Fukushima: A Region of Resilience and Transformation
Related Articles: Fukushima: A Region of Resilience and Transformation
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Fukushima: A Region of Resilience and Transformation. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Fukushima: A Region of Resilience and Transformation

Fukushima, a prefecture located in the northeastern region of Japan, holds a complex and multifaceted history. While the 2011 earthquake and tsunami, and the subsequent nuclear disaster, have etched a lasting mark on the region, Fukushima also possesses a rich cultural heritage, diverse landscapes, and a strong spirit of resilience. Understanding the geographical context of Fukushima is crucial to appreciating its past, present, and future.
Geographical Context:
Fukushima Prefecture encompasses a diverse range of landscapes, from the rugged mountains of the Abukuma Mountains in the west to the fertile plains of the Abukuma River in the east. The prefecture is bordered by the Pacific Ocean to the east, and the Tohoku region to the north.
Key Geographical Features:
- Mount Bandai: A prominent stratovolcano located in the west of the prefecture, Mount Bandai is known for its dramatic landscape and history of volcanic activity.
- Lake Inawashiro: The largest lake in Fukushima, Lake Inawashiro is a popular destination for recreation and tourism.
- Abukuma River: The longest river in Fukushima, the Abukuma River flows through the prefecture from west to east, providing fertile land for agriculture and supporting diverse ecosystems.
- Coastline: Fukushima boasts a coastline along the Pacific Ocean, offering access to the Sea of Japan and providing opportunities for fishing and tourism.
Historical Significance:
Fukushima’s history is intertwined with its geographical features. The fertile plains of the Abukuma River have supported agriculture for centuries, making the region a center of rice production. The rugged mountainous terrain provided a natural barrier against invaders, contributing to the region’s unique cultural identity.
The 2011 Disaster and its Aftermath:
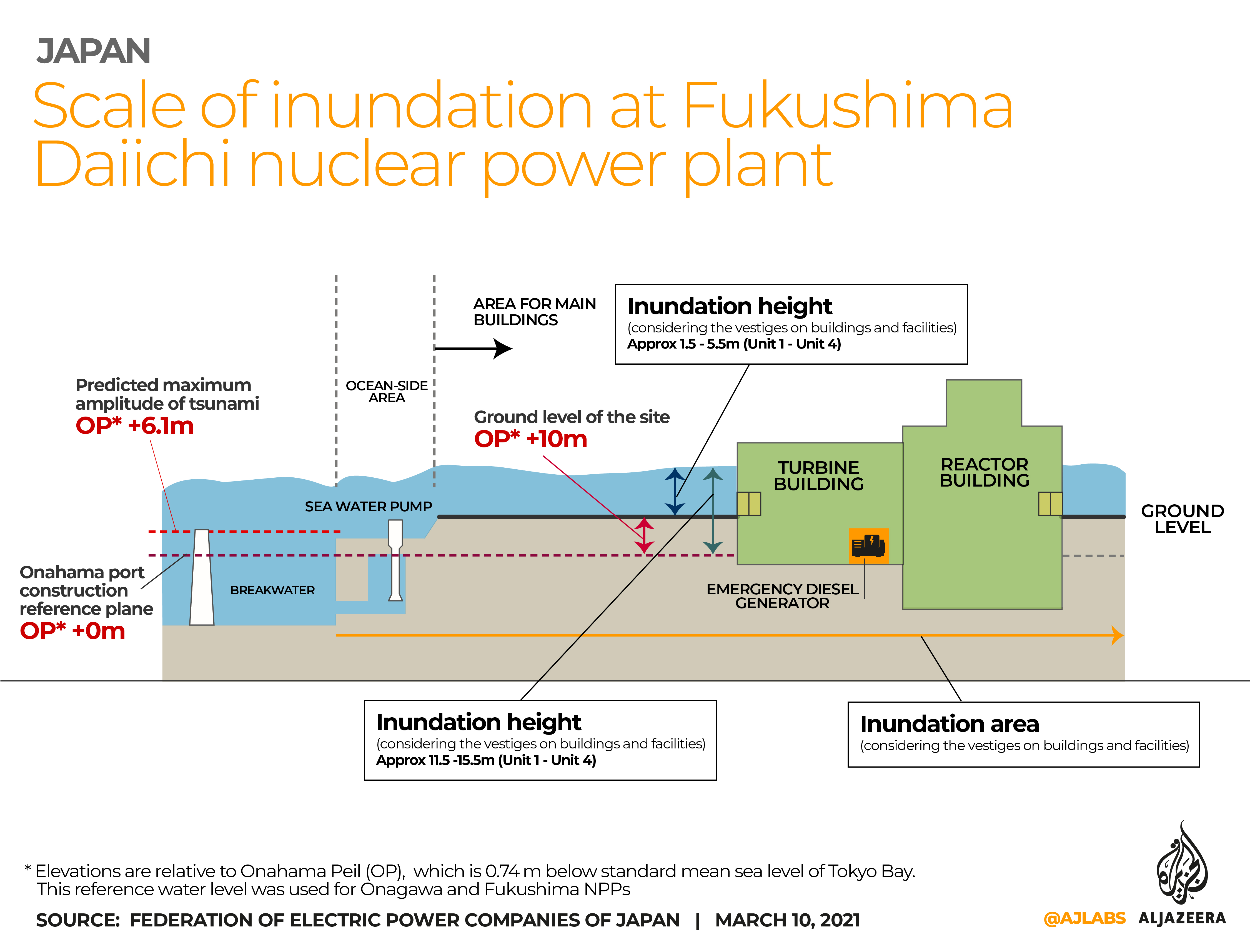
