A Comparative Look at the Maps of Eritrea and Ethiopia: Tracing History, Geography, and Conflict
Related Articles: A Comparative Look at the Maps of Eritrea and Ethiopia: Tracing History, Geography, and Conflict
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Comparative Look at the Maps of Eritrea and Ethiopia: Tracing History, Geography, and Conflict. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Comparative Look at the Maps of Eritrea and Ethiopia: Tracing History, Geography, and Conflict
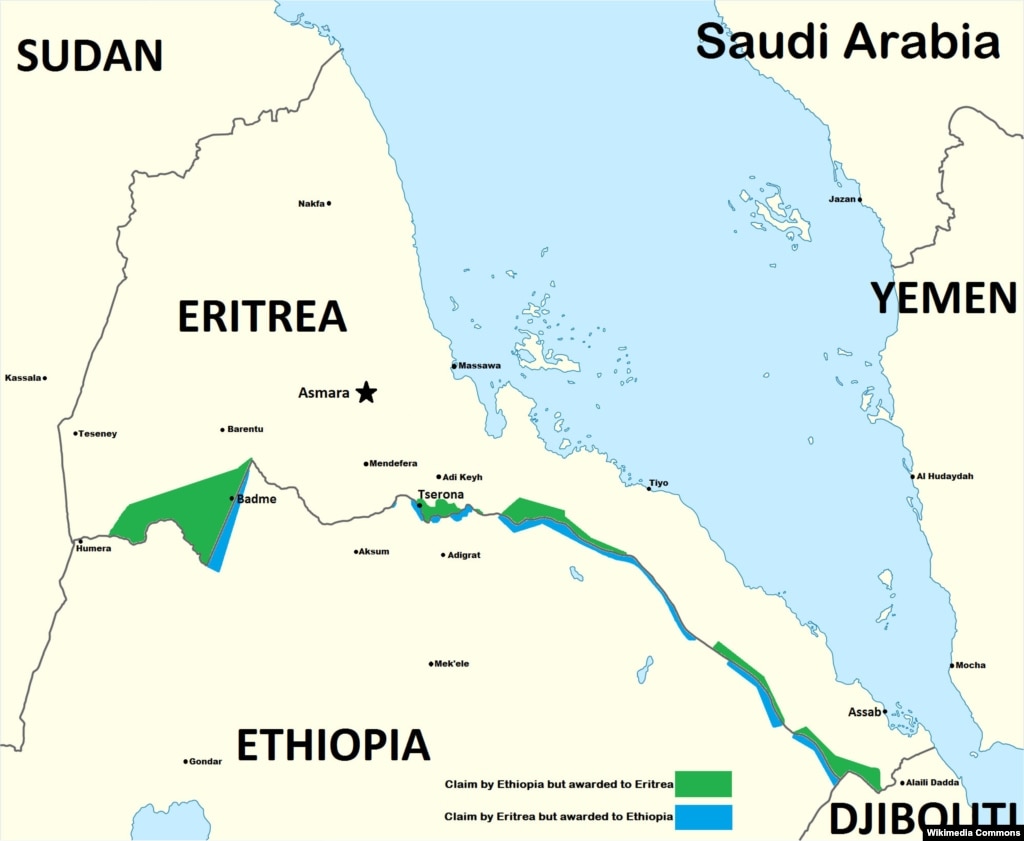
The Horn of Africa, a region steeped in history and marked by complex political landscapes, is home to two neighboring nations: Eritrea and Ethiopia. While geographically intertwined, their maps tell distinct stories of struggle, resilience, and a shared heritage. Understanding the intricacies of their respective cartographies provides crucial insight into their past, present, and future.
