A Comprehensive Guide to the Geography of North Carolina
Related Articles: A Comprehensive Guide to the Geography of North Carolina
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to A Comprehensive Guide to the Geography of North Carolina. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Comprehensive Guide to the Geography of North Carolina
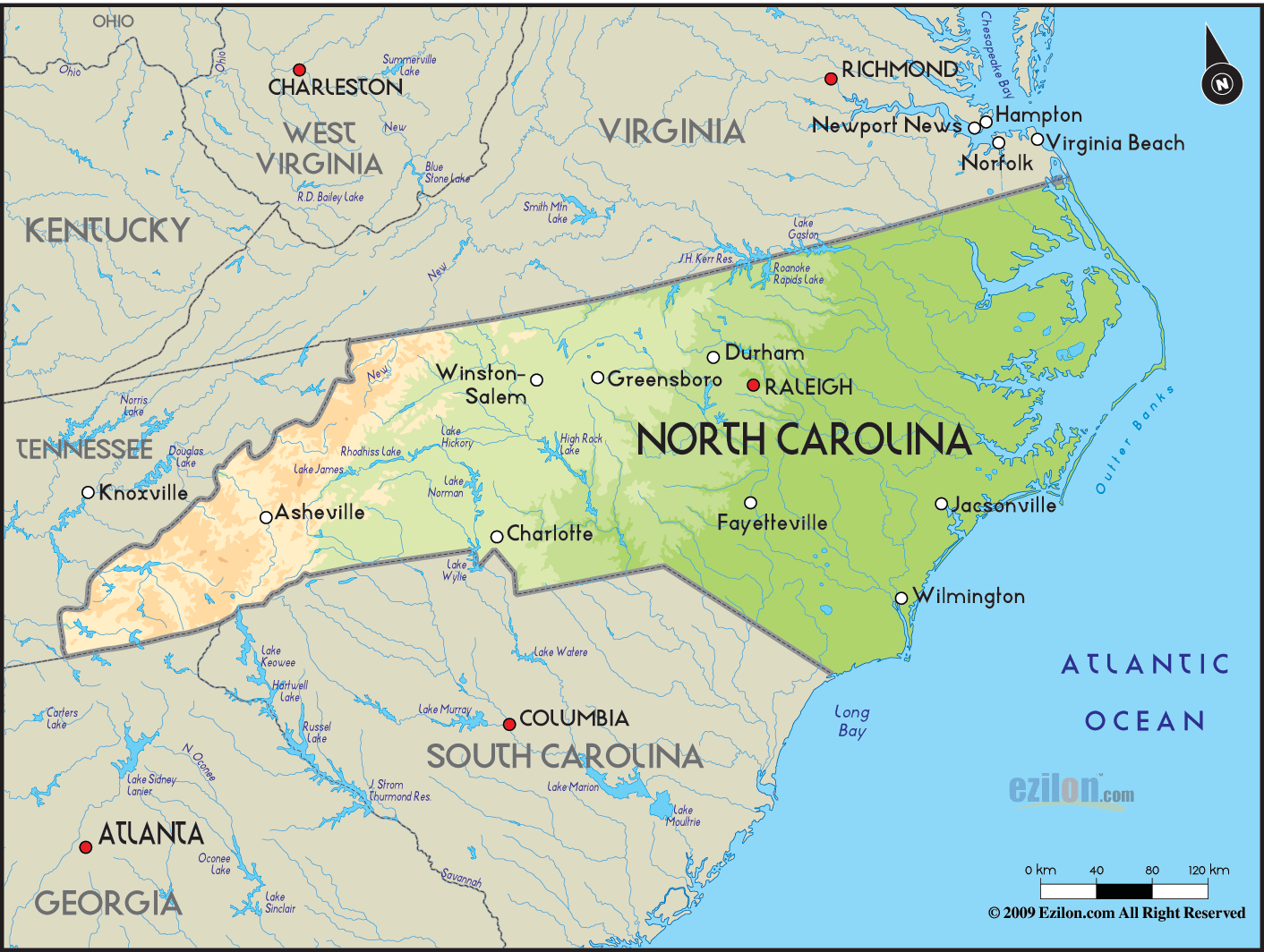
North Carolina, the Tar Heel State, is a captivating tapestry of diverse landscapes, boasting a rich history and vibrant culture. Understanding its geographical makeup is crucial for appreciating its unique character, its economic drivers, and its environmental challenges. This guide delves into the intricacies of North Carolina’s geography, providing a comprehensive overview of its physical features, climate, and ecological significance.