The 2011 Tohoku earthquake and tsunami devastated Fukushima, causing widespread damage and leading to the nuclear disaster at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant. The disaster had a profound impact on the region, forcing evacuations, disrupting livelihoods, and leaving a lasting mark on the landscape.
Post-Disaster Recovery and Transformation:
Despite the immense challenges, Fukushima has demonstrated remarkable resilience. The prefecture has embarked on a path of reconstruction, focusing on revitalizing infrastructure, supporting local businesses, and addressing the long-term health and environmental consequences of the disaster.
Tourism and Cultural Attractions:
Beyond the tragic events, Fukushima offers a wealth of cultural attractions and natural beauty. Visitors can explore historical sites like the Aizu Domain, immerse themselves in traditional crafts like Aizu lacquerware, or enjoy the scenic beauty of Lake Inawashiro and Mount Bandai.
Economic Development and Innovation:
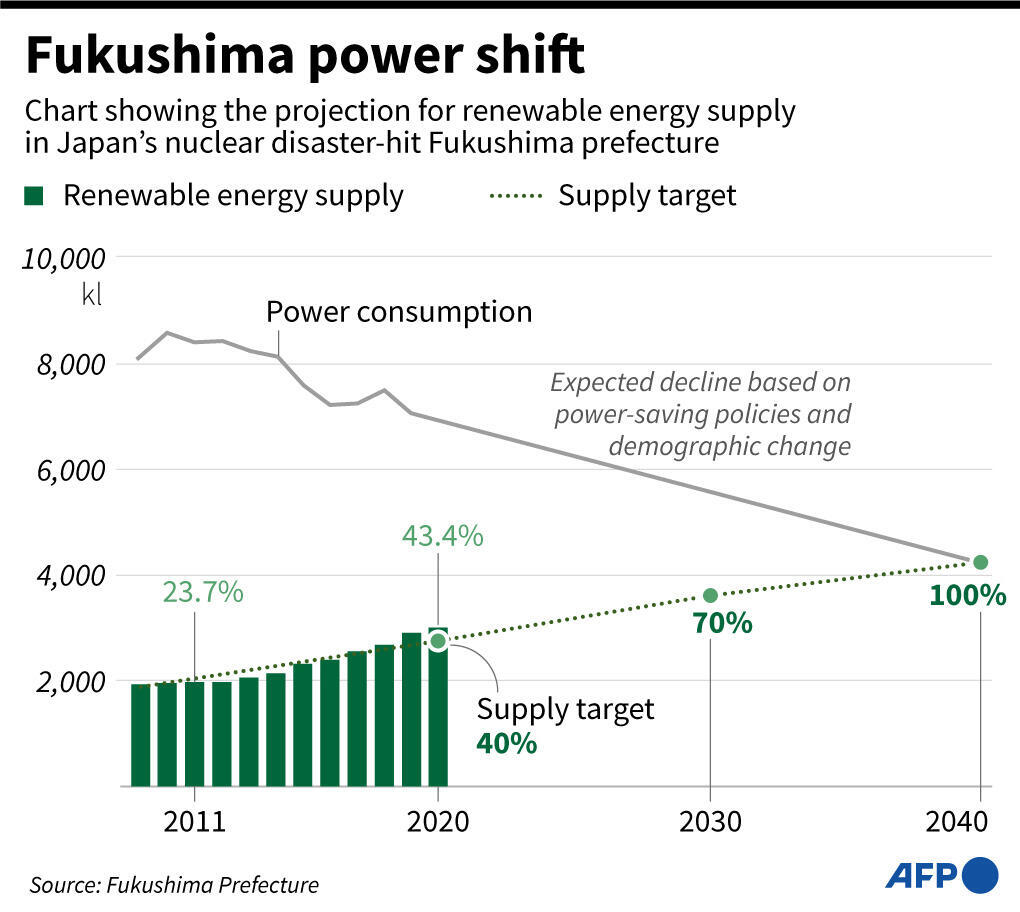
Fukushima is actively pursuing sustainable economic development, leveraging its natural resources, agricultural potential, and technological expertise. The prefecture is focusing on renewable energy, sustainable tourism, and agricultural innovation.
Understanding Fukushima’s Geography:
By understanding Fukushima’s geographical context, we can gain a deeper appreciation for its history, the challenges it has faced, and the remarkable resilience it has shown. The region’s diverse landscapes, cultural heritage, and ongoing recovery efforts paint a complex and compelling picture of a prefecture grappling with the past while building a brighter future.
FAQs about Fukushima:
Q: What is the capital of Fukushima Prefecture?
A: The capital of Fukushima Prefecture is Fukushima City, located in the central part of the prefecture.
Q: What is the population of Fukushima Prefecture?
A: As of 2023, the population of Fukushima Prefecture is estimated to be around 1.8 million.
Q: What is the main industry in Fukushima Prefecture?