Eritrea: A Land of Independence and Resilience
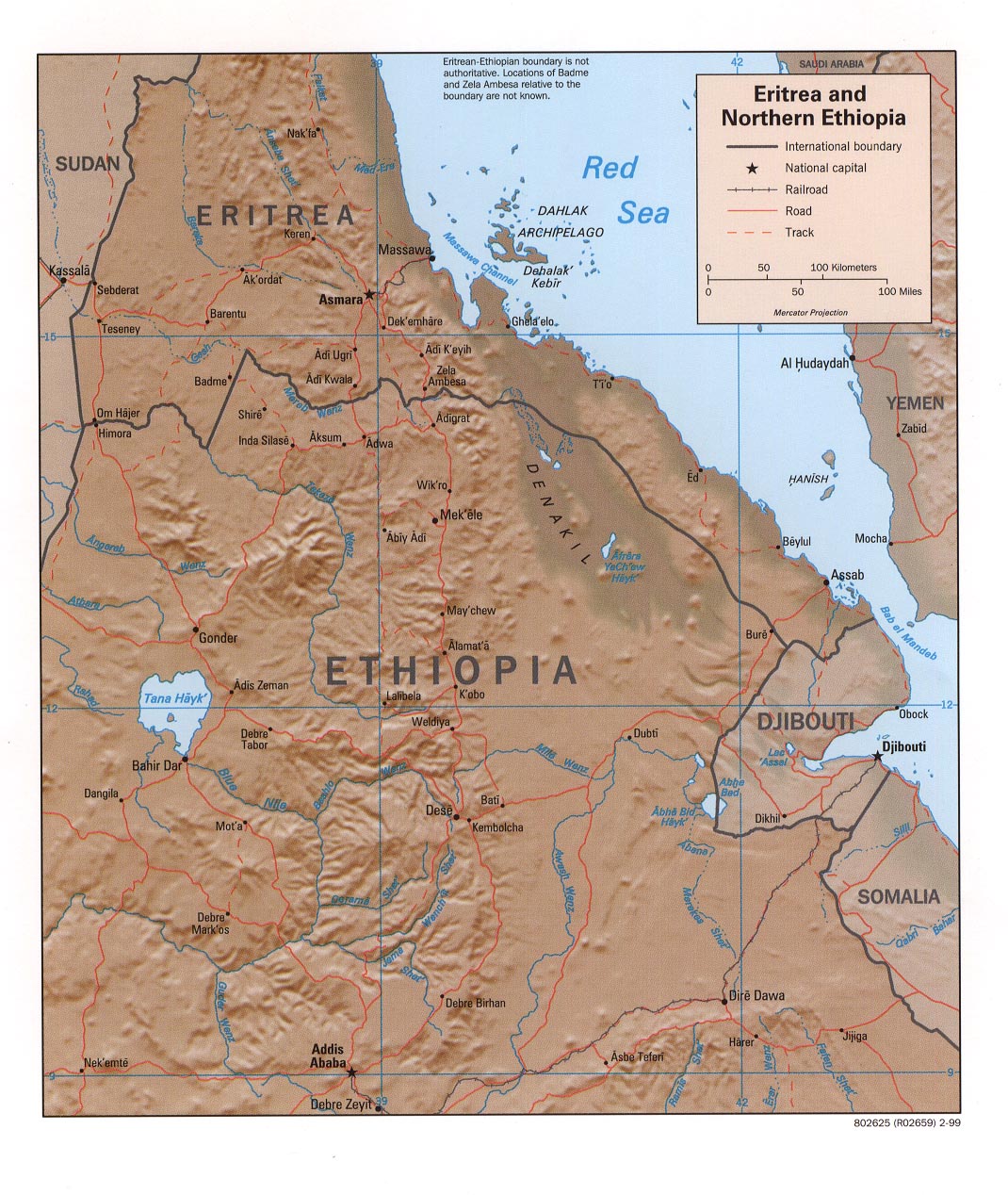
Eritrea, a nation nestled on the Red Sea, emerged from a long and arduous struggle for independence from Ethiopia in 1993. Its map, shaped like a crescent moon, reflects its unique geographical characteristics. The rugged terrain, dominated by the Danakil Depression and the Eritrean Highlands, has shaped its people’s resilience and their relationship with the surrounding world.