A Land of Diverse Terrain
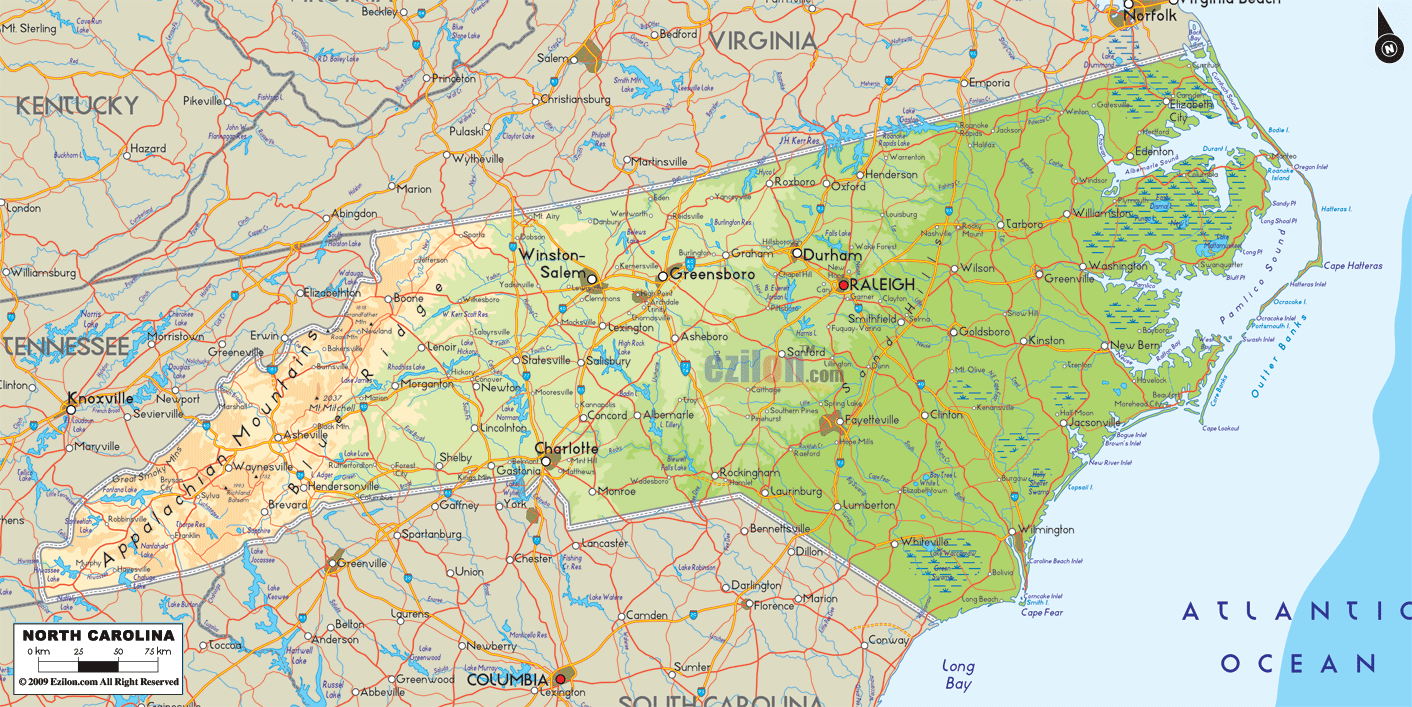
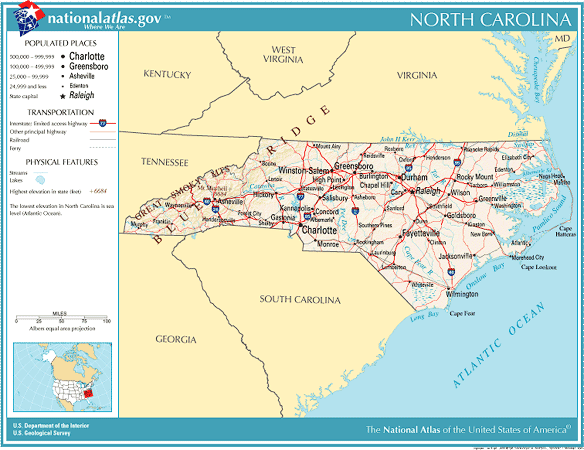
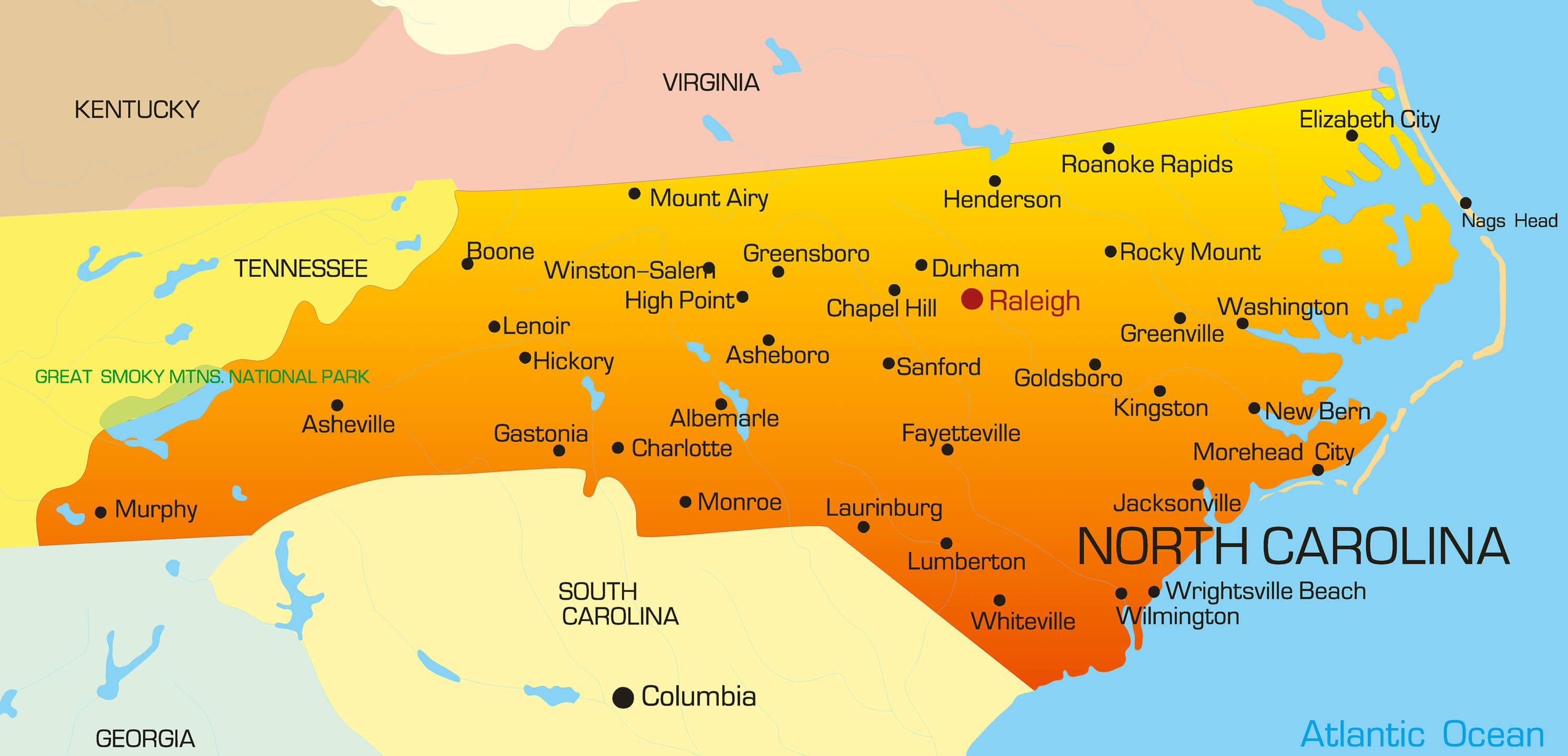
North Carolina’s geography is characterized by a remarkable variety of terrain, ranging from the majestic Appalachian Mountains in the west to the expansive coastal plains in the east.