A: Agriculture is a significant industry in Fukushima, with rice production being a major focus. Other industries include manufacturing, tourism, and renewable energy.
Q: What are some popular tourist destinations in Fukushima?
A: Popular tourist destinations in Fukushima include Mount Bandai, Lake Inawashiro, the Aizu Domain, and the Fukushima Prefectural Museum of Art.
Q: What are the major environmental concerns in Fukushima?
A: The major environmental concerns in Fukushima include the long-term health and environmental consequences of the 2011 nuclear disaster, including radiation levels and the management of contaminated water.
Q: What are the challenges facing Fukushima in its recovery efforts?
A: The challenges facing Fukushima in its recovery efforts include the long-term health and environmental consequences of the nuclear disaster, the need to revitalize the economy, and the ongoing psychological impact of the disaster on residents.
Tips for Visiting Fukushima:
- Research the area: Before visiting, learn about the history, culture, and attractions of Fukushima.
- Be respectful: Be mindful of the cultural sensitivities of the region, especially in light of the 2011 disaster.
- Consider visiting rural areas: Explore the diverse landscapes and local communities outside of major cities.
- Learn about the recovery efforts: Engage with local initiatives and organizations working on the recovery and transformation of Fukushima.
- Support local businesses: Patronize local businesses and contribute to the economic revitalization of the region.
Conclusion:
Fukushima is a region of resilience and transformation. While the 2011 disaster left a lasting impact, the prefecture is actively working towards a sustainable future. By understanding its geography, history, and ongoing recovery efforts, we can appreciate the complex and compelling story of a region that continues to rise from adversity. The spirit of Fukushima serves as an inspiration to all, demonstrating the power of human resilience and the unwavering determination to build a brighter future.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Fukushima: A Region of Resilience and Transformation. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!