- The Red Sea Coast: Eritrea’s coastline, stretching over 1,000 kilometers, is a vital economic lifeline. Its ports, like Massawa and Assab, connect the country to international trade routes and serve as critical hubs for Eritrean commerce.
- The Eritrean Highlands: These highlands, rising to over 3,000 meters, are home to the majority of the Eritrean population and are characterized by fertile land suitable for agriculture. The highlands also hold immense historical and cultural significance, housing ancient monasteries and traditional villages.
- The Danakil Depression: This desolate and inhospitable region, located in the south of Eritrea, is one of the hottest and lowest places on Earth. Its volcanic landscapes and salt flats offer a stark contrast to the highlands and the coastline, showcasing the diverse geography of Eritrea.
Ethiopia: A Land of Ancient Kingdoms and Modern Growth
Ethiopia, a nation with a rich history and diverse landscapes, is the second-most populous country in Africa. Its map, a complex tapestry of highlands, lowlands, and deserts, reflects its geographical and cultural diversity.
- The Ethiopian Highlands: The "Roof of Africa," the Ethiopian Highlands, are home to the majority of the country’s population and its major cities, including Addis Ababa, the capital. The highlands are characterized by fertile volcanic soils, supporting a diverse agricultural sector.
- The Rift Valley: This geological feature, stretching through Ethiopia, is home to stunning landscapes, including the Great Rift Valley lakes, volcanic peaks, and deep gorges. The Rift Valley plays a crucial role in Ethiopia’s biodiversity, hosting unique flora and fauna.
- The Ethiopian Lowlands: These lowlands, bordering Somalia and Sudan, are characterized by arid landscapes and semi-desert conditions. They hold immense cultural and historical significance, housing ancient ruins and nomadic communities.
A Shared History and a Complex Relationship
The maps of Eritrea and Ethiopia are inextricably linked by a shared history and a complex relationship. For centuries, both nations were part of a larger Ethiopian empire, with Eritrea serving as a vital port for trade and a strategic outpost. This shared history has left a lasting mark on both cultures, evident in their languages, customs, and traditions.
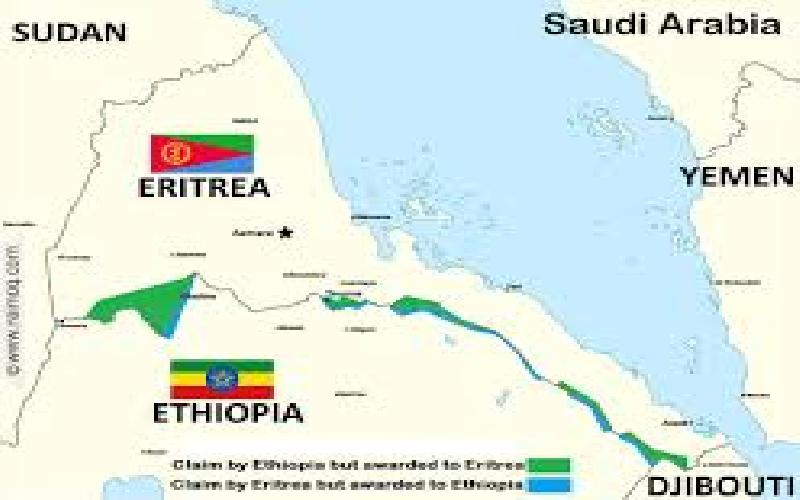
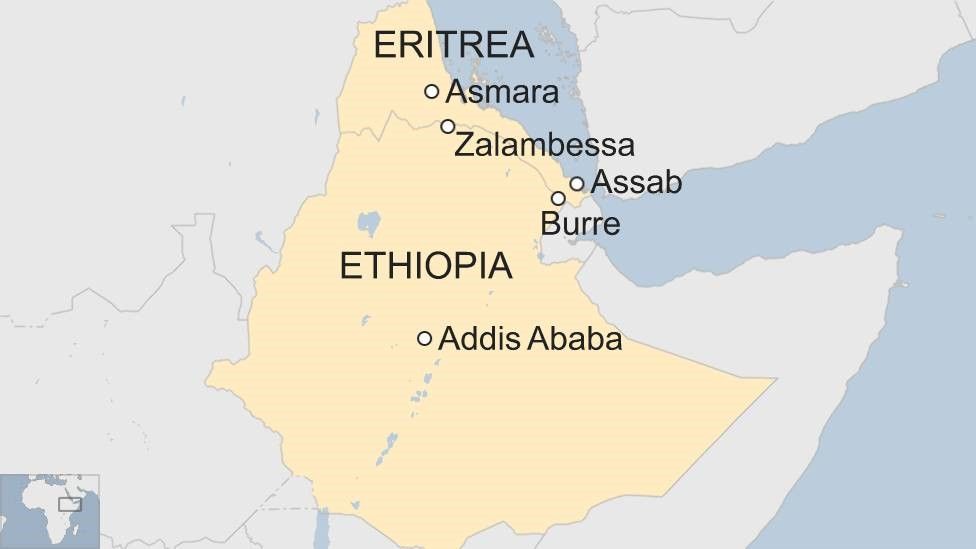
However, the colonial era and the subsequent struggle for independence in Eritrea led to a bitter conflict between the two nations. The Eritrean-Ethiopian War (1998-2000) resulted in a border dispute and a deep-seated mistrust between the two countries.
The Post-Conflict Landscape
Despite the war and the lingering animosity, there have been attempts at rapprochement in recent years. The two countries have engaged in dialogue and have begun to address the border dispute. However, progress remains fragile, and the potential for renewed conflict remains a concern.