The Appalachian Mountains:
- Blue Ridge Mountains: The Blue Ridge Mountains, a subrange of the Appalachians, dominate the western portion of the state. They are known for their stunning scenery, with peaks reaching elevations exceeding 6,000 feet. Mount Mitchell, the highest point east of the Mississippi River, stands proudly in the Blue Ridge.
- Piedmont Plateau: Transitioning eastward from the mountains lies the Piedmont Plateau, a rolling, gently sloping region with fertile soils and abundant forests. This region is home to major cities like Charlotte, Greensboro, and Raleigh.
Coastal Plains:
- Outer Banks: The Outer Banks, a chain of barrier islands along the Atlantic coast, are renowned for their pristine beaches, lighthouses, and rich maritime history. These islands provide vital protection for the mainland from storm surges and erosion.
- Coastal Plain: The Coastal Plain stretches inland from the Outer Banks, encompassing a broad expanse of low-lying land. This region is characterized by its flat topography, fertile soils, and extensive agricultural lands.
Waterways and Wetlands:
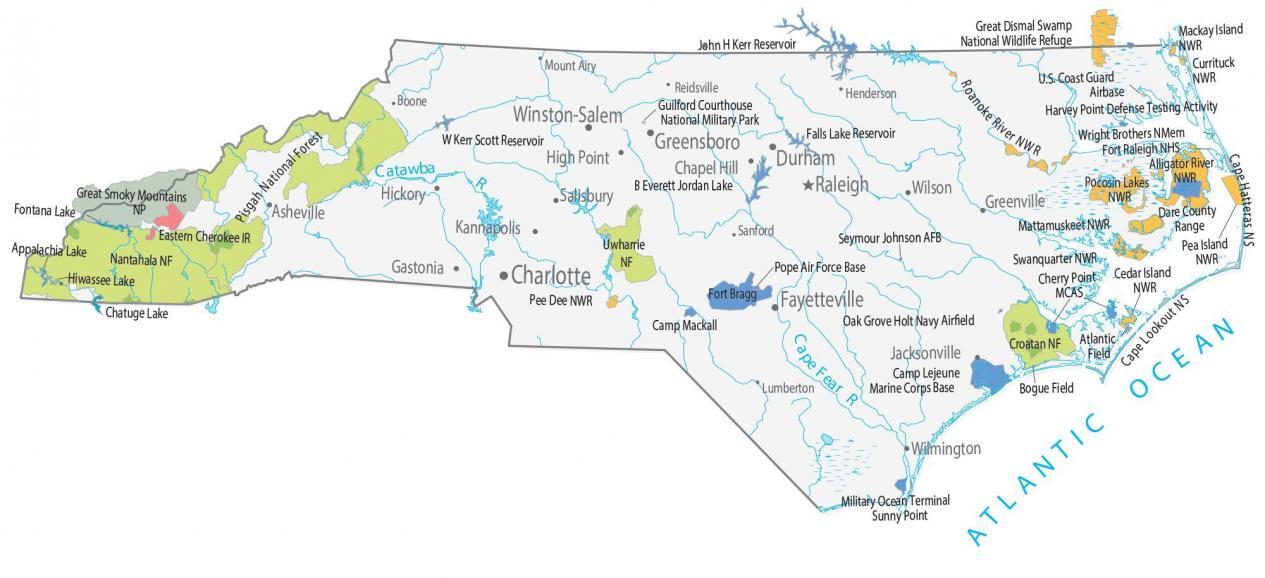
- Rivers and Lakes: North Carolina is crisscrossed by numerous rivers, including the Roanoke, Cape Fear, and Neuse, which flow eastward towards the Atlantic Ocean. The state also boasts numerous lakes, including Lake Norman, the largest man-made lake in the eastern United States.
- Wetlands: North Carolina’s coastal region is home to extensive wetlands, including swamps, marshes, and bogs. These ecosystems play a vital role in water filtration, flood control, and providing habitat for a diverse array of wildlife.
Climate Variations:
North Carolina’s diverse geography results in a range of climatic conditions.
