description: These maps focus on the shape and connectivity of objects, disregarding distances and angles. They are particularly useful for studying properties that remain invariant under continuous transformations.
- Applications: Topological maps are used in various fields, including topology, geometry, and knot theory, to study the underlying structure of objects and spaces.
7. Data Visualization Maps:
- Description: These maps use visual elements, such as colors, shapes, and sizes, to represent data. They are particularly useful for communicating complex data patterns and trends to a wider audience.
- Applications: Data visualization maps are widely used in data analysis, business intelligence, and scientific research to present insights and communicate findings effectively.
FAQs on Mathematical Maps
1. What are the benefits of using mathematical maps?
Mathematical maps offer numerous benefits, including:
- Enhanced comprehension of abstract concepts.
- Improved problem-solving skills.
- Fostered collaboration and knowledge sharing.
- Facilitated communication of complex ideas.
- Increased engagement and motivation in learning mathematics.
2. Are mathematical maps only used in academia?
While mathematical maps are extensively used in academia, they find practical applications in various fields, including:
- Data analysis and visualization.
- Computer science and software development.
- Engineering and design.
- Business and finance.
- Art and design.
3. How can I create my own mathematical maps?
There are various tools and resources available for creating mathematical maps, including:
- Software: Programs like GeoGebra, Desmos, and Wolfram Alpha offer interactive tools for creating various types of mathematical maps.
- Drawing tools: Traditional drawing tools, such as pencils, pens, and rulers, can be used to create simple maps by hand.
- Online resources: Numerous websites and online platforms offer templates and tutorials for creating different types of mathematical maps.
Tips for Creating Effective Mathematical Maps
- Choose the appropriate type of map: Consider the specific concept or data you want to represent and select the most suitable type of map for your purpose.
- Keep it simple and clear: Aim for clarity and avoid unnecessary complexity. Use visual elements effectively to convey information without overwhelming the viewer.
- Label elements clearly: Ensure all elements are labeled appropriately, providing context and understanding for the viewer.
- Use color and contrast effectively: Use colors and contrasts to highlight important elements and guide the viewer’s attention.
- Test and refine your map: Iterate and refine your map based on feedback and testing to ensure it effectively communicates the intended message.
Conclusion
Mapping mathematics is a powerful tool for understanding, exploring, and communicating complex concepts. By visualizing abstract ideas, maps bridge the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical application, fostering deeper comprehension and unlocking new avenues of exploration. As we continue to delve deeper into the world of mathematics, the role of mapping will only grow more significant, offering a visual language for navigating the intricate landscape of mathematical knowledge.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Mapping the Landscape of Mathematics: A Comprehensive Exploration. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!