The Importance of Understanding the Maps
Understanding the maps of Eritrea and Ethiopia is crucial for comprehending the complex dynamics of the Horn of Africa. The geographical features, historical legacies, and political realities depicted on these maps provide a framework for understanding the challenges and opportunities facing these two nations.
FAQs
Q1: What are the main geographical differences between Eritrea and Ethiopia?
A1: Eritrea is characterized by its coastal region, the Eritrean Highlands, and the Danakil Depression, while Ethiopia boasts the Ethiopian Highlands, the Rift Valley, and the Ethiopian Lowlands.
Q2: What is the significance of the Red Sea Coast for Eritrea?
A2: The Red Sea Coast is vital for Eritrea’s economy, providing access to international trade routes and serving as a crucial hub for commerce.
Q3: What is the historical relationship between Eritrea and Ethiopia?
A3: Both nations were part of a larger Ethiopian empire for centuries, with Eritrea serving as a vital port and strategic outpost.
Q4: What are the main challenges facing Eritrea and Ethiopia today?
A4: Both nations face challenges related to poverty, limited access to resources, and political instability. Eritrea also faces the legacy of the Eritrean-Ethiopian War.
Q5: What are the prospects for peace and cooperation between Eritrea and Ethiopia?
A5: While progress has been made in recent years, the potential for renewed conflict remains a concern. The future of the relationship will depend on the willingness of both countries to address the remaining issues and to build trust.
Tips
- When studying the maps of Eritrea and Ethiopia, it is crucial to consider the historical context and the political realities that have shaped these nations.
- Pay attention to the geographical features and their impact on the lives of the people, the economy, and the environment.
- Look for patterns and connections between the maps and the history, culture, and politics of the region.
- Engage with diverse perspectives and seek to understand the complexities of the relationship between Eritrea and Ethiopia.
Conclusion
The maps of Eritrea and Ethiopia offer a window into the history, geography, and challenges of these two nations. They highlight their shared heritage, their unique identities, and the complex relationship that binds them. Understanding these maps is essential for navigating the complexities of the Horn of Africa and for promoting peace, cooperation, and development in the region.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Comparative Look at the Maps of Eritrea and Ethiopia: Tracing History, Geography, and Conflict. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!