- Mountain Climate: The mountains experience a cooler, wetter climate with distinct seasons. Winter brings snow and freezing temperatures, while summers are relatively mild.
- Piedmont Climate: The Piedmont enjoys a more moderate climate with warm, humid summers and mild winters.
- Coastal Climate: The coastal region experiences a subtropical climate with hot, humid summers and mild winters. Hurricanes are a significant threat to coastal areas.
Ecological Significance:
North Carolina’s diverse geography and climate support a rich and varied ecosystem.
- Forests: Forests cover approximately 50% of the state, providing essential habitat for a wide range of plant and animal species. The state is home to numerous tree species, including pines, oaks, and maples.
- Wildlife: North Carolina is home to a diverse array of wildlife, including black bears, deer, bobcats, and numerous bird species. The state’s coastal waters are rich in marine life, including dolphins, whales, and sea turtles.
- Biodiversity: The state’s varied landscapes and ecosystems contribute to its high level of biodiversity. North Carolina is home to numerous rare and endangered species.
Economic Importance:
North Carolina’s geography plays a significant role in its economic development.
- Agriculture: The state’s fertile soils and favorable climate support a thriving agricultural industry, with major crops including tobacco, cotton, soybeans, and corn.
- Tourism: North Carolina’s stunning natural beauty attracts millions of tourists each year. The state’s mountains, beaches, and historical sites are major tourism destinations.
- Industry: The state’s diverse geography has fostered the growth of a variety of industries, including manufacturing, technology, and finance.
Environmental Challenges:
While North Carolina boasts a rich and diverse natural environment, it also faces significant environmental challenges.
- Climate Change: Climate change is a major concern for North Carolina, with rising sea levels, more frequent and intense storms, and changes in precipitation patterns posing significant threats to coastal communities and ecosystems.
- Pollution: Pollution from industrial activities, agriculture, and urban runoff is a major environmental concern, impacting water quality and air quality.
- Deforestation: Deforestation is a threat to North Carolina’s forests, leading to habitat loss, soil erosion, and reduced water quality.
Understanding North Carolina’s Geography: A Key to Informed Decisions
A deep understanding of North Carolina’s geography is essential for navigating the state’s environmental challenges, promoting sustainable development, and making informed decisions about its future.
FAQs about North Carolina’s Geography:
1. What is the highest point in North Carolina?
Mount Mitchell, located in the Blue Ridge Mountains, is the highest point east of the Mississippi River, reaching an elevation of 6,684 feet.
2. What are the major rivers in North Carolina?
North Carolina is home to numerous rivers, including the Roanoke, Cape Fear, and Neuse, which flow eastward towards the Atlantic Ocean.
3. What are the major cities in North Carolina?
Major cities in North Carolina include Charlotte, Raleigh, Greensboro, Durham, Winston-Salem, and Asheville.
4. What is the climate like in North Carolina?
North Carolina’s climate varies depending on the region, ranging from a cooler, wetter mountain climate to a subtropical coastal climate.
5. What are some of the environmental challenges facing North Carolina?
North Carolina faces environmental challenges such as climate change, pollution, and deforestation.
Tips for Exploring North Carolina’s Geography:
- Visit State Parks: North Carolina boasts a network of state parks that offer opportunities to explore diverse landscapes, from mountains to beaches.
- Hike the Appalachian Trail: The Appalachian Trail traverses the Blue Ridge Mountains, offering stunning views and challenging hikes.
- Explore the Outer Banks: The Outer Banks offer pristine beaches, lighthouses, and a rich maritime history.
- Visit the Coastal Plain: The Coastal Plain offers a glimpse into North Carolina’s agricultural heritage and a chance to explore wetlands and wildlife refuges.
Conclusion:
North Carolina’s geography is a testament to the diversity and beauty of the natural world. From the majestic mountains to the expansive coastal plains, the state offers a unique tapestry of landscapes, each with its own distinct character and ecological significance. Understanding the state’s geography is essential for appreciating its rich history, its vibrant culture, and its environmental challenges. By embracing its geographical heritage, North Carolina can continue to thrive as a place of beauty, opportunity, and sustainability.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Comprehensive Guide to the Geography of North Carolina. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!